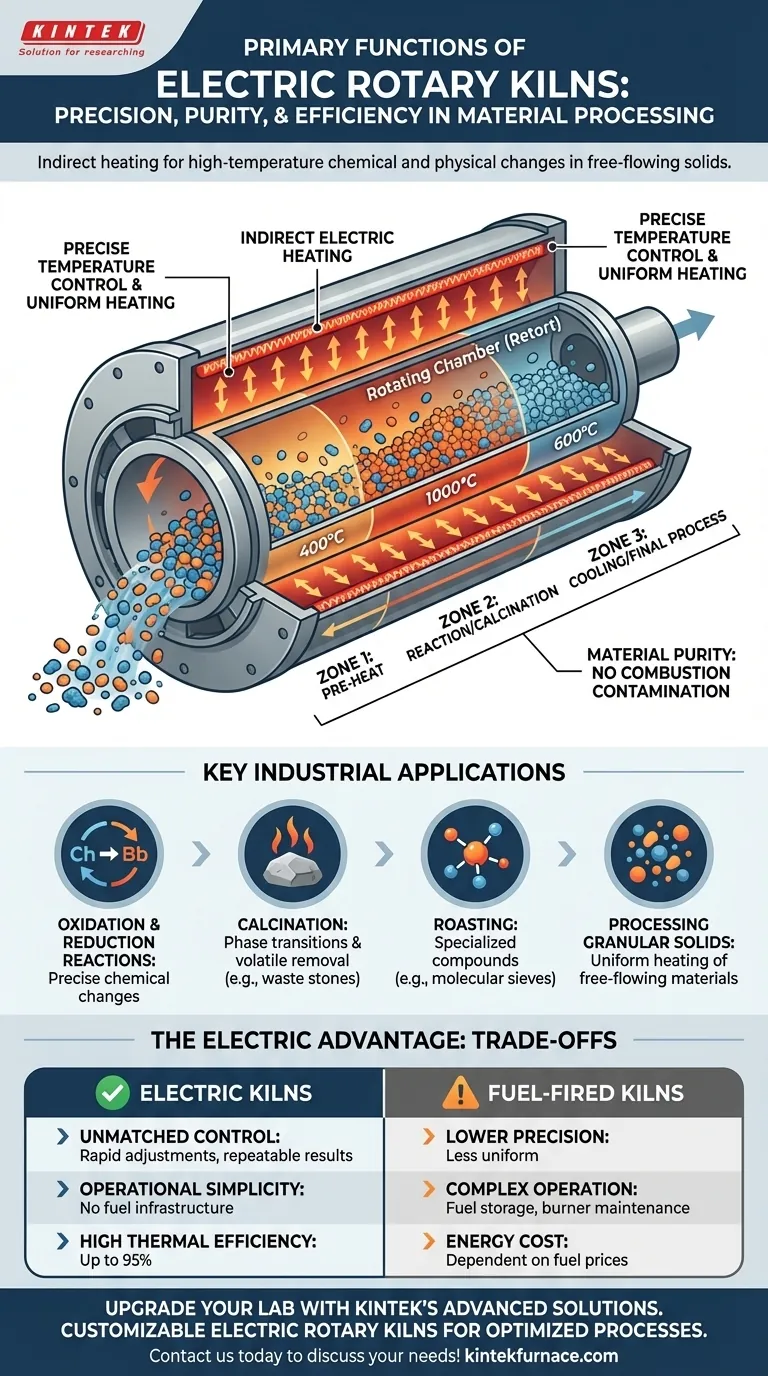
At their core, electric rotary kilns are industrial furnaces designed for high-temperature material processing. Their primary functions are to execute specific chemical and physical changes in free-flowing solids, such as performing oxidation and reduction reactions, calcining materials like waste stones, and roasting specialized compounds like chemical molecular sieves.
The decision to use an electric rotary kiln is driven by the need for exceptional process control. Its reliance on electrical energy allows for unparalleled precision in temperature, uniform heating, and repeatable results that are often difficult to achieve with traditional fuel-fired kilns.

The Principle: Indirect Heating for Superior Control
The defining feature of an electric kiln is how it generates and applies heat. Unlike direct combustion kilns, it separates the heat source from the material being processed.
How Electric Heating Works
Electric rotary kilns use an indirect heating method. The rotating chamber, or retort, is heated from the outside by electrical resistance heating elements.
This design prevents any contamination of the product from combustion byproducts, ensuring material purity. It also allows for extremely high thermal efficiency, with some systems reaching up to 95%.
Achieving Precise Temperature Zones
The key advantage of this design is precise temperature management. Kilns are often built with multiple, separately controllable heating zones.
For instance, an alloy-heated kiln might have four distinct zones, while a silicon carbide model may use a three-stage system. This allows operators to create a highly specific temperature profile along the length of the kiln, which is critical for complex, multi-stage reactions.
Key Industrial Applications
The precision of electric kilns makes them ideal for processes where temperature and consistency are non-negotiable.
High-Temperature Chemical Reactions
Electric kilns provide the stable, controlled environment needed for high-temperature oxidation and reduction reactions. The uniform heating ensures that every particle is exposed to the same conditions, leading to consistent and high-quality output.
Calcination and Roasting
Calcination is the process of heating a solid to a high temperature to cause a phase transition or remove a volatile component. Electric kilns are used to calcine materials ranging from small waste stones to specialized chemical compounds.
Similarly, they are used for roasting chemical molecular sieves, where precise temperature is crucial to achieving the desired porous structure without damaging the material.
Processing Granular Solids
The rotating motion of the kiln is designed to process free-flowing, granular solids. This ensures every part of the material is heated uniformly as it tumbles through the different temperature zones.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Electric vs. Fuel-Fired
While powerful, electric kilns are not the universal solution. The choice between electric and fuel-fired heating involves clear trade-offs.
Advantage: Unmatched Temperature Control
Electricity allows for rapid temperature adjustments and a level of control that direct combustion of gas or oil cannot match. This leads to highly repeatable, high-quality results, which is essential for sensitive industrial applications.
Advantage: Operational Simplicity and Efficiency
Electric kilns eliminate the entire infrastructure of fuel management, including storage, piping, and burner maintenance. This simplifies operation and, combined with high thermal efficiency, can make them more economical in the long run.
Consideration: Energy Source and Cost
The primary trade-off is the reliance on electrical energy. While operationally simple, the cost of electricity versus fossil fuels like heavy oil or natural gas can be a deciding factor. The "more economical" aspect depends heavily on local energy prices and the efficiency gains for your specific process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The decision to use an electric rotary kiln should be based on your process's most critical requirement.
- If your primary focus is process precision and product purity: Choose an electric kiln for its unmatched temperature control and indirect heating method.
- If your primary focus is high-volume processing of less-sensitive materials: A direct-fired gas or oil kiln might be a more cost-effective choice, assuming you can tolerate less precise temperature control.
- If your primary focus is operational simplicity and high thermal efficiency: An electric kiln eliminates fuel management complexity and often delivers superior energy efficiency.
Ultimately, choosing an electric rotary kiln is an investment in process control and consistency.
Summary Table:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Oxidation and Reduction Reactions | Enables precise chemical changes in solids with uniform heating for consistent results. |
| Calcination | Heats materials to high temperatures for phase transitions or volatile removal, e.g., waste stones. |
| Roasting | Processes specialized compounds like chemical molecular sieves to achieve desired structures without damage. |
| Processing Granular Solids | Tumbles free-flowing solids for even heating across multiple temperature zones. |
Upgrade your lab's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced electric rotary kilns! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Experience unmatched temperature control, purity, and efficiency—contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
People Also Ask
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained



















