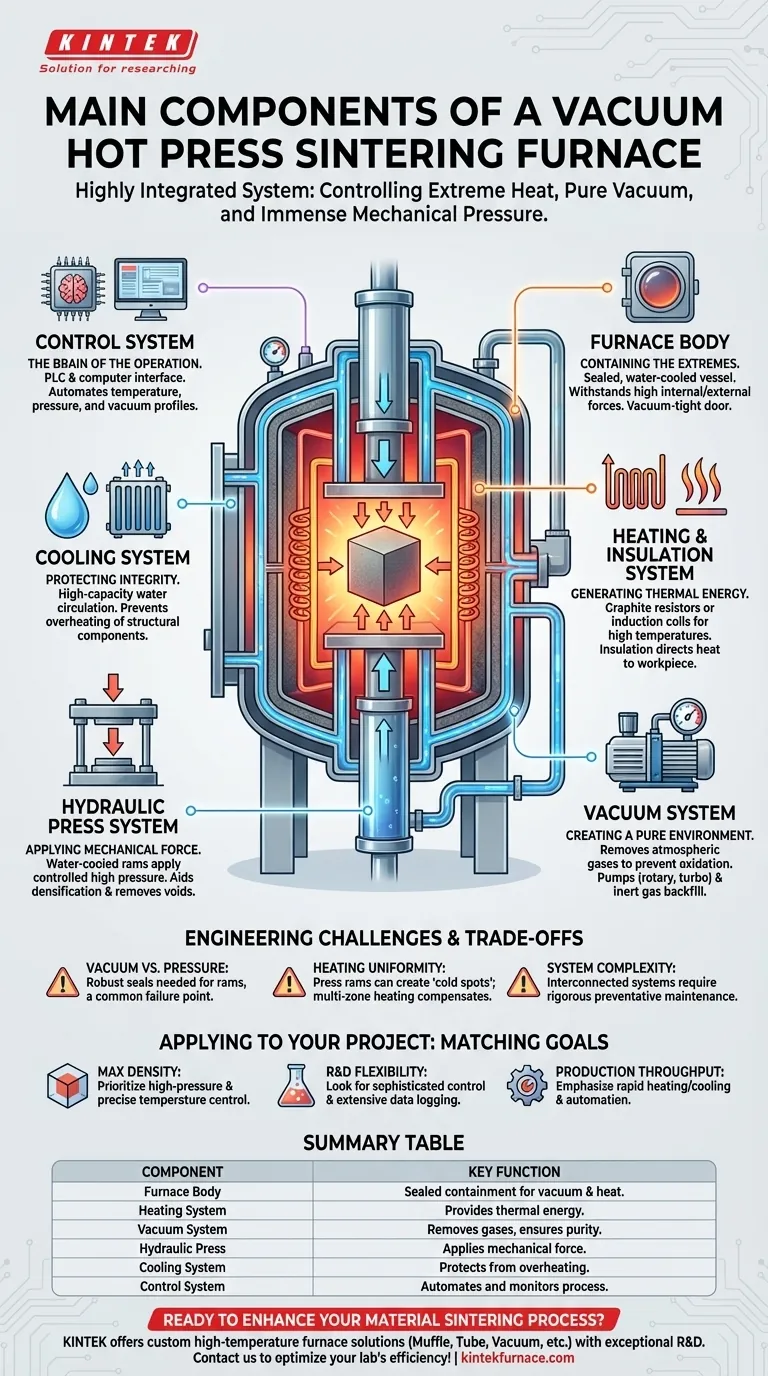
In short, a vacuum hot press sintering furnace is a highly integrated system built around several key functional units. These include the furnace body, a heating system, a vacuum system to control the atmosphere, a hydraulic press to apply mechanical force, and a master control system to orchestrate the entire process.
A vacuum hot press is not merely a furnace; it's a sophisticated machine designed to precisely control three critical variables simultaneously: extreme heat, a pure vacuum environment, and immense mechanical pressure. Understanding how these systems interact is the key to mastering the material densification process.
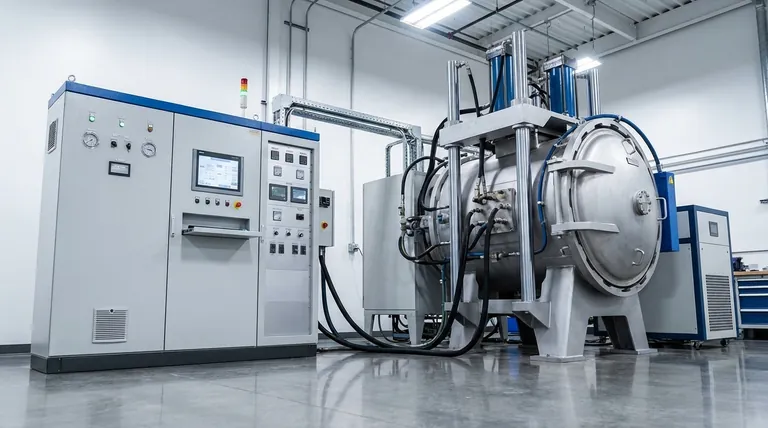

The Core Systems of a Vacuum Hot Press Furnace
A vacuum hot press furnace functions by integrating distinct systems, each with a specific role. While designs vary, the fundamental components work together to create a highly controlled environment for consolidating powders or materials into dense, solid parts.
