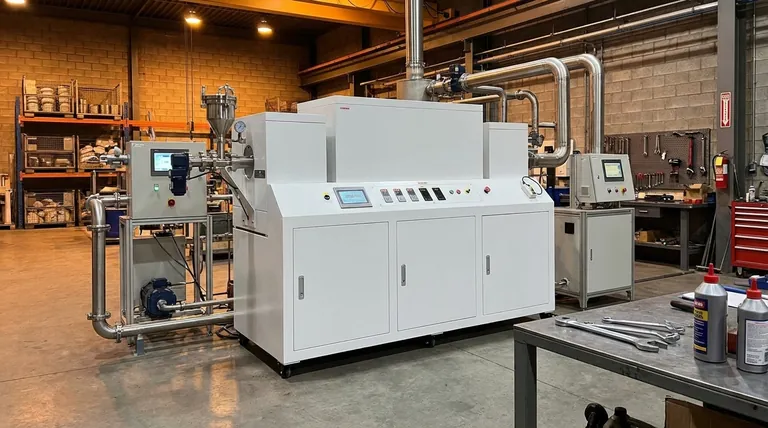
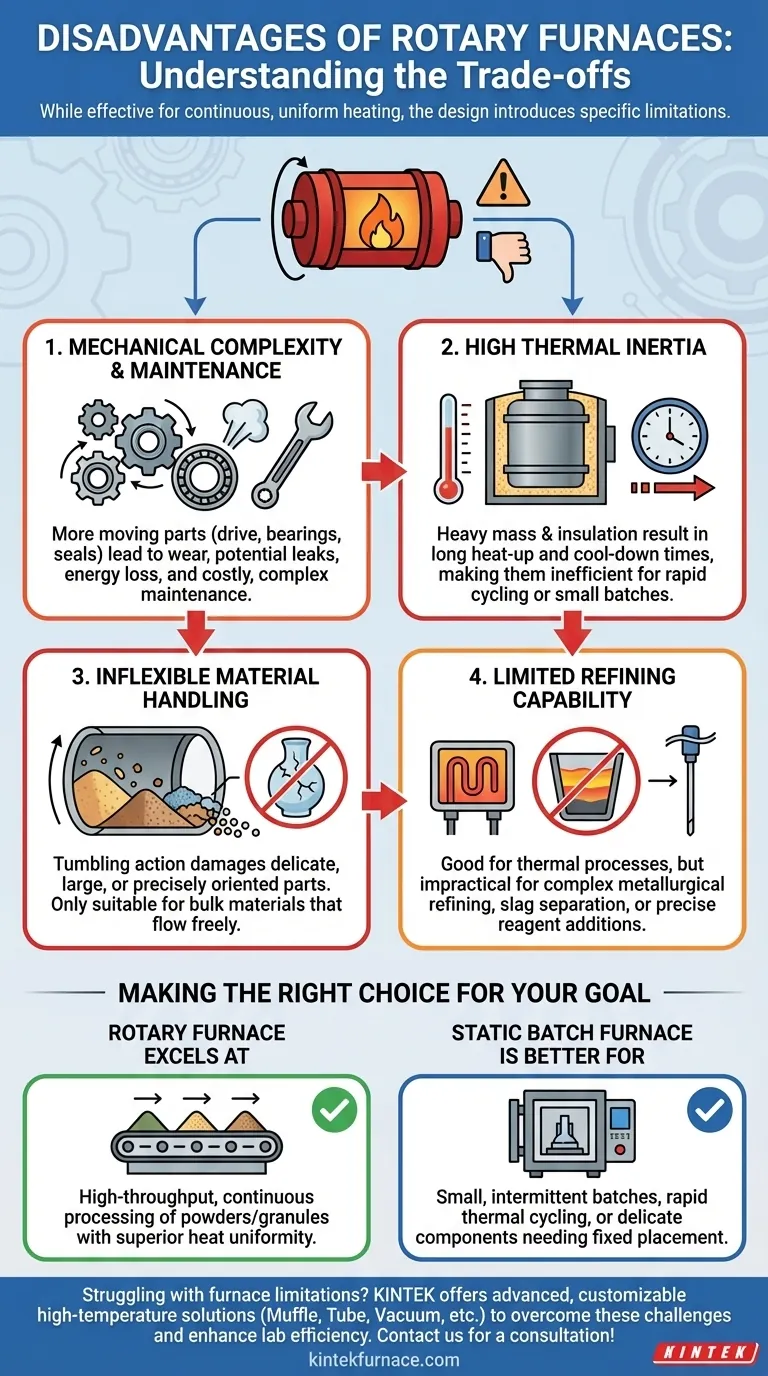
While highly effective for specific applications, rotary furnaces have several distinct disadvantages you must consider. The primary drawbacks stem from their mechanical complexity, thermal properties, and material handling limitations, including challenges with maintenance, long initial warm-up times, and a limited capacity for refining raw materials.
