Fundamentally, Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements are engineered for the most demanding high-temperature environments. They are a ceramic-metallic composite defined by their ability to operate reliably at extreme temperatures up to 1850°C, their long service life, and their unique self-healing properties in oxidizing atmospheres.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) offers the highest operational temperatures and longest lifespan of any metallic heating element, but this performance is contingent on operating within an oxidizing atmosphere and handling the material carefully due to its inherent brittleness at room temperature.
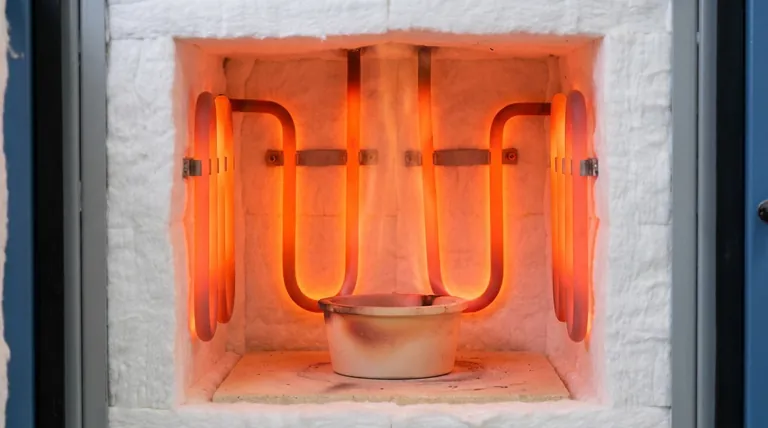

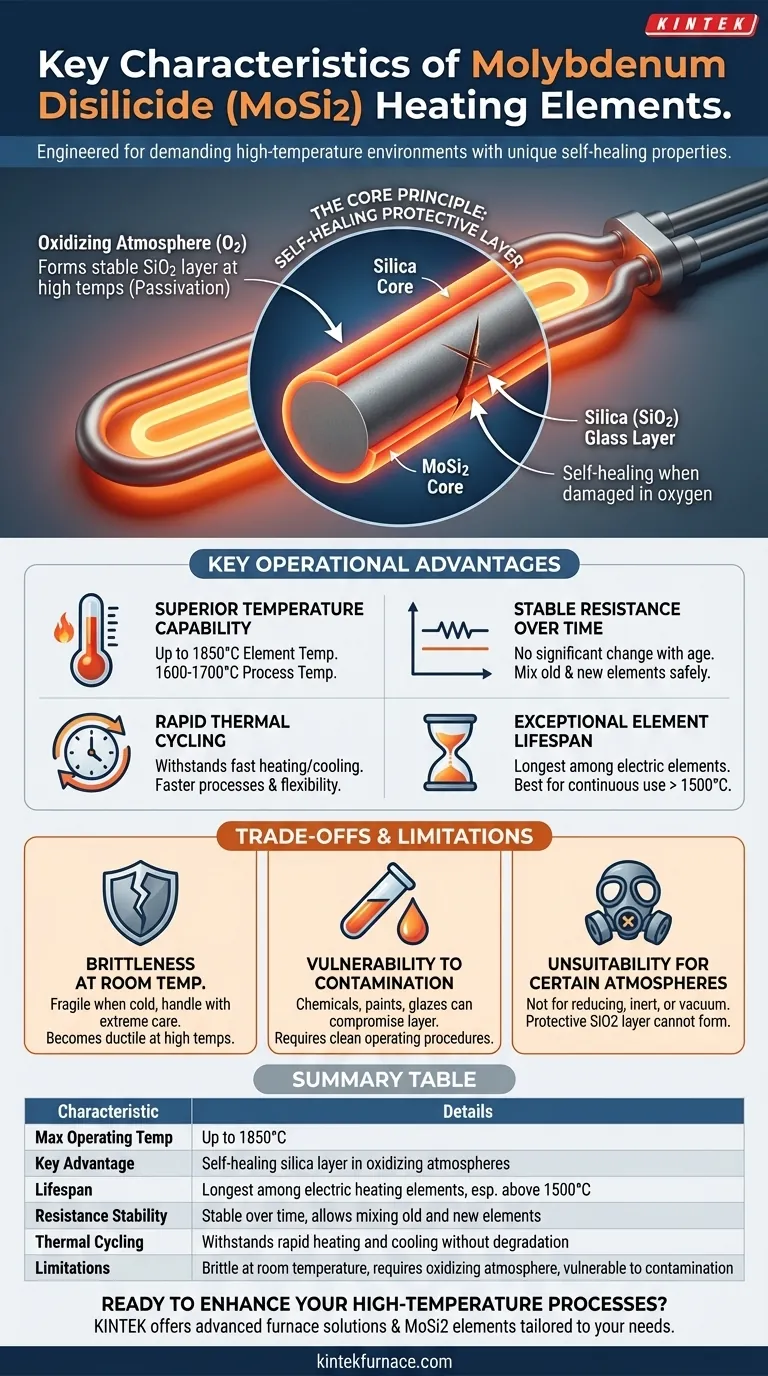
The Core Principle: A Self-Healing Protective Layer
The defining characteristic of MoSi2 is not just its high melting point, but its ability to protect itself from degradation at extreme temperatures. This is the key to its performance and longevity.
