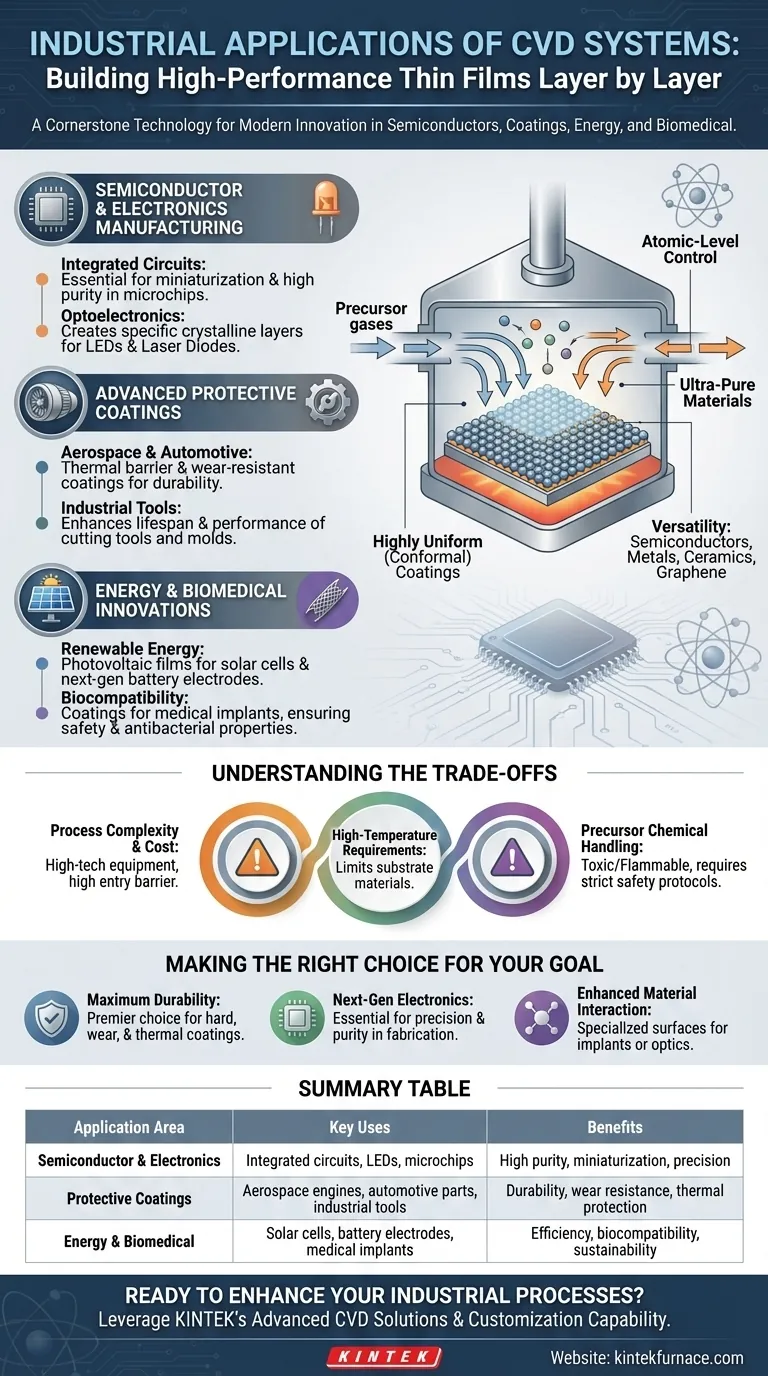
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a cornerstone technology used to build high-performance thin films for a vast range of industrial products. Its primary applications are found in semiconductor manufacturing, protective coatings for aerospace and automotive parts, renewable energy components like solar cells, and advanced biomedical devices.
The true value of CVD lies not in the specific industries it serves, but in its fundamental ability to deposit exceptionally pure, uniform, and functional layers of material onto a surface. This process allows engineers to fundamentally alter an object's properties, making it stronger, more efficient, or electronically active.

The Principle: Why CVD is a Pillar of Modern Industry
Understanding CVD's industrial role requires looking beyond a list of applications and focusing on its core capabilities. It is a process that gives engineers atomic-level control over material fabrication.
