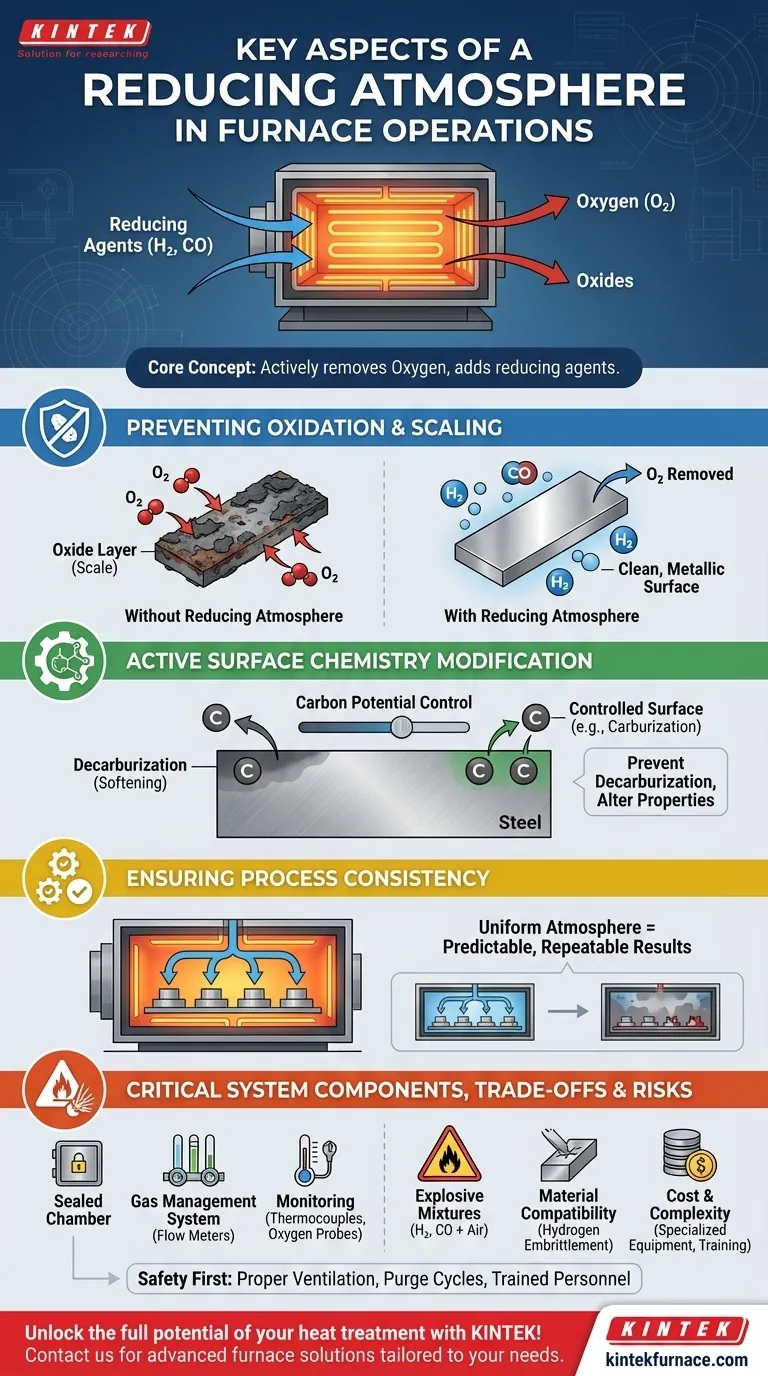
At its core, a reducing atmosphere is a carefully controlled gaseous environment inside a furnace that actively removes oxygen and adds reducing agents like hydrogen or carbon monoxide. Its primary purpose is to prevent surface reactions like scaling and oxidation on a workpiece during high-temperature heat treatment, ensuring the material's integrity and achieving specific surface properties.
A reducing atmosphere is not merely a protective blanket; it is an active chemical agent in the heat treatment process. Mastering its composition and control is the key to preventing unwanted oxidation and precisely modifying a material's surface chemistry for desired performance characteristics.

The Fundamental Role of a Reducing Atmosphere
To understand its importance, you must see the atmosphere as an ingredient in the process, just as critical as time and temperature. It directly influences the final quality and properties of the material being treated.
Preventing Oxidation and Scaling
At the high temperatures required for heat treatment, most metals will readily react with any available oxygen. This reaction forms an oxide layer, or "scale," on the material's surface.