The very design that makes a rotary furnace excel at uniform, continuous heating—a slowly rotating tube—is also the source of its primary drawbacks. It trades operational flexibility and simple maintenance for high-throughput processing of bulk materials.

How a Rotary Furnace's Design Creates Its Weaknesses
A rotary furnace operates by tumbling material inside a long, heated, and slowly rotating barrel. This ensures every particle is exposed to the heat source, delivering exceptional temperature uniformity for powders, granules, and other bulk solids.
However, this mechanical action is the direct cause of its principal limitations.
Challenge 1: Mechanical Complexity and Maintenance
Unlike a static box furnace, a rotary furnace has numerous moving parts. The rotating tube requires a robust drive system, bearings, and, most critically, effective seals at both the inlet and outlet.
These components are points of failure. Seals wear down over time, leading to potential atmosphere leakage or energy loss. The drive and bearing systems require regular lubrication and inspection, making maintenance more complex and costly than for a comparable static system.
Challenge 2: High Thermal Inertia
Rotary furnaces are designed with heavy-duty barrels and thick insulation to withstand continuous operation and retain heat. This significant thermal mass means they take a long time to heat up to the target temperature and a long time to cool down.
This characteristic makes them inefficient for processes that require rapid thermal cycling or for running small, infrequent batches. The energy and time spent on the initial warm-up are wasted if the production run is short.
Challenge 3: Inflexible Material Handling
The tumbling action that guarantees uniform heating also means you have no control over material placement. This design is fundamentally unsuitable for processing delicate components, large single parts, or any material that could be damaged by constant motion.
It is exclusively designed for bulk materials that can flow and tumble freely. Attempting to process items that require precise orientation or are sensitive to abrasion will lead to product damage.
Challenge 4: Limited Refining Capability
Rotary furnaces excel at thermal processes like drying, calcining, and roasting. However, they have a very limited capacity for metallurgical refining.
Complex refining often requires a static environment for separating slag from molten metal, introducing specific reagents, or taking precise samples from a melt pool. The continuous movement and enclosed nature of a rotary furnace make these tasks impractical, meaning it typically requires pre-processed or purified input materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Uniformity vs. Simplicity
The disadvantages of a rotary furnace do not exist in a vacuum; they are the price paid for its unique advantages. The choice to use one is a classic engineering trade-off.
Where Rotary Furnaces Excel
The key advantages are uniform heating and continuous throughput. For producing large volumes of powders or granules where every particle must reach the same temperature, no other furnace design is as effective. Their ability to run 24/7 makes them an energy-efficient workhorse in high-volume industrial settings.
Where They Fall Short
The trade-off is a loss of flexibility and simplicity. A simple box furnace is easier to maintain, heats up faster for single batches, and can hold any type of part in a fixed position. While it cannot match the uniform heat transfer for bulk materials, it offers far greater versatility for lab work or varied production runs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct equipment, you must weigh the furnace's capabilities against your primary operational need.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput, continuous processing of powders or granules: The benefits of automation and superior heat uniformity will likely outweigh the maintenance demands.
- If your primary focus is processing small, intermittent batches or delicate components: The long warm-up times and tumbling action make a static batch furnace a far more logical and efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is complex chemical synthesis or metallurgical refining: The inherent design limitations mean you should investigate specialized static, induction, or arc furnaces designed for those tasks.
By understanding these inherent limitations, you can confidently determine if a rotary furnace is an asset or a liability for your specific operational goals.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Mechanical Complexity | More moving parts lead to higher maintenance costs and potential failures. |
| High Thermal Inertia | Long heat-up and cool-down times reduce efficiency for rapid cycling. |
| Inflexible Material Handling | Tumbling action limits use to bulk materials, not delicate or large parts. |
| Limited Refining Capability | Unsuitable for complex metallurgical processes requiring static environments. |
Struggling with furnace limitations? KINTEK offers advanced high-temperature solutions tailored to your needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems with deep customization to overcome challenges like maintenance issues and material handling constraints. Enhance your lab's efficiency and precision—contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Control
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation
- What are some applications of rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Continuous High-Temperature Material Processing
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput



















