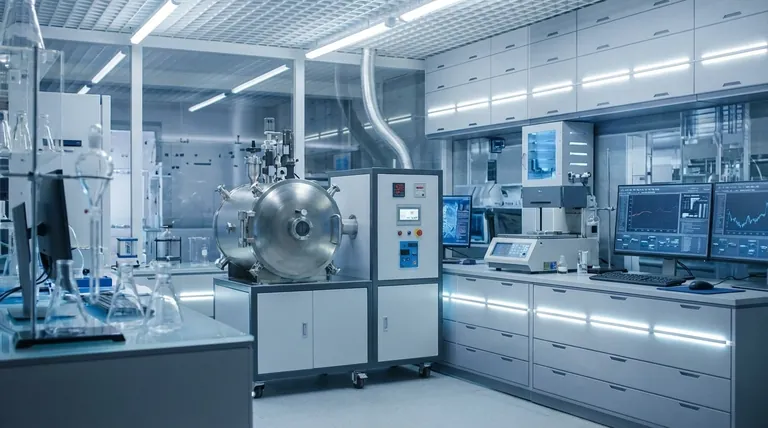
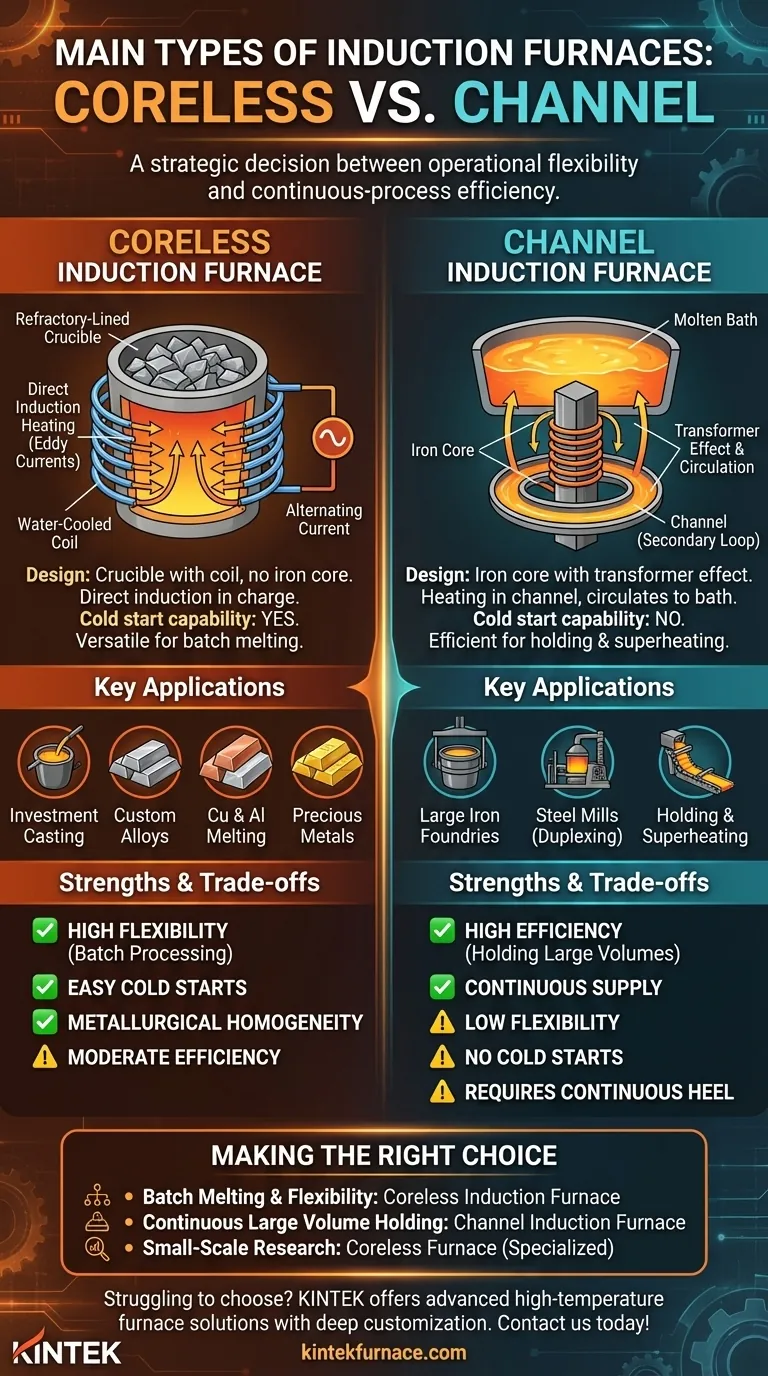
At its core, induction furnace technology is divided into two primary designs. These are the coreless induction furnace and the channel induction furnace. A coreless furnace operates like a simple crucible surrounded by an electrical coil, while a channel furnace functions more like a transformer where a loop of molten metal acts as the secondary component.