How the Silica (SiO2) Layer Forms
When heated in the presence of oxygen, the surface of a MoSi2 element forms a thin, non-porous layer of pure silica, or glass (SiO2). This process is known as passivation.
This silica layer is highly stable and acts as a barrier, preventing the underlying Molybdenum Disilicide from further oxidation and subsequent failure.
The Importance of an Oxidizing Atmosphere
The formation of this protective layer is entirely dependent on the presence of oxygen. This makes MoSi2 elements exceptionally well-suited for operation in air or other oxygen-rich environments.
If the layer is ever scratched or damaged, the exposed material will simply re-form the protective silica layer as long as it remains in an oxidizing atmosphere, giving it a "self-healing" quality.
Key Operational Advantages
The unique properties of MoSi2 translate into several distinct advantages for high-temperature furnace design and operation.
Superior Temperature Capability
MoSi2 elements have the highest operating temperatures among common resistance heating elements, capable of reaching element temperatures of 1850°C and enabling furnace process temperatures of 1600-1700°C.
Stable Resistance Over Time
Unlike many other heating elements, the electrical resistance of MoSi2 does not change significantly with age or use. This stability is a critical advantage for furnace maintenance and control.
Because the resistance is stable, new elements can be wired in series with old elements without causing imbalances in power distribution or overheating.
Rapid Thermal Cycling
These elements can withstand rapid heating and cooling cycles without suffering from thermal shock or degradation. This allows for faster process times and more flexible furnace operation.
Exceptional Element Lifespan
Due to the stable, protective silica layer, MoSi2 elements offer the longest inherent service life of all electric heating element types, especially when operated continuously at temperatures above 1500°C.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
To leverage MoSi2 effectively, it is critical to understand its specific limitations. These are not flaws, but inherent properties that must be accounted for in design and operation.
Brittleness at Room Temperature
MoSi2 is a cermet (ceramic-metallic) material and is very brittle and fragile at room temperature. The elements must be handled with extreme care during installation and maintenance to avoid fracture.
While brittle when cold, the material becomes more ductile at high operating temperatures.
Vulnerability to Contamination
The integrity of the protective silica layer can be compromised by certain chemical reactions. Contaminants from paints, glazes, or improperly dried materials can attack the element surface and lead to premature failure.
Proper furnace maintenance and clean operating procedures are essential to maximize the lifespan of MoSi2 elements.
Unsuitability for Certain Atmospheres
The protective mechanism of MoSi2 requires oxygen. Therefore, these elements are generally not suitable for use in reducing atmospheres (like hydrogen or cracked ammonia) or in a hard vacuum, as the protective SiO2 layer cannot form or be maintained.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a heating element requires matching its characteristics to your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature and long-term stability: MoSi2 is the superior choice for high-temperature oxidizing atmospheres, offering unparalleled performance and lifespan.
- If your furnace undergoes frequent mechanical shock or rough handling: The inherent brittleness of MoSi2 requires careful design and strict handling protocols to prevent breakage.
- If you require operation in a reducing, inert, or vacuum atmosphere: MoSi2 is likely unsuitable, and you should consider alternative materials like tungsten, molybdenum metal, or graphite.
By understanding both its unparalleled strengths and its specific limitations, you can confidently leverage MoSi2 technology for the most demanding high-temperature applications.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Details |
|---|---|
| Maximum Operating Temperature | Up to 1850°C |
| Key Advantage | Self-healing silica layer in oxidizing atmospheres |
| Lifespan | Longest among electric heating elements, especially above 1500°C |
| Resistance Stability | Stable over time, allows mixing old and new elements |
| Thermal Cycling | Withstands rapid heating and cooling without degradation |
| Limitations | Brittle at room temperature, requires oxidizing atmosphere, vulnerable to contamination |
Ready to enhance your high-temperature processes with reliable heating solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our MoSi2 heating elements and other innovations can deliver superior performance and longevity for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity



















