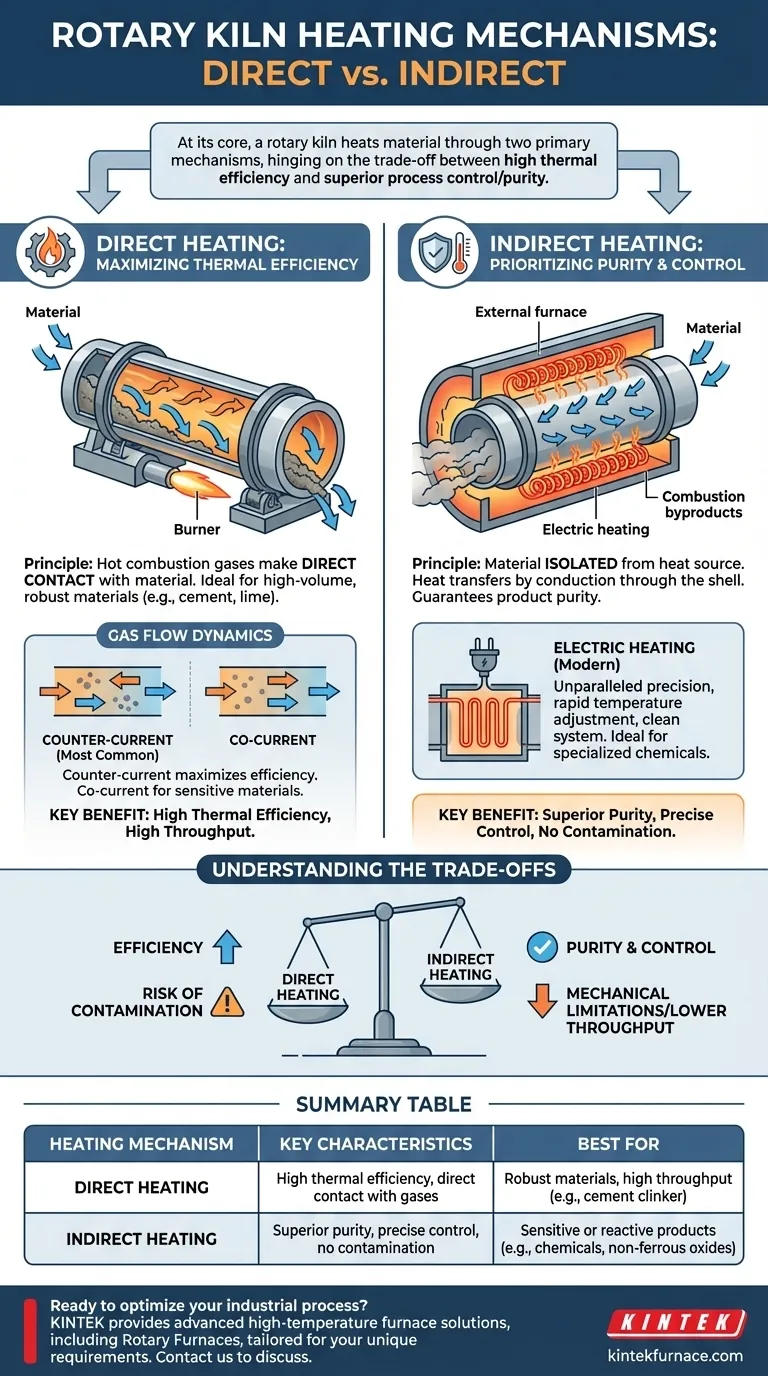
At its core, a rotary kiln heats material through two primary mechanisms: direct heating and indirect heating. In direct heating, hot combustion gases pass through the inside of the kiln, making direct contact with the material. In indirect heating, the kiln is heated from the outside, and heat transfers through the shell to the material without any contact between it and the combustion gases.
The fundamental choice between heating mechanisms hinges on a single trade-off: direct heating offers high thermal efficiency for robust, high-volume materials, while indirect heating provides superior process control and purity for sensitive or reactive products.
