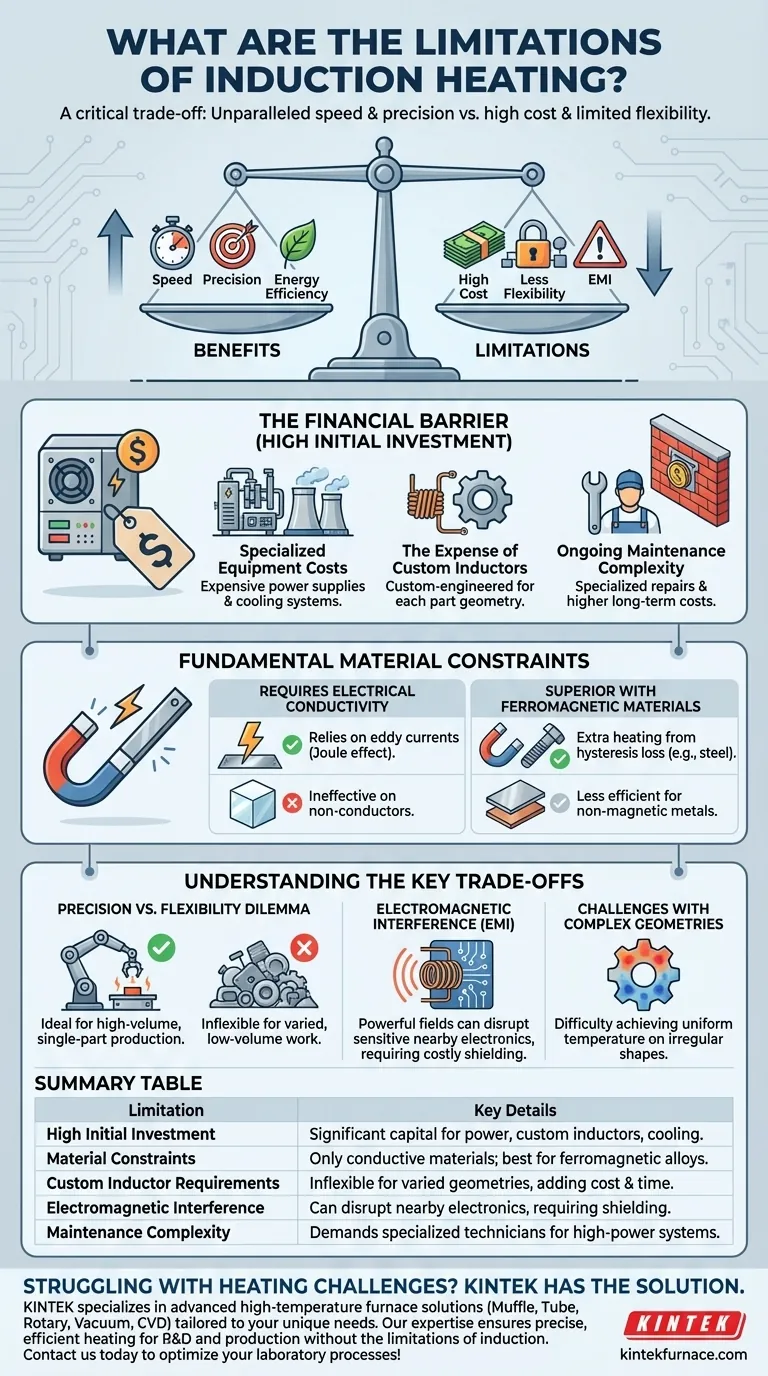
While remarkably efficient and precise, induction heating is not a universal solution for every application. Its primary limitations stem from high initial equipment costs, strict material requirements, the need for custom-designed inductors for each unique part, and the potential for creating electromagnetic interference with nearby systems.
The decision to use induction heating hinges on a critical trade-off. You gain unparalleled speed, precision, and energy efficiency, but you must accept a higher upfront investment and significantly less flexibility in materials and part geometry compared to conventional heating methods.
