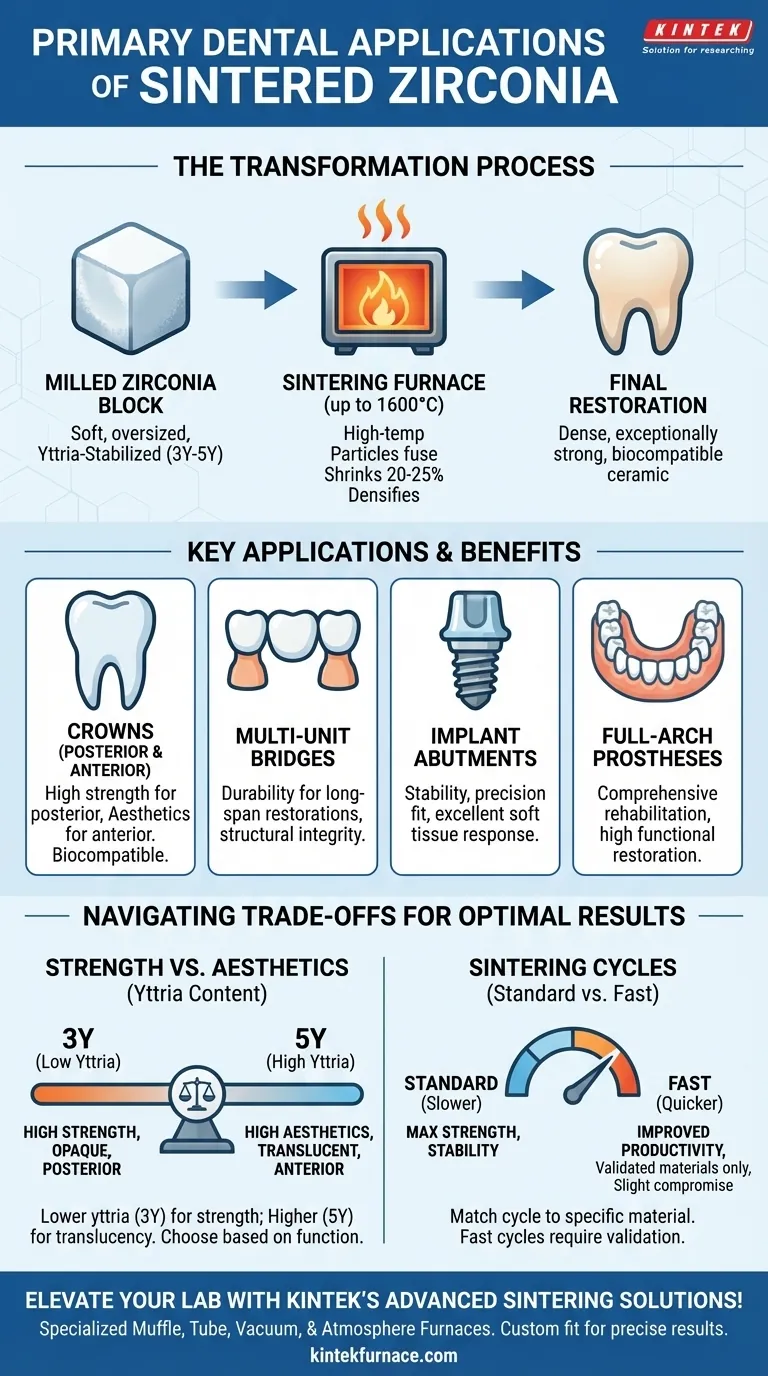
In modern dentistry, sintered zirconia is the foundational material for creating a wide range of highly durable and aesthetic dental restorations. Its primary applications are for fabricating crowns, multi-unit bridges, implant abutments, and in some cases, full-arch prostheses. The sintering process is what transforms the pre-shaped zirconia into a final restoration with its renowned strength and biocompatibility.
The core value of sintered zirconia lies not just in the material itself, but in the thermal sintering process that unlocks its properties. This controlled heating process converts a soft, milled zirconia block into a dense, exceptionally strong ceramic suitable for the demanding environment of the oral cavity.

