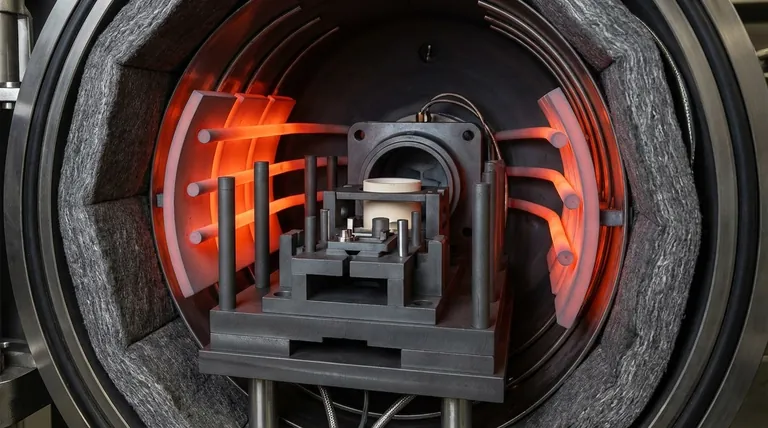
In a vacuum furnace, graphite is the material of choice for three primary functions: generating heat as heating elements, containing that heat as thermal insulation, and holding the workpieces as structural fixtures and tooling. Its unique combination of properties makes it nearly irreplaceable for high-temperature applications requiring a controlled, non-reactive environment.
While graphite's famous resistance to extreme heat is its most obvious benefit, its true value lies in a unique trio of properties: exceptional thermal stability, excellent machinability, and a low coefficient of thermal expansion, which together create a predictable and controllable furnace environment.

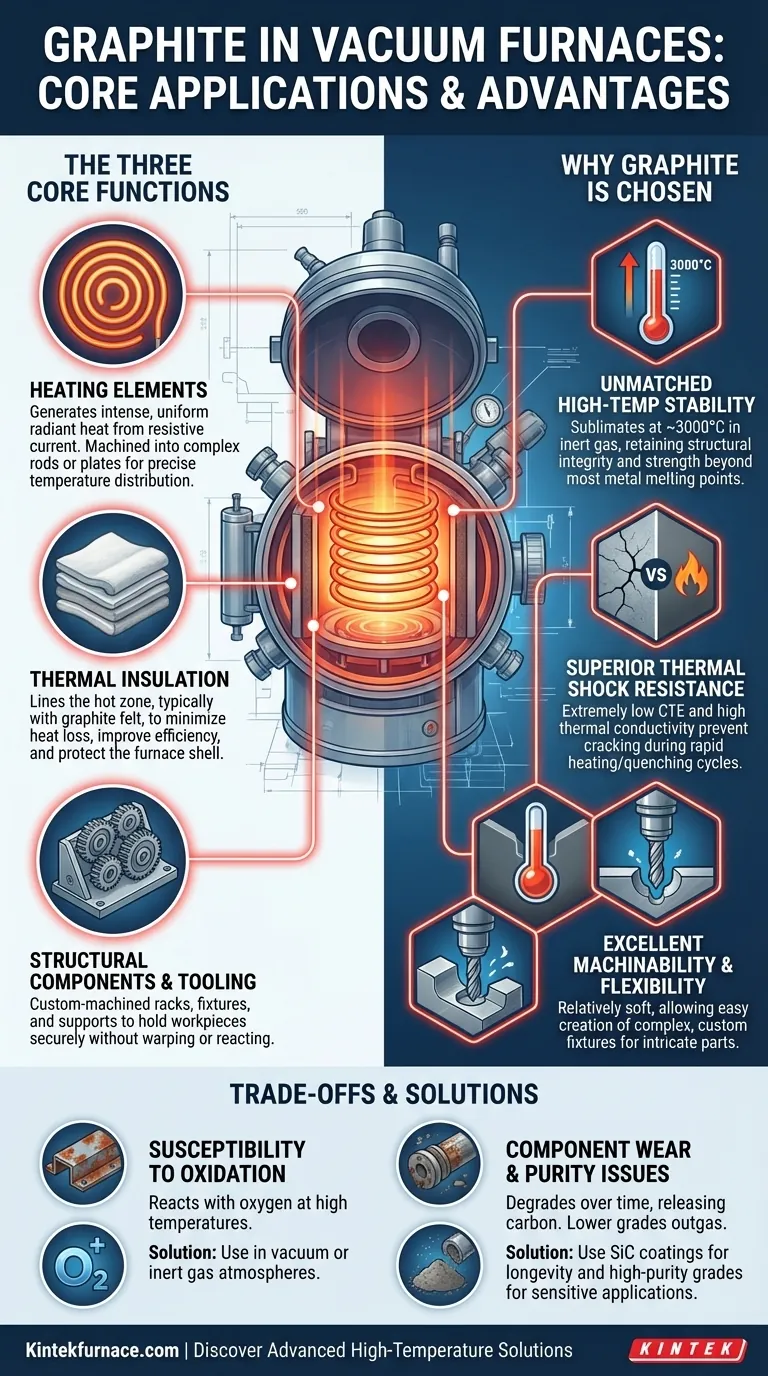
The Core Functions of Graphite in a Vacuum Furnace
Graphite's versatility allows it to serve multiple, distinct roles within the same furnace system. Each function leverages a different aspect of its material properties.
