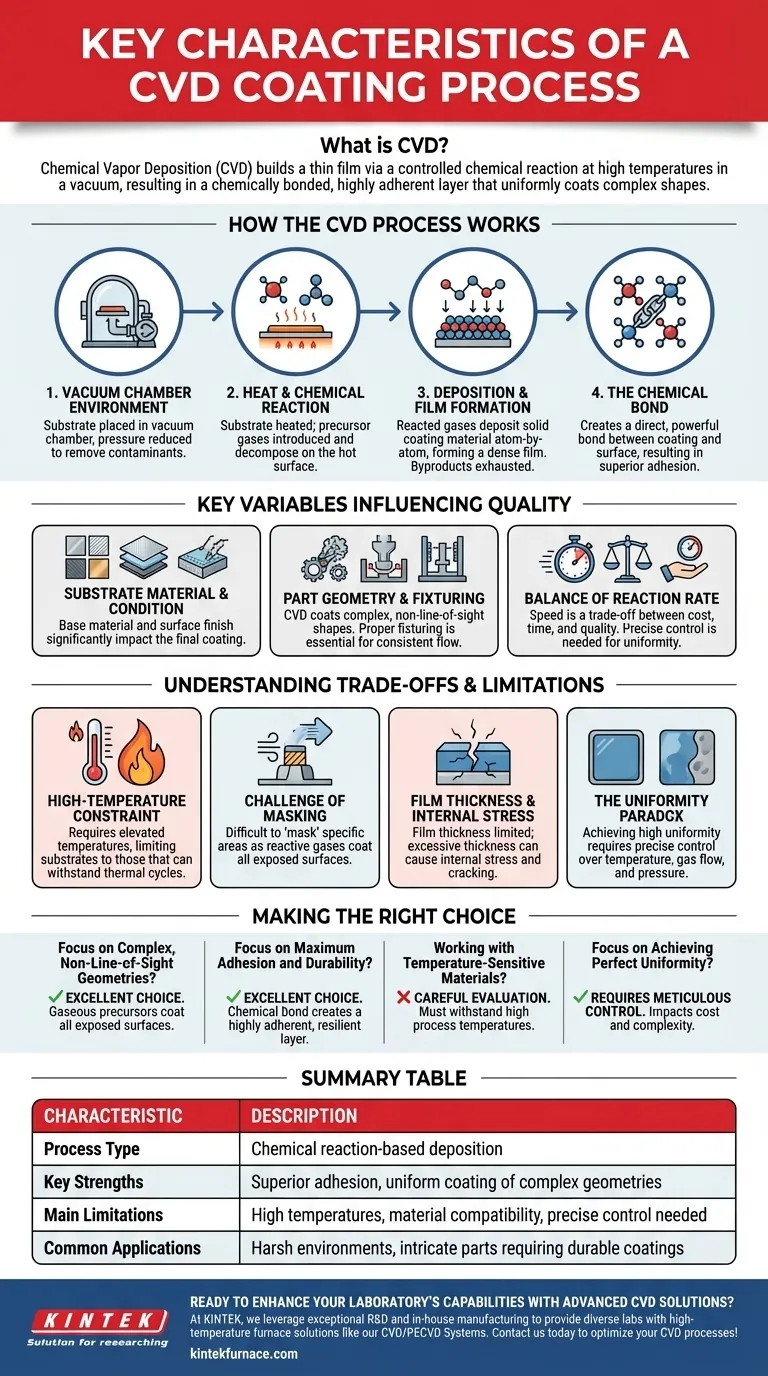
In essence, the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process is a method that builds a thin film on a component's surface through a controlled chemical reaction. Its defining characteristics are the use of high temperatures and a vacuum environment to convert gaseous precursor chemicals into a solid coating. This process results in a chemically bonded, highly adherent layer that can coat complex shapes uniformly, as it is not limited to a line-of-sight application.
The core strength of CVD lies in its fundamental mechanism: a chemical reaction. This reaction creates exceptionally strong coating adhesion and the ability to cover intricate geometries, but it also imposes significant constraints, primarily related to temperature, material compatibility, and the precision required to achieve uniformity.
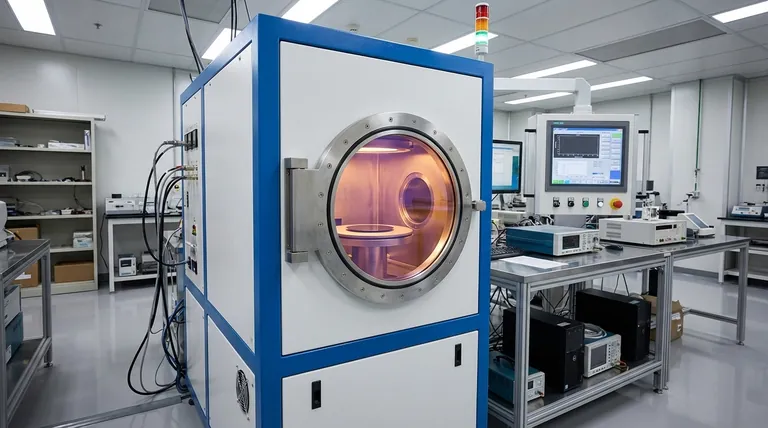

How the CVD Process Works
To understand its characteristics, you must first understand its mechanism. CVD is not a simple spray-on application; it is a process of building a new surface, molecule by molecule.
