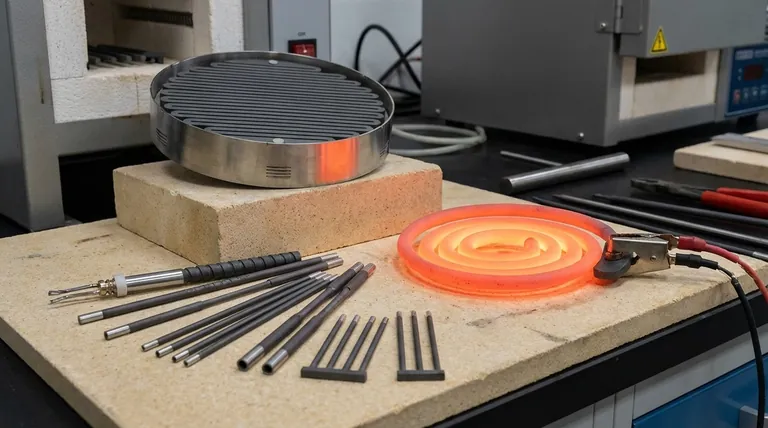
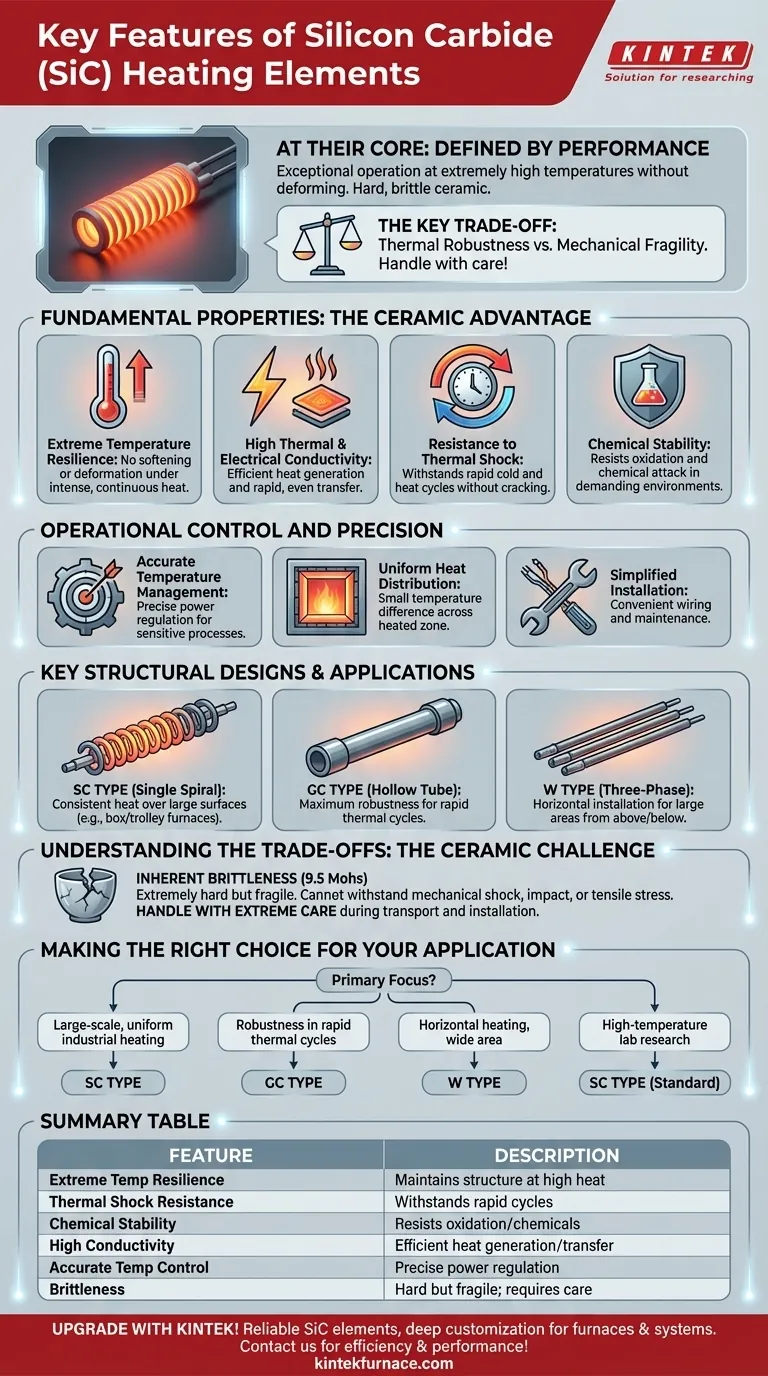
At their core, Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements are defined by their exceptional ability to operate at extremely high temperatures without deforming. They are hard, brittle ceramic components prized for their thermal shock resistance, chemical stability, and capacity for delivering precise and uniform heat.
