At its core, silicon carbide (SiC) is an ideal material for heating elements due to its unique combination of high-temperature strength, excellent thermal conductivity, and robust chemical resistance. These properties allow it to generate and transfer intense heat efficiently while surviving the extreme conditions inside a furnace, ensuring both performance and longevity.
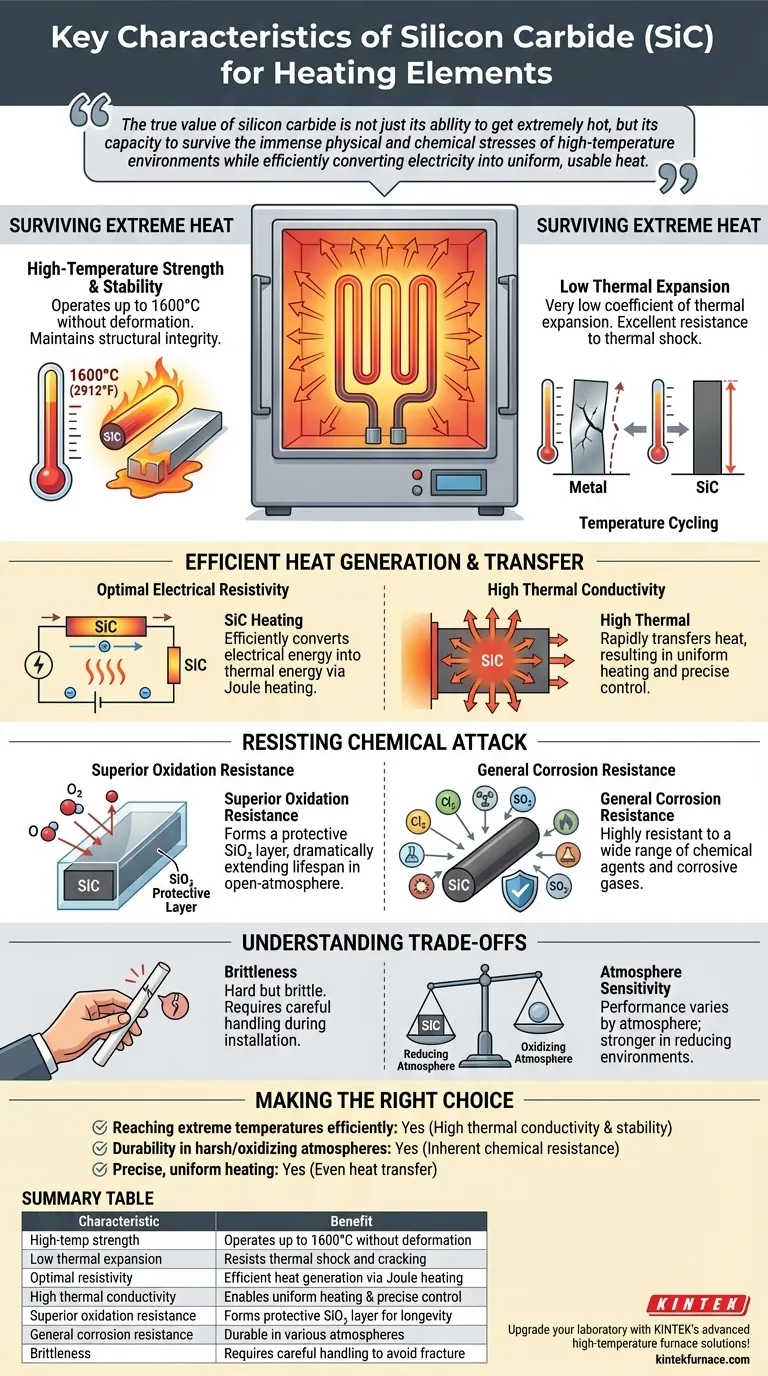
The true value of silicon carbide is not just its ability to get extremely hot, but its capacity to survive the immense physical and chemical stresses of high-temperature environments while efficiently converting electricity into uniform, usable heat.
