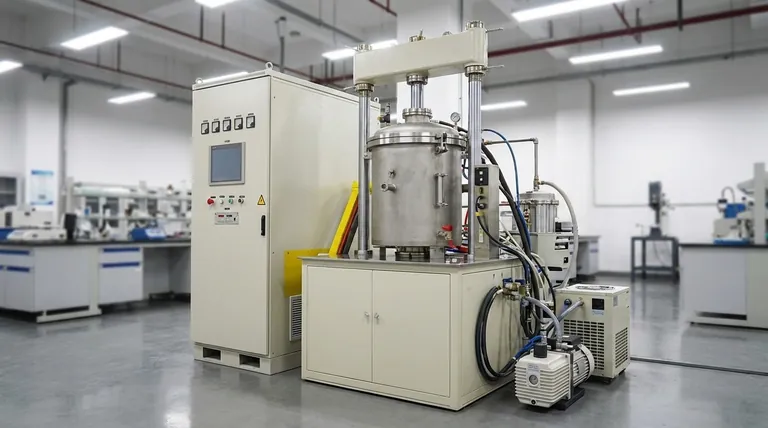
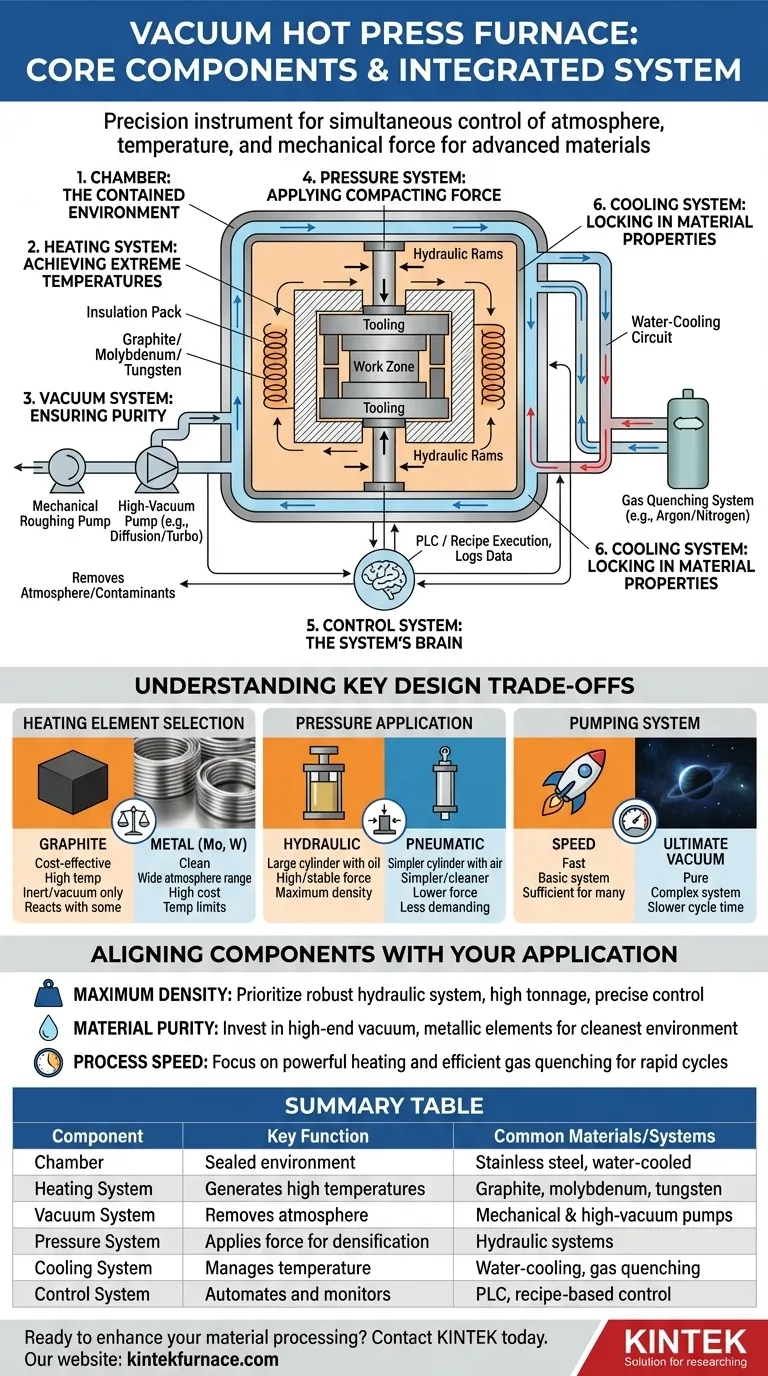
At its core, a vacuum hot press furnace is an integrated system defined by six primary components working in unison. These are the furnace body or chamber, a heating system, a vacuum system to remove atmosphere, a pressure system to apply force, a water cooling system for thermal management, and a control system to orchestrate the entire process.
A vacuum hot press furnace is not merely a collection of parts. It is a precision instrument designed for the simultaneous and independent control of atmosphere, temperature, and mechanical force, enabling the creation of advanced materials that are impossible to produce by other means.