The fundamental difference between induction furnace types is not their size or shape, but their method of applying electromagnetic energy. Your choice between a coreless and a channel furnace is a strategic decision between operational flexibility and continuous-process efficiency.

The Two Fundamental Designs: Coreless vs. Channel
Understanding how each furnace generates heat is the key to understanding its ideal application. The design dictates everything from startup procedure to metallurgical capability.
The Coreless Induction Furnace: Versatility for Batch Melting
A coreless induction furnace consists of a refractory-lined crucible encircled by a water-cooled copper coil. When alternating current flows through the coil, it creates a powerful electromagnetic field.
This field directly induces eddy currents within the metal charge placed inside the crucible, generating intense heat and melting the material from the inside out. This design does not require an iron core to function.
Because the entire charge is contained within the crucible and heated directly, coreless furnaces are exceptionally versatile. They can be started from cold with a solid charge and can be completely emptied after each melt.
The Channel Induction Furnace: Efficiency for Holding & Superheating
A channel furnace uses an iron core to create a transformer effect. It has a primary coil wrapped around the core and a secondary "loop" or "channel" formed by molten metal.
The intense heating is concentrated in this small channel of metal. The rest of the metal in the main furnace bath is then heated through circulation and contact with the superheated metal from the channel.
This design is highly energy-efficient for maintaining a large volume of molten metal at a specific temperature. However, it cannot be started from cold; it requires a continuous "heel" of molten metal to complete the secondary circuit.
Key Applications and Use Cases
The distinct operating principles of coreless and channel furnaces make them suited for very different industrial tasks.
Where Coreless Furnaces Excel
The ability to start and stop easily makes the coreless furnace the standard for applications requiring batch processing and frequent alloy changes.
Its applications include investment casting, custom copper and aluminum melting, and the production of specialized alloys. It is also the preferred choice for melting precious metals, where small, clean, and well-controlled batches are essential.
Where Channel Furnaces Dominate
The channel furnace's efficiency makes it ideal for holding large quantities of a single type of molten metal for long periods.
They are often used in large iron foundries and steel mills as "duplexing" vessels. In this role, they receive molten metal from a primary melting furnace and hold it at a precise temperature before it's moved to the casting line, ensuring a continuous supply.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong furnace type for your process leads to inefficiency, high operational costs, and metallurgical challenges.
Flexibility vs. Efficiency
The coreless furnace offers maximum flexibility. You can melt different materials back-to-back and shut the furnace down when not in use. This flexibility comes at the cost of slightly lower electrical efficiency compared to a channel furnace operating under ideal conditions.
The channel furnace offers superior electrical efficiency, but only when holding a stable volume of metal continuously. It is highly inflexible, as shutting it down is a major operation that requires draining the molten heel.
Cold Starts and Metallurgy
A coreless furnace can melt a charge from solid, room-temperature scrap. This is its single greatest operational advantage for most foundries. The electromagnetic stirring action within the crucible also provides excellent metallurgical homogeneity for creating alloys.
A channel furnace cannot be started cold. It must be pre-filled with molten metal to function. This makes it completely unsuitable for intermittent work or for facilities that do not operate 24/7.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your selection should be based entirely on your operational requirements, not on the furnace technology itself.
- If your primary focus is batch melting, alloy development, or frequent startups: A coreless induction furnace is the clear choice for its unmatched flexibility.
- If your primary focus is holding very large volumes of a single alloy continuously: A channel induction furnace will provide the highest energy efficiency for this specific task.
- If your primary focus is small-scale research or specialized part manufacturing: You will likely use a coreless furnace, potentially in a specific form factor like a small-capacity tube or split-furnace design.
Ultimately, matching the furnace's fundamental operating principle to your production goal is the most critical decision you will make.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Coreless Induction Furnace | Channel Induction Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Crucible with coil, no iron core | Iron core with transformer effect, requires molten metal channel |
| Heating Method | Direct induction in charge | Heating in channel, circulates to bath |
| Cold Start Capability | Yes | No |
| Flexibility | High (batch processing, alloy changes) | Low (continuous operation) |
| Efficiency | Moderate | High for holding large volumes |
| Key Applications | Investment casting, custom alloys, precious metals | Large foundries, steel mills for holding and superheating |
Struggling to choose the right induction furnace for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for batch melting or continuous processes. Contact us today to enhance your efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity



