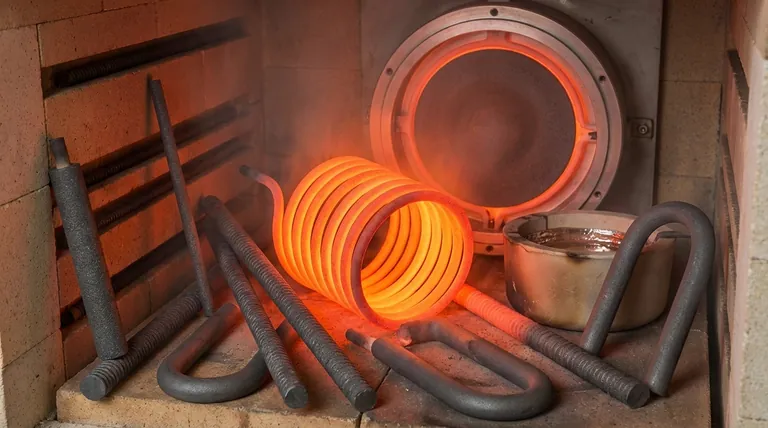

The Foundation: Surviving Extreme Heat
Before a material can be an effective heater, it must first endure the environment it creates. Silicon carbide excels at withstanding the immense thermal and physical stress of industrial heating processes.
High-Temperature Strength and Stability
Silicon carbide is a ceramic material with an exceptionally high decomposition temperature. This allows SiC elements to operate at surface temperatures up to 1600°C (2912°F) without melting, deforming, or breaking down.
Unlike many metals that soften significantly at high temperatures, SiC maintains its structural integrity, ensuring a long and reliable service life.
Low Thermal Expansion
A material's tendency to expand when heated and contract when cooled is a primary cause of mechanical failure. SiC has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion, meaning it changes size very little during temperature cycles.
This property provides excellent resistance to thermal shock, preventing the element from cracking or fracturing when heated or cooled rapidly.
The Core Function: Efficient Heat Generation and Transfer
A heating element has two jobs: generate heat and deliver it effectively. SiC's electrical and thermal properties are perfectly suited for both tasks.
Optimal Electrical Resistivity
Heating elements work by resisting the flow of electricity, a principle known as Joule heating. SiC possesses the ideal electrical resistivity to convert electrical energy into thermal energy with high efficiency.
Its wide bandgap energy also allows it to maintain this optimal resistivity at very high temperatures, ensuring consistent performance where other materials might fail.
High Thermal Conductivity
Once heat is generated within the element, it must be transferred to the surrounding environment. SiC features high thermal conductivity, meaning it moves heat away from itself and into the furnace chamber very efficiently.
This results in more uniform heating and allows for precise temperature control, which is critical for sensitive industrial and laboratory applications.
The Key to Longevity: Resisting Chemical Attack
The inside of a furnace is often a chemically aggressive environment, especially at high temperatures. SiC's inherent durability protects it from degradation.
Superior Oxidation Resistance
When exposed to air at high temperatures, most materials rapidly oxidize and degrade. Silicon carbide, however, forms a thin, protective layer of silicon dioxide (SiO₂) on its surface.
This passive layer inhibits further oxidation, dramatically extending the element's lifespan in open-atmosphere furnaces.
General Corrosion Resistance
Beyond just oxygen, SiC is highly resistant to a wide range of chemical agents and corrosive gases. This makes it a reliable choice for processes involving various atmospheres where other elements, like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2), might be more vulnerable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every situation. Understanding SiC's limitations is key to using it correctly.
Brittleness vs. Ductility
As a ceramic, silicon carbide is hard but brittle. Unlike metal heating elements that have high ductility and can be easily drawn into wire or bent, SiC elements can fracture if subjected to mechanical shock or impact. Care must be taken during installation and maintenance.
Atmosphere Sensitivity
While SiC has excellent oxidation resistance, its performance relative to other materials can vary by atmosphere. For example, certain specialized elements like MoSi2 may offer advantages in specific high-temperature oxidizing environments, though SiC is often stronger in reducing atmospheres.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right heating element depends entirely on your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme temperatures efficiently: SiC's combination of high thermal conductivity and superior high-temperature stability makes it a premier choice.
- If your primary focus is durability in harsh or oxidizing atmospheres: SiC's inherent chemical resistance ensures a longer service life with less maintenance than many metallic alternatives.
- If your primary focus is precise, uniform heating for sensitive processes: SiC's ability to transfer heat evenly allows for the exceptional temperature control required in laboratory and research settings.
Ultimately, selecting silicon carbide is a decision for robust performance and reliability in applications where other materials would fail.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Benefit |
|---|---|
| High-temperature strength | Operates up to 1600°C without deformation |
| Low thermal expansion | Resists thermal shock and cracking |
| Optimal electrical resistivity | Efficient heat generation via Joule heating |
| High thermal conductivity | Enables uniform heating and precise control |
| Superior oxidation resistance | Forms protective SiO₂ layer for longevity |
| General corrosion resistance | Durable in various atmospheres |
| Brittleness | Requires careful handling to avoid fracture |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable heating elements and systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your high-temperature applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability



