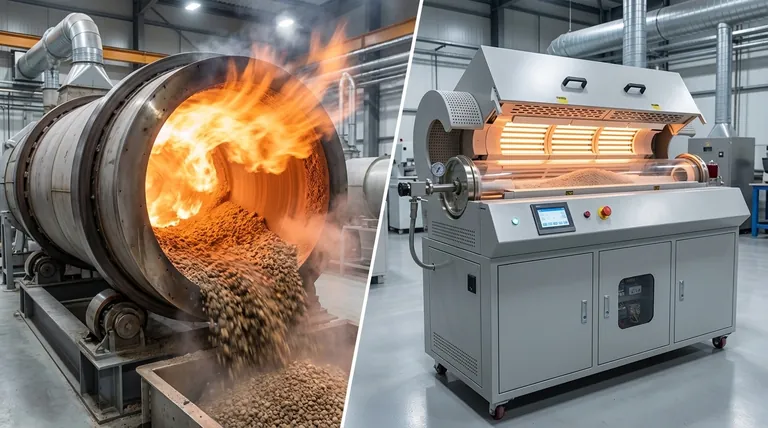

Direct Heating: Maximizing Thermal Efficiency
Directly heated kilns are the workhorses of heavy industry, designed for high temperatures and large throughput.
The Principle of Direct Contact
In this design, a burner is typically positioned at the discharge end of the kiln. It generates a powerful flame and hot gases that travel up the length of the rotating drum.
As material tumbles down the inclined kiln, it comes into direct contact with these hot gases, facilitating rapid and efficient heat transfer. This method is ideal for processes like cement clinker production or lime calcination.
Understanding Gas Flow Dynamics
The direction of gas flow relative to the material flow is a critical design choice.
Counter-current flow is most common. Hot gases enter at the material discharge end and exit at the feed end. This maximizes thermal efficiency because the hottest gases meet the hottest material, ensuring a steep temperature gradient along the entire kiln.
Co-current flow, where gas and material move in the same direction, is used for materials that are sensitive to thermal shock or have specific reaction requirements.
Indirect Heating: Prioritizing Purity and Control
Indirectly heated kilns are used when material purity is paramount or when the process atmosphere must be tightly controlled.
Isolate the Material, Control the Heat
In an indirect kiln, the material is completely isolated from the heat source. The rotary drum is enclosed within a furnace or wrapped with electric heating elements.
Heat is transferred by conduction through the kiln shell to the material tumbling inside. This prevents any contamination from combustion byproducts like ash or sulfur.
The Rise of Electric Heating
Electric rotary kilns represent a modern form of indirect heating. They use resistance materials as heating elements, offering unparalleled precision.
Because there is no combustion, temperature can be adjusted rapidly and maintained with extreme accuracy. This makes electric kilns ideal for roasting specialized chemical products and non-ferrous metal oxides where even minor temperature deviations can spoil the batch.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heating mechanism is a matter of balancing competing operational priorities.
Direct Heating: Efficiency vs. Contamination
The primary advantage of direct heating is its high thermal efficiency and ability to reach very high process temperatures.
However, the direct contact between the fuel's combustion gas and the process material creates an inherent risk of contamination. This makes it unsuitable for high-purity applications.
Indirect Heating: Purity vs. Mechanical Limitations
Indirect heating guarantees product purity and allows for a controlled atmosphere inside the kiln.
The main trade-off is mechanical. The kiln shell is subjected to extreme thermal stress, which can limit the maximum achievable temperature and the diameter of the kiln. This often results in lower throughput compared to direct-fired systems.
Fuel Source: Combustion vs. Electric
Combustion fuels (gas, oil) are energy-dense and cost-effective for large-scale direct heating.
Electric heating, while often more expensive per unit of energy, provides superior control, a closed and clean system, and longer equipment life due to more uniform heating and the absence of corrosive flue gases.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The optimal heating mechanism is determined entirely by your material characteristics and process goals.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and thermal efficiency for a robust material: Choose a direct-fired, counter-current kiln.
- If your primary focus is absolute product purity and avoiding contamination: An indirectly heated kiln is the only viable option.
- If your primary focus is precision temperature control and process automation: An electric indirect rotary kiln provides the highest degree of control.
Ultimately, selecting the correct heating method ensures your process is not only effective but also economically and operationally sound.
Summary Table:
| Heating Mechanism | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Heating | High thermal efficiency, direct contact with gases | Robust materials, high throughput (e.g., cement clinker) |
| Indirect Heating | Superior purity, precise control, no contamination | Sensitive or reactive products (e.g., chemicals, non-ferrous oxides) |
Ready to optimize your industrial process with the right rotary kiln? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, tailored for diverse laboratories. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you need high efficiency, purity, or control. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
People Also Ask
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing



