Why Sintering is Essential for Zirconia Restorations
Zirconia does not start as a strong material. In the dental lab, it begins as a chalky, oversized block that is milled into the precise shape of a crown or bridge using CAD/CAM technology. This pre-sintered state is intentionally soft to allow for easy and accurate milling.
The Material: Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia
The material used is typically yttria-stabilized zirconia (Y-TZP), a zirconium oxide with small amounts of yttrium oxide added to it.
The concentration of yttria (e.g., 3Y, 4Y, 5Y) dictates the final properties of the restoration. Lower yttria content (3Y) produces higher strength, while higher content (5Y) improves translucency, making it more aesthetic for anterior teeth.
The Transformation: The Sintering Process
Sintering is a high-temperature firing process that takes place in a specialized dental furnace after the restoration is milled.
During this process, the zirconia particles fuse together, causing the restoration to shrink by a precise amount (typically 20-25%) and densify into its final, hardened state.
The Equipment: The Specialized Furnace
Zirconia sintering furnaces are engineered to reach extremely high temperatures, often up to 1600°C (2912°F).
They must maintain these temperatures with absolute uniformity for prolonged periods. Precise temperature control and advanced heating elements are critical to ensure every part of the restoration is sintered evenly, achieving consistent strength and a predictable fit.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variables
While sintered zirconia offers exceptional benefits, achieving optimal results depends on controlling several key variables. The choices made directly impact the final balance between strength and aesthetics.
Strength vs. Aesthetics
There is an inherent trade-off between the mechanical strength and the translucency (and thus, aesthetic quality) of zirconia.
High-strength zirconia (like 3Y-TZP) is more opaque and is best suited for posterior crowns and long-span bridges where durability is paramount.
High-translucency zirconia (like 5Y-TZP) is less strong but offers superior aesthetics, making it ideal for highly visible anterior crowns that must mimic natural teeth.
The Impact of Sintering Cycles
The sintering cycle—the combination of temperature, heating rate, and holding time—profoundly affects the final microstructure.
"Fast sintering" cycles can improve lab productivity but may not achieve the same level of strength or long-term stability as a conventional, slower cycle. The choice of cycle must be matched to the specific zirconia material being used.
The Importance of Material Sourcing
Not all zirconia powders are created equal. Differences in powder sourcing, purity, and blending can lead to variations in sintering behavior and final properties, even among products with the same yttria classification.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct type of zirconia and sintering protocol is crucial for clinical success. Your decision should be guided by the specific functional and aesthetic demands of the restoration.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength for posterior restorations: Choose a low-translucency, high-strength zirconia (typically 3Y) and use a standard, manufacturer-recommended sintering cycle.
- If your primary focus is superior aesthetics for anterior crowns: Opt for a high-translucency zirconia (4Y or 5Y) to achieve a more natural, lifelike appearance.
- If your primary focus is laboratory efficiency: You can utilize fast-sintering cycles, but only with zirconia materials specifically validated for that purpose, and understand there may be a slight compromise in maximum strength.
Ultimately, mastering zirconia restorations requires a deep understanding of how the material, milling process, and sintering protocol work together to produce a predictable outcome.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Features | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Crowns | High strength, biocompatibility | Posterior and anterior teeth |
| Bridges | Durability for multi-unit spans | Long-span restorations |
| Implant Abutments | Stability and precision | Dental implants |
| Full-Arch Prostheses | Comprehensive restoration | Full-mouth rehabilitation |
Elevate your dental lab's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced sintering solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your unique zirconia sintering needs, enhancing restoration quality and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can benefit your practice!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How often should dental furnaces be calibrated? Ensure Precision for Perfect Restorations
- What are the recommended maintenance practices for dental furnaces? Ensure Precision and Longevity for Your Lab
- What aspects of a dental restoration are directly impacted by the choice of a dental sintering furnace? Ensure Fit, Strength & Longevity
- Why is using a universal setting for all materials in a dental furnace a mistake? Master Precision Sintering for Perfect Restorations
- Why is accurate temperature control important in dental furnaces? Ensure Perfect Restorations Every Time



















