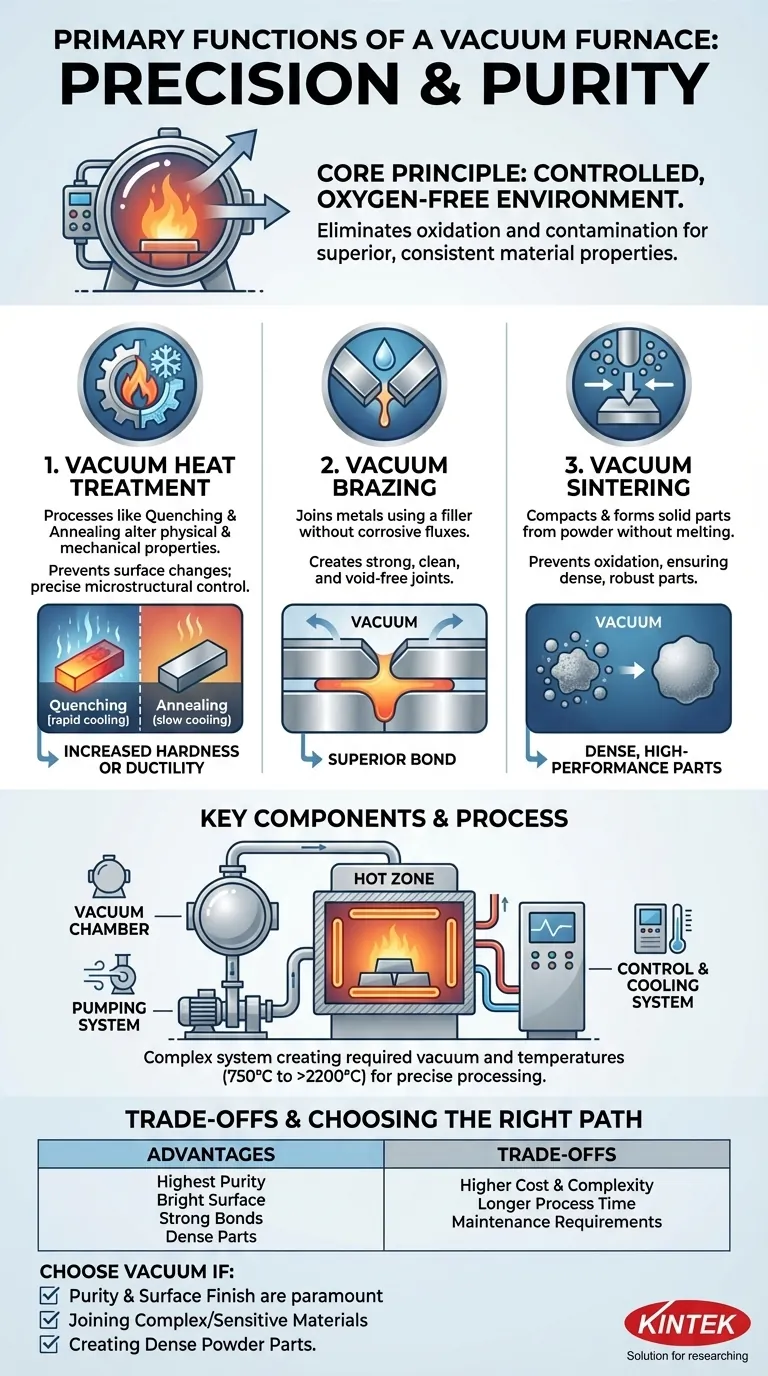
At its core, a vacuum furnace is a specialized system designed to heat materials in a controlled, oxygen-free environment. Its primary functions are to perform heat treatments like quenching and annealing, join materials through brazing, and consolidate metal powders via sintering. By removing atmospheric gases, these processes achieve a level of purity, strength, and surface quality that is unattainable in a conventional furnace.
A vacuum furnace is not just a tool for heating; it is a precision instrument for material transformation. Its fundamental purpose is to eliminate unwanted chemical reactions—primarily oxidation—by creating a near-perfect vacuum, enabling processes that result in superior and highly consistent material properties.

The Core Principle: Why a Vacuum is Necessary
The defining feature of a vacuum furnace is its ability to create a controlled atmosphere. This single capability is what separates it from all other types of thermal processing equipment.
Eliminating Oxidation and Contamination
When metals are heated in the presence of air, oxygen reacts with their surface, creating an oxide layer, or scale. This contamination can compromise the material's structural integrity, surface finish, and performance.
A vacuum furnace solves this by using a pumping system to remove almost all the air and other gases from a sealed chamber before heating begins. This protective environment ensures the material remains bright, clean, and free from unwanted surface reactions.
Achieving Unmatched Purity and Consistency
By preventing contamination, vacuum processing leads to finished parts with exceptional consistency and purity. This is critical for high-performance applications in industries like aerospace, medical, and electronics, where even microscopic imperfections can lead to failure.