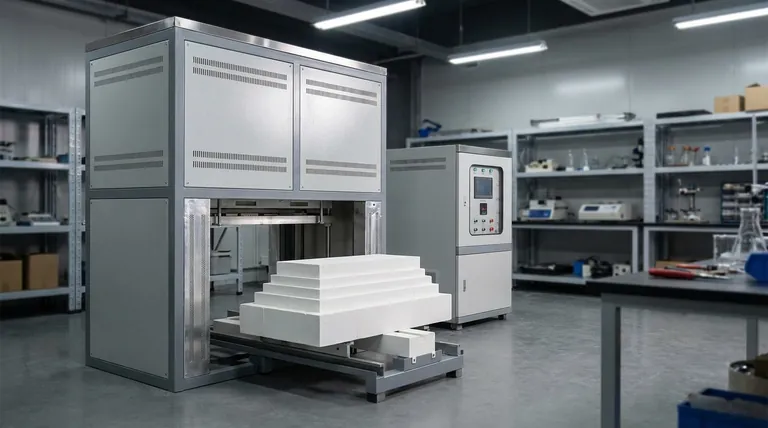

The Financial Barrier: High Initial Investment
Induction heating systems often require a significant capital outlay before you can begin operation. This cost is a major factor when comparing it to simpler, more traditional heating technologies like gas furnaces or resistance ovens.
Specialized Equipment Costs
The power supplies that generate the high-frequency alternating current are complex and expensive. These units, along with the necessary water-cooling systems to protect the electronics and the induction coil itself, represent a substantial upfront cost.
The Expense of Custom Inductors
The induction coil, or inductor, is not a one-size-fits-all component. It must be carefully designed and fabricated to match the specific geometry of the part being heated for maximum efficiency. This custom engineering adds considerable cost and time, especially for complex parts or low-volume production runs.
Ongoing Maintenance Complexity
The high-power electronics and advanced cooling systems demand more specialized maintenance than simpler heating systems. Repairing or servicing these components requires trained technicians and can lead to higher long-term operational expenses.
Fundamental Material Constraints
The physics of induction heating inherently restricts the types of materials it can process effectively. The method relies entirely on the electromagnetic properties of the workpiece.
The Requirement for Electrical Conductivity
Induction heating works by inducing electrical currents (eddy currents) within a material. If a material is not electrically conductive, like most ceramics, polymers, or glass, it cannot generate these currents and therefore will not heat up directly.
The Joule Effect and Resistance
The heat itself is generated by the material's resistance to the flow of these eddy currents, a phenomenon known as the Joule effect. Materials with very low resistance may require extremely high currents to heat effectively, impacting efficiency.
Superior Performance with Ferromagnetic Materials
Materials like iron, nickel, and cobalt benefit from a secondary heating effect called hysteresis loss. This makes induction exceptionally effective for steels and other magnetic alloys, but less so for non-magnetic conductive materials like aluminum or copper at lower frequencies.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing induction heating means accepting specific operational limitations in exchange for its unique benefits. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for making an informed decision.
The Precision vs. Flexibility Dilemma
A custom-designed inductor provides extremely localized and repeatable heating, which is ideal for automated, high-volume production of a single part. However, this same inductor is useless for a part with a different size or shape, making the process highly inflexible for varied, low-volume work.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
Induction systems generate powerful magnetic fields that can disrupt or damage nearby sensitive electronic equipment. Proper shielding and facility planning are essential to mitigate this electromagnetic interference, adding another layer of complexity and cost to implementation.
Challenges with Complex Geometries
Achieving a uniform temperature on parts with complex shapes, sharp corners, or holes can be difficult. The magnetic field may couple unevenly, leading to hot spots and cool spots that can compromise the quality of processes like heat treating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
By weighing these limitations against your specific goals, you can determine if induction is the correct technology for your application.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, repeatable production of a specific metal part: Induction heating is likely an excellent long-term investment, as its speed and consistency will outweigh the initial cost.
- If your primary focus is R&D or heating many different part geometries: The high cost and inflexibility of custom inductors may make conventional furnace or flame heating more practical.
- If your primary focus is heating non-conductive materials: You must either select a different technology or investigate indirect induction heating, which uses a conductive sleeve (a susceptor) to transfer heat.
Understanding these constraints is the key to correctly leveraging induction heating's powerful capabilities for the right application.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Key Details |
|---|---|
| High Initial Investment | Significant capital for power supplies, custom inductors, and cooling systems. |
| Material Constraints | Only works with electrically conductive materials; best for ferromagnetic alloys. |
| Custom Inductor Requirements | Inflexible for varied geometries, adding cost and time for unique parts. |
| Electromagnetic Interference | Can disrupt nearby electronics, requiring shielding and careful planning. |
| Maintenance Complexity | Demands specialized technicians for high-power electronics and cooling systems. |
Struggling with heating challenges? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems with deep customization capabilities. Whether you're in high-volume production or R&D, our expertise ensures precise, efficient heating without the limitations of induction. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your laboratory processes and deliver reliable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment



















