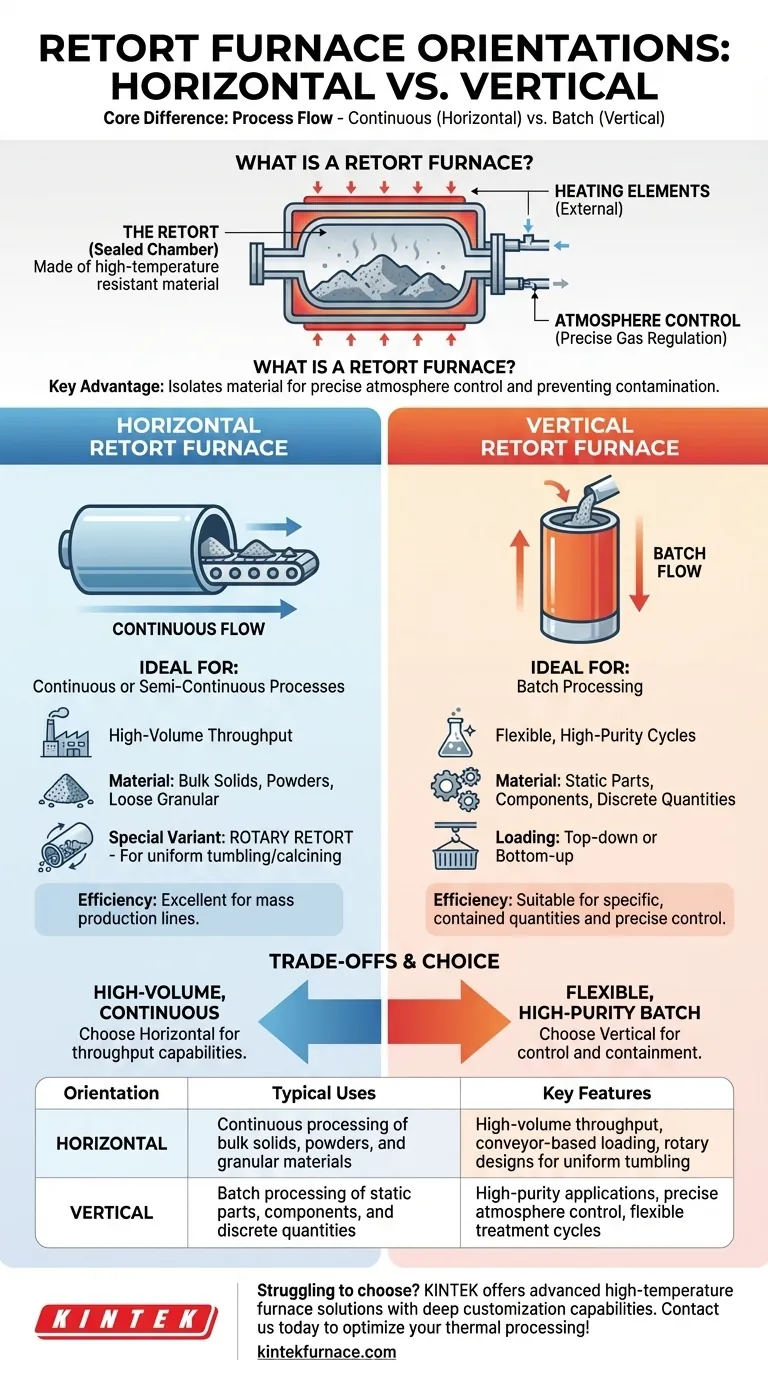
At its core, a retort furnace's orientation is determined by its intended process flow. The two primary configurations are horizontal, which is ideal for continuous processing of materials, and vertical, which is better suited for handling discrete batches.
The decision between a horizontal and vertical retort furnace is not about which is superior, but which aligns with your specific operational need: high-volume continuous throughput versus high-precision batch processing.

What Defines a Retort Furnace?
Before comparing orientations, it's crucial to understand the fundamental design of a retort furnace. Its defining feature is a sealed, gas-tight chamber—the retort—that contains the material being processed.
The Sealed Retort Principle
The retort, typically made of high-temperature resistant steel, isolates the material from the furnace's heating elements and the external environment.
This separation is the key to its advantages. It allows for precise control over the internal atmosphere by introducing specialized gases while preventing contamination.
Core Components
A retort furnace consists of several key systems working in concert:
- The Retort: The central, sealed chamber holding the material.
- Heating Elements: The system (electric or gas) that heats the retort from the outside.
- Atmosphere Control: A system to introduce, regulate, and purge gases like nitrogen, argon, or hydrogen within the retort.
- Temperature Control: A precise system to regulate the heat applied to the retort, ensuring uniform material processing.
Analyzing Furnace Orientations
The orientation—horizontal or vertical—directly impacts how material is loaded, processed, and unloaded.
The Horizontal Retort Furnace
A horizontal configuration is designed for continuous or semi-continuous processes. Material is typically pushed or conveyed through the heated retort from one end to the other.
This design is highly efficient for high-volume production where a consistent flow of material is required.
A specialized version is the rotary retort furnace. In this design, the horizontal tube rotates, making it exceptionally effective for tumbling and uniformly processing loose, granular materials like powders or pellets during applications like calcining.
The Vertical Retort Furnace
A vertical retort furnace is the standard for batch processing. Material is loaded into the top or bottom of the retort, treated in a static state, and then removed.
This configuration is ideal for applications requiring high purity, precise atmospheric changes during a cycle, or the treatment of individual parts that must not move during heating. Its top-down or bottom-up loading makes it suitable for specific, contained quantities.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an orientation involves clear trade-offs tied directly to your production goals and material type.
Process Type: Continuous vs. Batch
The most significant factor is the process type. Horizontal furnaces excel at continuous throughput, making them a cornerstone of mass production lines.
Vertical furnaces provide the flexibility of batch processing, allowing for unique treatment cycles for different products or smaller quantities without reconfiguring an entire production line.
Material Handling and Form
Horizontal and rotary furnaces are purpose-built for bulk solids, powders, and loose materials that can be easily conveyed or tumbled.
Vertical furnaces are better suited for static parts, components, or specific arrangements where material movement is undesirable.
Efficiency and Atmosphere Control
Because retort furnaces are sealed, both orientations offer excellent atmospheric control and thermal efficiency, leading to reduced fuel consumption and quicker heating times.
The choice is less about general efficiency and more about matching the furnace's mechanical operation to the material's physical form and the desired production volume.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your selection should be guided by a clear understanding of your primary operational requirement.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production of loose materials: A horizontal or rotary retort furnace is the definitive choice for its throughput capabilities.
- If your primary focus is flexible, high-purity batch processing of parts or distinct quantities: A vertical retort furnace provides the necessary control and containment for precise, individualized cycles.
Ultimately, aligning the furnace orientation with your process mechanics is the key to achieving efficient and reliable thermal processing.
Summary Table:
| Orientation | Typical Uses | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Horizontal | Continuous processing of bulk solids, powders, and granular materials | Ideal for high-volume throughput, conveyor-based loading, and rotary designs for uniform tumbling |
| Vertical | Batch processing of static parts, components, and discrete quantities | Suited for high-purity applications, precise atmosphere control, and flexible treatment cycles |
Struggling to choose the right retort furnace for your lab? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements—whether you need continuous throughput or batch precision. Contact us today to optimize your thermal processing and boost efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of continuous sample movement in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency
- What are the key features of rotary tube furnaces regarding heat treatment? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries
- What are some applications of rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Continuous High-Temperature Material Processing



