While SiC elements provide unmatched performance in high-temperature environments, their key characteristic is the trade-off between thermal robustness and mechanical fragility. Understanding that they are hard but brittle ceramics is the most critical factor in selecting and implementing them successfully.

Fundamental Properties: The Ceramic Advantage
The value of Silicon Carbide originates from its inherent material properties, which make it ideal for extreme thermal applications where traditional metallic elements would fail.
Extreme Temperature Resilience
SiC elements possess outstanding high-temperature strength. Unlike metals, they do not soften or deform under continuous, intense heat, ensuring structural integrity and consistent performance over their operational life.
High Thermal & Electrical Conductivity
As a ceramic material, SiC has high electrical conductivity that allows it to generate heat efficiently. This is paired with good thermal conductivity, enabling the element to transfer that heat rapidly and evenly to the furnace environment.
Resistance to Thermal Shock
A key feature is their resistance to rapid cold and heat cycles. This makes them suitable for processes that require fast ramp-up and cool-down times, where other materials might crack or degrade.
Chemical Stability
SiC is a chemically stable material, offering robustness in demanding environments. This resistance to oxidation and chemical attack contributes to a longer service life in various industrial atmospheres.
Operational Control and Precision
Beyond raw thermal performance, SiC elements are engineered for processes that demand accuracy and consistency.
Accurate Temperature Management
These elements enable a high degree of temperature control accuracy. Their predictable resistance and stable performance allow for precise power regulation, which is essential for sensitive research and manufacturing processes.
Uniform Heat Distribution
SiC elements are known for producing a small temperature difference across the heated zone. This spatial temperature uniformity is crucial for applications like metal treatment and ceramics firing, where consistency is paramount.
Simplified Installation
The design of many SiC elements facilitates convenient wiring and installation. This simplifies furnace construction and maintenance, reducing downtime and operational complexity.
Key Structural Designs and Their Applications
SiC elements are not one-size-fits-all. Different shapes are engineered to optimize performance for specific heating configurations and industrial needs.
SC Type (Single Spiral)
The SC Type features a single spiral rod design. It is highly effective in systems requiring consistent heat distribution over large surfaces, such as the bottom or sides of large box furnaces, trolley furnaces, and laboratory equipment.
GC Type (Hollow Tube)
Characterized by a hollow tubular structure with thickened ends, the GC Type is engineered for maximum robustness. Its design is especially suited for handling rapid thermal cycles and providing enhanced chemical stability.
W Type (Three-Phase)
The W Type consists of three SiC rods joined at one end. This configuration is specifically designed for horizontal installation and is ideal for uniformly heating large surface areas from above or below.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Ceramic Challenge
To use SiC elements effectively, it is critical to acknowledge their limitations. Their primary strength—being a hard ceramic—is also the source of their main weakness.
Inherent Brittleness
With a hardness of 9.5 on the Mohs scale, SiC is extremely hard but also very brittle. It cannot withstand mechanical shock, impact, or tensile stress. Dropping an element or overtightening a connection clamp can easily cause it to fracture.
Considerations for Handling
Due to this brittleness, SiC elements must be handled with extreme care during transportation, installation, and furnace maintenance. They require support structures that do not impose mechanical stress, especially as the furnace expands and contracts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct SiC element requires matching its specific design features to your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, uniform industrial heating: The SC type's ability to provide consistent heat over large surfaces makes it ideal for box and trolley furnaces.
- If your primary focus is robustness in rapid thermal cycles: The GC type's hollow tubular design is engineered specifically for this demanding condition.
- If your primary focus is horizontal heating over a wide area: The W-type element is uniquely designed for this configuration, ensuring uniform heat distribution.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature laboratory research: The reliability, stability, and precise control offered by standard SC-type elements are essential for experimental work.
By matching the distinct features of each SiC element type to your operational needs, you ensure reliable and efficient performance in the most demanding high-temperature applications.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Extreme Temperature Resilience | Maintains structural integrity without deformation at high temperatures. |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Withstands rapid heating and cooling cycles without cracking. |
| Chemical Stability | Resists oxidation and chemical attack for longer service life. |
| High Thermal & Electrical Conductivity | Efficient heat generation and uniform distribution. |
| Accurate Temperature Control | Enables precise power regulation for sensitive processes. |
| Key Types (SC, GC, W) | Designed for specific applications like uniform heating, robustness, and horizontal installation. |
| Brittleness | Hard but fragile; requires careful handling to avoid fractures. |
Upgrade your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable Silicon Carbide heating elements tailored to your needs. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions



