Creating Purity and Precision
CVD builds thin films layer by layer from chemical precursors in a gas state. This bottom-up approach results in ultra-pure materials and highly uniform (conformal) coatings, even over complex 3D shapes. This precision is impossible to achieve with many conventional coating methods.
Versatility in Materials
The process is incredibly versatile. By changing the precursor gases, engineers can deposit a wide array of materials, including semiconductors (like silicon), metals, ceramics (like nitrides and oxides), and even advanced materials like graphene.
Core Application: Semiconductor and Electronics Manufacturing
The modern digital world is built on CVD. The technology is indispensable for fabricating the microchips that power everything from smartphones to data centers.
Building Integrated Circuits
CVD is used to deposit the multiple, intricate layers of conductive and insulating materials that form an integrated circuit. This process is critical for achieving the ongoing miniaturization of electronic components.
Enabling Optoelectronics
The manufacturing of Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs) and laser diodes relies on CVD to create the specific crystalline semiconductor layers that generate light efficiently.
Core Application: Advanced Protective Coatings
CVD provides a way to give ordinary materials extraordinary surface properties. This is most evident in industries where durability and performance under stress are critical.
Aerospace and Automotive Durability
In aerospace, CVD is used to apply thermal barrier coatings to engine components, protecting them from extreme heat. In the automotive industry, wear-resistant coatings on engine parts and fuel injection systems reduce friction, improve fuel efficiency, and extend component life.
Enhancing Industrial Tools
Hard coatings like titanium nitride are deposited onto cutting tools and industrial molds using CVD. This dramatically increases their lifespan and performance, allowing them to operate faster and more effectively.
Core Application: Energy and Biomedical Innovations
CVD is also a key enabler for technologies focused on health and sustainability.
Powering Renewable Energy
The production of high-efficiency solar cells depends on CVD to deposit the thin photovoltaic films that convert sunlight into electricity. It is also being used to develop next-generation battery electrodes for improved energy storage.
Engineering Biocompatibility
Medical implants, such as artificial joints or stents, are often coated using CVD. These biocompatible coatings ensure the device is not rejected by the body and can even be designed to have antibacterial properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs of CVD
While powerful, CVD is not a universal solution. Its application involves specific challenges and considerations that are critical to understand.
Process Complexity and Cost
CVD systems are sophisticated pieces of equipment that are expensive to acquire and operate. They require high-vacuum environments, precise temperature control, and expert oversight, making the barrier to entry significant.
High-Temperature Requirements
Many CVD processes operate at very high temperatures. This can limit the types of substrate materials that can be coated, as some materials may warp or melt under such conditions.
Precursor Chemical Handling
The precursor gases used in CVD can be toxic, flammable, or corrosive. Safely handling, storing, and disposing of these chemicals requires stringent protocols and specialized infrastructure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying CVD effectively means matching its capabilities to a specific engineering challenge.
- If your primary focus is maximum component durability: CVD is the premier choice for creating hard, wear-resistant, and thermal barrier coatings that dramatically extend product lifespan.
- If your primary focus is fabricating next-generation electronics: CVD is non-negotiable, providing the essential precision and purity for creating semiconductor and optoelectronic devices.
- If your primary focus is enhancing material interaction: CVD enables the creation of highly specialized surfaces, whether for biocompatible medical implants or for precise optical coatings on lenses.
By understanding its fundamental ability to engineer surfaces at the atomic level, you can leverage Chemical Vapor Deposition as a powerful tool for material innovation.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Semiconductor & Electronics | Integrated circuits, LEDs, microchips | High purity, miniaturization, precision |
| Protective Coatings | Aerospace engines, automotive parts, industrial tools | Durability, wear resistance, thermal protection |
| Energy & Biomedical | Solar cells, battery electrodes, medical implants | Efficiency, biocompatibility, sustainability |
Ready to enhance your industrial processes with advanced CVD solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems, including CVD/PECVD Systems, Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, delivering superior thin films for semiconductors, protective coatings, energy, and biomedical applications. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can drive your innovation forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What role does PECVD play in optical coatings? Essential for Low-Temp, High-Precision Film Deposition
- What is the second benefit of deposition within a discharge in PECVD? Enhance Film Quality with Ion Bombardment



