The Furnace Body: Containing the Extremes
The furnace body, or vacuum chamber, is the structural heart of the machine. It is engineered to safely withstand the immense internal and external forces at play.
This double-walled, water-cooled steel vessel creates the sealed environment necessary for both creating a vacuum and containing the high temperatures. The furnace door provides access for loading and unloading material and must create a perfect, vacuum-tight seal.
The Heating & Insulation System: Generating and Directing Thermal Energy
This system provides the thermal energy required for sintering. The choice of heating element is critical and depends on the maximum required temperature.
Common elements include graphite resistors for many applications or induction coils for rapid, targeted heating. This core is surrounded by layers of insulation, typically graphite felt or ceramic fiber, to direct the heat toward the workpiece and protect the furnace chamber walls.
The Vacuum System: Creating a Pure Environment
The vacuum system removes atmospheric gases from the chamber, which is critical for preventing oxidation and removing contaminants from the material during heating.
It consists of a series of vacuum pumps (e.g., rotary pumps for roughing and diffusion or turbomolecular pumps for high vacuum) and gauges. Many furnaces also include an inflation system to backfill the chamber with a precise amount of inert gas like argon, creating a specific pressure or protective atmosphere.
The Hydraulic Press System: Applying Mechanical Force
This is the defining component that separates a "hot press" from a standard sintering furnace. The hydraulic system applies controlled, high-force pressure to the material during the heating cycle.
This mechanical pressure, delivered via water-cooled press rams, physically aids in densification, collapsing pores and voids in the material. This results in parts with significantly higher density and improved mechanical properties compared to pressureless sintering.
The Cooling System: Protecting the Furnace's Integrity
A high-capacity water cooling system is non-negotiable. It continuously circulates water through the furnace body, door, power leads, and press rams.
Its primary function is to prevent the structural components of the furnace from overheating and failing. Failure of the cooling system during operation can be catastrophic, leading to severe equipment damage.
The Control System: The Brain of the Operation
The control system is the central nervous system that integrates and automates the entire process. It manages temperature, pressure, vacuum levels, and gas flow according to a programmed recipe.
Modern systems use a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) and a computer interface to precisely execute complex heating, pressing, and cooling profiles, ensuring process repeatability and logging critical data for quality control.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
The integration of these powerful systems creates unique operational challenges. Acknowledging them is crucial for successful operation and troubleshooting.
The Battle Between Vacuum and Pressure
One of the core engineering challenges is applying mechanical force from the outside world into a sealed vacuum chamber. The seals on the press rams must be robust enough to withstand high pressure while maintaining a hard vacuum, making them a common point of failure or leaks.
Heating Uniformity Under Load
The physical presence of the press rams and tooling can create "cold spots" or non-uniform temperature distribution within the workpiece. Sophisticated furnace designs use multi-zone heating and advanced control logic to compensate for this and ensure the entire part reaches the target temperature uniformly.
System Complexity and Maintenance
A vacuum hot press is a complex machine with interconnected electrical, hydraulic, vacuum, and water systems. A failure in one system, like a minor water leak or a faulty sensor, can halt production or cause a cascade of issues. Rigorous preventative maintenance is essential for reliable operation.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your specific material and process goals will determine which furnace components and capabilities are most important for your application.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum final density: Prioritize a system with a very high-pressure hydraulic capability and advanced multi-zone temperature control to ensure uniform consolidation.
- If your primary focus is R&D and material development: Look for a furnace with a sophisticated, flexible control system, extensive data logging, and the ability to handle various tooling sizes.
- If your primary focus is production throughput: Emphasize rapid heating and cooling rates, a large usable work zone, and a high degree of automation to minimize cycle time and operator intervention.
Ultimately, a vacuum hot press furnace is a powerful tool for creating advanced materials that are impossible to produce through other means.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function |
|---|---|
| Furnace Body | Sealed, water-cooled chamber for vacuum and heat containment |
| Heating System | Provides thermal energy with elements like graphite resistors |
| Vacuum System | Removes gases to prevent oxidation and ensure purity |
| Hydraulic Press | Applies mechanical force for densification |
| Cooling System | Protects components from overheating with water circulation |
| Control System | Automates and monitors temperature, pressure, and vacuum levels |
Ready to enhance your material sintering process with a custom high-temperature furnace solution? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, whether for R&D, production throughput, or achieving maximum density. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role do a laboratory pressure machine and a steel die-set play in the preparation of Mn2AlB2 compacts?
- What considerations guide the selection of heating elements and pressurization methods for a vacuum hot press furnace?
- What are the advantages of vacuum hot press furnaces? Achieve Superior Material Density & Purity
- What is a vacuum hot press furnace? Unlock Superior Material Performance
- Why are precision molds and laboratory presses critical for niobium-doped TiO2 ceramics? Achieve 94% Theoretical Density



