Heating Elements
Graphite is used to construct the resistive heating elements that are the heart of the furnace. When a high electrical current is passed through them, their inherent resistance generates intense, uniform radiant heat.
These elements can be machined into complex shapes like rods, plates, or cylinders to ensure precise and even temperature distribution throughout the furnace's hot zone.
Thermal Insulation
The furnace's hot zone is lined with graphite-based insulation to prevent heat from escaping. This is most commonly achieved using graphite felt, a soft, lightweight material with outstanding insulating properties in a vacuum.
This felt minimizes heat loss, which improves energy efficiency and protects the furnace's outer steel shell. In some cases, rigid graphite boards are also used for structural insulation.
Structural Components and Tooling
Graphite is the ideal material for building the internal structures that hold the products being heat-treated. This includes racks, fixtures, holders, and support posts.
Because graphite is easily machined, these components can be custom-designed for specific parts, ensuring they are held securely without warping or reacting with the material during the heating cycle. Graphite retorts, or specialized containers, are also used for processes like sintering where materials must be contained.
Why Graphite is the Material of Choice
Other materials can withstand high temperatures, but none offer the same balanced profile of thermal, mechanical, and practical advantages as graphite for vacuum applications.
Unmatched High-Temperature Stability
Graphite does not melt at atmospheric pressure. Instead, it sublimates (turns directly from a solid to a gas) at temperatures approaching 3,000°C (over 5,400°F) in an inert environment.
This incredibly high sublimation point means it retains its structural integrity and strength far beyond the melting point of most metals, ensuring the furnace interior remains stable during operation.
Superior Thermal Shock Resistance
Thermal shock is the stress a material endures when it undergoes a rapid temperature change. Graphite has an extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), meaning it barely expands or contracts when heated or cooled.
Combined with its high thermal conductivity, which dissipates thermal stress quickly, this low CTE gives graphite exceptional resistance to cracking during rapid heating or quenching cycles.
Excellent Machinability and Design Flexibility
Despite its strength at high temperatures, graphite is a relatively soft material that is easy to machine into complex and precise shapes.
This allows for the creation of custom fixtures tailored to intricate parts found in the aerospace and electronics industries, enhancing process efficiency and final product quality.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, graphite is not without its operational considerations. Understanding its limitations is key to maximizing performance and component lifespan.
Susceptibility to Oxidation
Graphite's primary weakness is its reaction with oxygen at high temperatures. Even small air leaks into a vacuum furnace can cause graphite components to rapidly oxidize and degrade.
This is precisely why graphite is used in vacuum or inert gas atmospheres, which protect it from being consumed by oxygen.
Component Lifespan and Wear
Over many cycles, graphite components will naturally degrade, releasing fine carbon dust. This requires periodic furnace cleaning and eventual component replacement.
To combat this, advanced solutions like protective silicon carbide (SiC) coatings are often applied. This coating creates a durable, non-porous barrier that significantly extends the life of heating elements and fixtures.
Purity and Outgassing
For ultra-sensitive applications like semiconductor manufacturing, the purity of the graphite is critical. Lower-grade graphite can release trapped impurities ("outgassing") at high temperatures, potentially contaminating the workpiece.
Using high-purity graphite grades is essential in these contexts to maintain the integrity of the process and the final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific grade and form of graphite you use should align directly with your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is process precision and purity: Invest in high-purity graphite and custom-machined fixtures to ensure dimensional stability and prevent product contamination.
- If your primary focus is maximizing component life and reducing maintenance: Opt for components with a protective silicon carbide (SiC) coating and use high-quality felt insulation to improve thermal efficiency.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treating: Standard, well-machined graphite fixtures and reliable heating elements will provide a robust and cost-effective solution for most applications.
By understanding these properties and trade-offs, you can leverage graphite to achieve unparalleled control and reliability in your high-temperature processes.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Heating Elements | Uniform radiant heat, precise temperature control, complex shapes for even distribution |
| Thermal Insulation | High efficiency with graphite felt, minimizes heat loss, protects furnace structure |
| Structural Components | Easy machinability, custom fixtures, secure workpiece holding without warping |
| Why Chosen | High-temperature stability (sublimates at ~3000°C), thermal shock resistance, design flexibility |
| Limitations | Susceptible to oxidation, requires vacuum/inert gas, periodic replacement, purity concerns for sensitive applications |
Ready to elevate your high-temperature processes with reliable graphite solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and product quality. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does Vacuum Hot Press equipment contribute to the energy and power generation sector? Boost Efficiency and Durability
- Which process parameters must be optimized for specific materials in a vacuum hot press furnace? Achieve Optimal Density and Microstructure
- How does a vacuum or protective atmosphere reduce oxidation in molten metals? Prevent Oxide Inclusions for Stronger Metals
- What are the overall benefits of using hot pressing in manufacturing? Achieve Superior Performance and Precision
- What is the process of hot pressing? A Guide to Achieving Superior Material Density



