A Breakdown of Key Functions
The controlled environment of a vacuum furnace enables several specialized thermal processes that are difficult or impossible to perform otherwise.
Vacuum Heat Treatment (Quenching & Annealing)
Heat treatment alters a material's physical and mechanical properties. Processes like quenching (rapid cooling) increase hardness, while annealing (slow cooling) increases ductility and reduces internal stresses.
Performing these treatments in a vacuum ensures the part's surface remains chemically unchanged. The precise temperature and cooling controls allow engineers to target very specific microstructures and performance characteristics.
Vacuum Brazing
Brazing is a process that joins two or more metal items by melting and flowing a filler metal into the joint. The filler metal has a lower melting point than the adjoining metal.
In a vacuum, brazing creates exceptionally strong, clean, and void-free joints without the need for corrosive chemical fluxes. The vacuum pulls the molten filler metal into the tightest crevices, resulting in a superior bond.
Vacuum Sintering
Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material from powder by heating it without melting it to the point of liquefaction.
This is essential for creating parts from high-performance metals and ceramics. The vacuum prevents the fine powder particles from oxidizing, which would inhibit them from bonding together effectively, ensuring a dense and robust final part.
Understanding the Key Components
A vacuum furnace is a complex system where several components work in concert to achieve the desired outcome.
The Vacuum Chamber and Pumping System
The vacuum chamber is the double-walled, sealed vessel that contains the material. The pumping system, consisting of various pumps, valves, and gauges, is responsible for removing air to create and maintain the required level of vacuum.
The Hot Zone and Heating Elements
The hot zone is the insulated interior of the furnace where heating occurs. It is built with materials like graphite or high-temperature metals.
Heating elements, made of materials like graphite or molybdenum, generate the extreme temperatures required for processing, which can range from 750 °C to over 2200 °C.
The Control and Cooling Systems
The temperature control system precisely manages heating rates and hold times. The cooling system, which may use inert gas or water-cooled jackets, is equally critical for controlling the cooling rate to achieve the final material properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are not the solution for every heating application. It's important to understand their limitations.
Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are significantly more complex and expensive to purchase and operate than standard atmospheric furnaces. The vacuum pumps, seals, and advanced control systems add substantial cost.
Process Time
Achieving a deep vacuum takes time. The pump-down cycle can add significant time to the overall process, making vacuum furnaces better suited for batch processing rather than high-volume, continuous production lines.
Maintenance Requirements
The high-performance components, especially the vacuum pumps and chamber seals, require regular and specialized maintenance to ensure the integrity of the vacuum and the reliability of the furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal processing method depends entirely on your material requirements and production goals.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest material purity and a bright, oxide-free surface finish: A vacuum furnace is the only choice for your heat treatment needs.
- If your primary focus is joining complex or sensitive materials with a strong, clean bond: Vacuum brazing provides superior results without the risk of corrosive flux residue.
- If your primary focus is creating dense, high-performance parts from metal powders: Vacuum sintering is essential to prevent particle oxidation and ensure proper bonding.
- If your primary focus is simple bulk heating where cost is the main driver and surface oxidation is acceptable: A conventional atmospheric furnace is likely the more economical and efficient solution.
Ultimately, a vacuum furnace is an investment in control, granting you the power to transform materials with unparalleled precision.
Summary Table:
| Function | Description | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Heat Treatment | Processes like quenching and annealing in a vacuum to alter material properties. | Prevents oxidation, ensures precise temperature control, and improves material strength and ductility. |
| Vacuum Brazing | Joins metals using a filler metal in a vacuum without fluxes. | Creates strong, clean joints free from contamination, ideal for complex or sensitive materials. |
| Vacuum Sintering | Compacts and forms solid parts from metal powders by heating in a vacuum. | Prevents oxidation, ensures dense and robust parts, and maintains high purity for performance applications. |
Ready to elevate your material processing with precision and purity? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in aerospace, medical, or electronics, our vacuum furnaces deliver unmatched control and consistency. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a high-precision vacuum drying oven contribute to the preparation of LiFePO4 electrode slurries?
- What evidence does vacuum tensile testing equipment provide for hydrogen embrittlement? Discover Gas Release Secrets
- Why is a vacuum heating and cooling stage necessary for SWCNT research? Unlock Precision in Thermal Conductivity
- What experimental conditions does a high vacuum annealing furnace provide? Testing Diffusion Barrier Stability
- What is the primary function of a vacuum arc melting furnace? Expert Solutions for High-Entropy Alloy Production
- Why is the selection of insulation layer materials critical for vacuum sintering furnace design? Boost Thermal Efficiency
- How does a vacuum distillation system achieve the separation of titanium? Advanced Metal Refining Insights
- How does a Vacuum Drying Oven contribute to solid-state electrolyte films? Enhance Film Density and Purity



