How Key Components Work in Concert
Understanding a vacuum hot press requires seeing its components not as a list, but as an interactive system. Each part has a distinct function that enables the precise, repeatable conditions necessary for advanced material processing like sintering and diffusion bonding.
The Chamber: The Contained Environment
The furnace body, or vacuum chamber, is the sealed vessel where the entire process takes place. It is typically a double-walled, water-cooled structure made from stainless steel to withstand high vacuum and prevent contamination.
The furnace door provides access for loading and unloading materials and must create a perfect, vacuum-tight seal when closed.
The Heating System: Achieving Extreme Temperatures
Heating elements are the heart of the furnace, responsible for generating the intense heat required for processing. These are typically made from materials like graphite, molybdenum, or tungsten, chosen for their ability to withstand extreme temperatures in a vacuum.
Surrounding the elements is an insulation pack, often made of graphite felt or metallic heat shields. This pack minimizes heat loss, protects the chamber walls, and ensures temperature uniformity throughout the work zone. Most modern designs are "cold wall," where the chamber walls remain cool to the touch.
The Vacuum System: Ensuring Purity
The vacuum system is responsible for removing air and other gases from the chamber. This prevents oxidation and removes contaminants that could interfere with the material's final properties.
This is typically a multi-stage system. Mechanical "roughing" pumps remove the bulk of the air, and then high-vacuum pumps (like diffusion or turbomolecular pumps) take over to achieve the required low-pressure environment.
The Pressure System: Applying Compacting Force
Unique to a hot press, the pressure system applies mechanical force to the material during the heating cycle. This is most often a hydraulic system capable of generating immense, controlled force to densify powders or bond separate components together.
A ram, typically entering through the top or bottom of the chamber, transmits this force to the tooling and workpiece inside.
The Control System: The System's Brain
The control system integrates and automates the entire process. Using a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) or a similar interface, it executes a programmed recipe.
This system precisely manages the heating rate, holding temperature, vacuum level, applied pressure, and cooling cycle. It also logs all data for quality control and process validation.
The Cooling System: Locking in Material Properties
A robust cooling system is critical for both the equipment's longevity and the material's final microstructure.
A water-cooling circuit continuously circulates water through the double-walled chamber, power feedthroughs, and door to keep them from overheating. For the workpiece itself, a gas quenching system can rapidly introduce inert gas like argon or nitrogen to cool the part at a controlled rate.
Understanding Key Design Trade-offs
The selection and configuration of these components involve critical trade-offs that directly impact the furnace's capabilities, cost, and ideal applications.
Heating Element Selection: Graphite vs. Metal
Graphite elements are cost-effective and excellent for high-temperature applications in inert or vacuum environments. However, they can react with certain materials and are not suitable for processes requiring an oxidizing atmosphere.
Metallic elements, like molybdenum or tungsten, offer a cleaner environment and can be used in a wider range of atmospheres but come at a significantly higher cost and have different temperature limitations.
Pressure Application: Hydraulic vs. Pneumatic
Hydraulic systems are the standard for hot pressing because they can generate extremely high and stable forces, which is essential for achieving maximum material density.
Pneumatic systems are simpler and cleaner but are generally limited to much lower force applications. They are not typically used for demanding densification processes.
Pumping System: Speed vs. Ultimate Vacuum
The choice of vacuum pumps is a balance between processing speed and purity. A basic two-stage system may be sufficient for many applications.
For processes demanding extreme purity, a more complex and expensive system involving turbomolecular or cryogenic pumps is necessary to achieve a deeper ultimate vacuum, though this may increase cycle time.
Aligning Components with Your Application
Choosing the right configuration depends entirely on your end goal. The interplay between components dictates the furnace's performance.
- If your primary focus is maximum material density: Prioritize a robust hydraulic pressure system with a high tonnage rating and precise force control.
- If your primary focus is material purity and reactive metals: Invest in a high-end vacuum system with metallic (molybdenum) heating elements to create the cleanest possible environment.
- If your primary focus is process speed and throughput: Focus on a powerful heating system and an efficient gas quenching system for rapid heating and cooling cycles.
Ultimately, a vacuum hot press is a powerful tool where each component is a critical link in the chain of producing advanced materials.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function | Common Materials/Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Chamber | Sealed environment for processing | Stainless steel, water-cooled |
| Heating System | Generates high temperatures | Graphite, molybdenum, tungsten elements |
| Vacuum System | Removes air and contaminants | Mechanical and high-vacuum pumps |
| Pressure System | Applies force for densification | Hydraulic systems |
| Cooling System | Manages temperature and equipment | Water-cooling circuits, gas quenching |
| Control System | Automates and monitors process | PLC, recipe-based control |
Ready to enhance your material processing with a custom vacuum hot press furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can optimize your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does precise temperature control affect Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Master Titanium Hot Pressing Accuracy
- Which process parameters must be optimized for specific materials in a vacuum hot press furnace? Achieve Optimal Density and Microstructure
- What is a vacuum hot press furnace? Unlock Superior Material Performance
- What is the process of hot pressing? A Guide to Achieving Superior Material Density
- What are the overall benefits of using hot pressing in manufacturing? Achieve Superior Performance and Precision



