A reducing atmosphere, rich in components like hydrogen (H₂) or carbon monoxide (CO), chemically counteracts this. It strips oxygen atoms from the surface, preventing oxides from forming and even "reducing" any existing light oxides back to their pure metallic state.
Active Surface Chemistry Modification
Beyond simple protection, a reducing atmosphere can be engineered to actively alter the surface of a material.
For example, by controlling the carbon potential of the gas, you can prevent decarburization—the loss of carbon from the surface of steel, which would soften it. In other processes, the atmosphere is deliberately designed to cause decarburization or other specific surface changes.
Ensuring Process Consistency
An inconsistent atmosphere is a primary cause of defects. If the gas composition varies within the furnace, a part can experience both reducing and oxidizing conditions on different areas of its surface.
Maintaining a uniform atmosphere with a consistent concentration of reducing agents ensures every part, and every surface of that part, receives the exact same treatment, guaranteeing predictable and repeatable results.
Key Components of an Atmosphere-Controlled System
Achieving and maintaining a precise reducing atmosphere requires specialized furnace hardware designed for containment and control.
The Sealed Heating Chamber
The foundation is a well-sealed chamber, often constructed from high-temperature-resistant alloys and insulating materials. Effective sealing mechanisms are critical to prevent the controlled atmosphere from leaking out and, more importantly, to stop outside air (oxygen) from leaking in.
Gas Management Systems
These systems introduce the desired gases and precisely control their mixture and flow rate. This includes gas inlets, outlets, and atmosphere control systems with flow meters and analyzers that allow operators to adjust the chemical potential of the environment.
Temperature and Atmosphere Monitoring
Continuous monitoring is non-negotiable for both quality and safety. Thermocouples track temperature, while dedicated sensors like oxygen probes measure the real-time composition of the furnace atmosphere, allowing for immediate corrective action.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Safety Risks
While powerful, reducing atmospheres introduce complexities and hazards that must be managed. A failure to respect these risks can lead to equipment damage, ruined product, or serious injury.
The Risk of Explosive Mixtures
Many gases used to create reducing atmospheres—especially hydrogen and carbon monoxide—are flammable and can be explosive when mixed with air in certain concentrations.
Proper engineering controls, such as operating in a well-ventilated area and using purge cycles with an inert gas like nitrogen before and after the process, are essential safety measures.
Material Compatibility and Unintended Effects
A reducing atmosphere is not a universal solution. For some alloys, a high concentration of hydrogen can lead to hydrogen embrittlement, a phenomenon where the metal becomes brittle and fails under stress. The atmosphere must be chosen based on the specific material being processed.
Cost and Complexity
Maintaining a controlled atmosphere is inherently more complex and costly than heating in open air. It requires specialized equipment, a continuous supply of process gases, sophisticated control systems, and properly trained personnel to operate the furnace safely and effectively.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The ideal atmosphere depends entirely on your material, your desired outcome, and your operational constraints.
- If your primary focus is preventing any surface oxidation on sensitive alloys: A high-purity hydrogen atmosphere or a high-vacuum environment is your most effective choice.
- If you are performing general heat treatment like annealing or normalizing on carbon steels: A cost-effective endothermic or exothermic generated gas will provide sufficient reducing potential.
- If your goal is to actively modify the surface chemistry (e.g., decarburization): You will need a specifically engineered atmosphere with controlled additions of gases like water vapor to drive the reaction.
- If safety and operational simplicity are the top priorities: Consider a nitrogen-based atmosphere with a small percentage of hydrogen, which minimizes flammability risks while still preventing most oxidation.
Ultimately, treating the furnace atmosphere as a critical process input—equal in importance to time and temperature—is the foundation of successful heat treatment.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Preventing Oxidation | Uses reducing agents like H₂ or CO to remove oxygen, preventing scaling and oxidation on materials. |
| Surface Chemistry Modification | Actively alters material surfaces, e.g., controlling carbon potential to prevent decarburization in steel. |
| Process Consistency | Maintains uniform atmosphere for predictable, repeatable results across all parts. |
| Safety Risks | Includes risks of explosive mixtures with gases like H₂ and CO, requiring proper ventilation and purging. |
| Material Compatibility | Must be chosen carefully to avoid issues like hydrogen embrittlement in certain alloys. |
Unlock the full potential of your heat treatment processes with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're working with sensitive alloys or carbon steels, our expertise ensures optimal performance and safety. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and achieve superior material outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