The Vacuum Chamber Environment
A component, or "substrate," is placed into a sealed deposition chamber. The chamber is put under a vacuum, meaning the pressure is reduced defectos below atmospheric levels, to remove contaminants and control the environment.
Volatile precursor gases, which contain the atoms of the desired coating material, are then introduced into the chamber in a highly controlled manner.
The Role of Heat and Chemical Reaction
The substrate is typically heated to an elevated temperature. This heat provides the energy needed to initiate a chemical reaction, causing the precursor gases to decompose on or near the hot surface of the component.
This reaction is the heart of the CVD process. The substrate itself can act as a catalyst, promoting the reaction directly on its surface.
Deposition and Film Formation
As the precursor gases react, they deposit the solid coating material onto the substrate, forming a thin, dense, and durable film. This deposition occurs atom-by-atom or molecule-by-molecule.
The remaining gaseous byproducts from the reaction are exhausted from the chamber and treated, as they can be toxic or flammable.
The Chemical Bond: Source of Superior Adhesion
Unlike a mechanical coating, the CVD film is not just sitting on top of the substrate. The chemical reaction creates a direct, powerful bond between the coating and the surface material. This results in superior adhesion that is exceptionally difficult to delaminate.
Key Variables That Influence Coating Quality
The final properties of a CVD coating are not guaranteed; they are the result of carefully managing several critical process variables.
Substrate Material and Condition
The base material of the part and its surface finish significantly impact the final coating. Exotic alloys may react differently than standard stainless steel, and a rough surface will coat differently than a highly polished one.
Part Geometry and Fixturing
Because the precursor gases can flow around the part, CVD excels at coating complex, non-line-of-sight geometries. However, extremely confined areas, like the bore of a tiny needle, may receive less coating.
Proper fixturing is essential to hold parts securely, prevent damage, and ensure the gases can flow consistently across all critical surfaces.
The Balance of Reaction Rate
The speed of the coating process is a trade-off between cost, time, and quality. A faster reaction may reduce cost, but it can also lead to variations in coating thickness and uniformity. Precise control is needed to find the right balance.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No process is perfect. The strengths of CVD are directly linked to its inherent limitations, which you must consider.
The High-Temperature Constraint
The elevated temperatures required to drive the chemical reaction are CVD's most significant limitation. This heat can alter the properties of the base material, limiting the process to substrates that can withstand the thermal cycle without softening, warping, or undergoing undesirable metallurgical changes.
The Challenge of Masking
Because CVD is a gaseous, non-line-of-sight process, it is inherently difficult to "mask" or protect specific areas of a part from being coated. The reactive gases will try to coat every exposed surface they can reach.
Film Thickness and Internal Stress
While the coating is strong, its thickness is limited. As the film builds up, internal stresses can develop. If the coating becomes too thick, this stress can cause it to crack or fail, limiting its practical application for very thick layers.
The Uniformity Paradox
CVD is capable of producing highly uniform coatings. However, this is only achievable with extremely precise control over temperature, gas flow, and pressure. Small variations in these parameters can lead to a product with poor uniformity and potential particle inclusions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the decision to use CVD depends on aligning its unique characteristics with your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, non-line-of-sight geometries: CVD is an excellent choice because its gaseous precursors coat all exposed surfaces.
- If your primary focus is maximum coating adhesion and durability: The chemical bond formed during the CVD process creates a highly adherent and resilient layer ideal for harsh environments.
- If you are working with temperature-sensitive materials: You must carefully evaluate if your substrate can withstand the high process temperatures required by most CVD methods.
- If your primary focus is achieving perfect uniformity: Be prepared for a process that requires meticulous control over many variables, which can impact cost and complexity.
By understanding these core characteristics, you can leverage CVD's unique strengths while successfully navigating its inherent limitations.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Chemical reaction-based deposition |
| Key Strengths | Superior adhesion, uniform coating of complex geometries |
| Main Limitations | High temperatures, material compatibility, precise control needed |
| Common Applications | Harsh environments, intricate parts requiring durable coatings |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's capabilities with advanced CVD solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse labs with high-temperature furnace solutions like our CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for superior coating adhesion and complex geometry coverage. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your CVD processes and deliver tailored results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What role does PECVD play in optical coatings? Essential for Low-Temp, High-Precision Film Deposition
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What gases are used in the PECVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precise Gas Selection
- What is the second benefit of deposition within a discharge in PECVD? Enhance Film Quality with Ion Bombardment



















