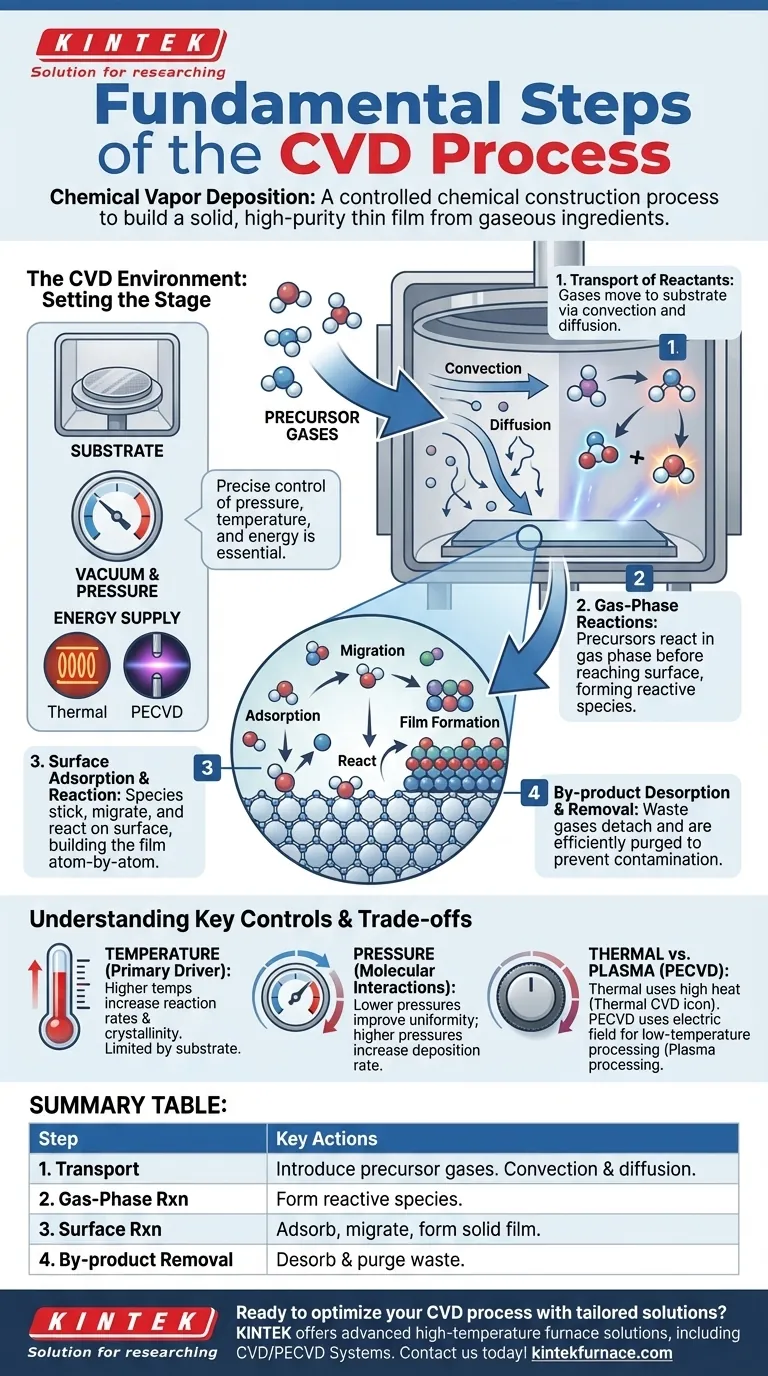
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a four-step process used to build a solid, high-purity thin film on a surface from gaseous ingredients. The fundamental steps involve transporting reactant gases to a substrate, inducing chemical reactions on or near that substrate, forming a solid film from those reactions, and removing the resulting waste products from the chamber.
Chemical Vapor Deposition is not merely a coating technique; it is a controlled chemical construction process. Success depends on precisely managing a sequence of physical transport and chemical reactions to build a material, atom-by-atom or molecule-by-molecule, from a gaseous state into a solid film.
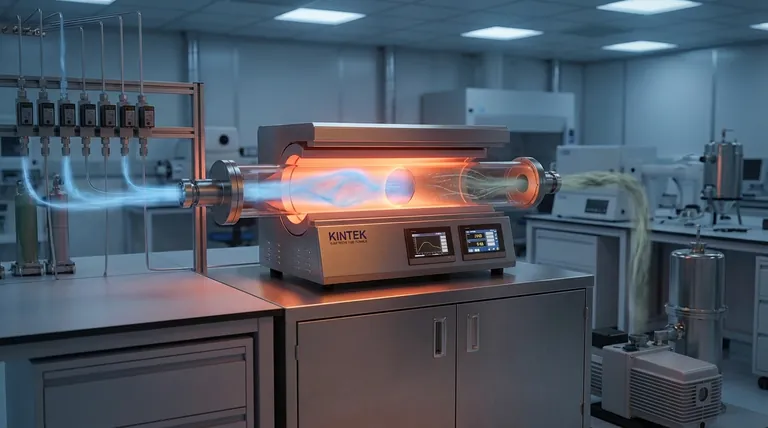

The CVD Environment: Setting the Stage
Before the core process begins, the environment must be perfectly prepared. This is not a step in the film growth itself, but a critical prerequisite for a successful outcome.
The Substrate and Chamber
A substrate, the material to be coated, is placed inside a sealed reaction chamber. The chamber's environment, primarily its pressure and temperature, is carefully controlled. Most CVD processes operate under a vacuum to remove contaminants and better control the behavior of the reactant gases.
Supplying the Energy
Chemical reactions require energy. In traditional CVD, this energy is thermal, supplied by heating the substrate and chamber to hundreds or even thousands of degrees Celsius. In other variants, like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD), the energy comes from an electric field that creates a reactive plasma.
The Four Core Stages of Film Growth
Once the environment is set, the process of building the film unfolds in four distinct, sequential stages.
Stage 1: Transport of Reactants
Precursor gases, which contain the atoms needed for the final film, are introduced into the chamber. These gases are transported towards the substrate surface through two primary mechanisms: convection (the bulk flow of gas) and diffusion (the random motion of molecules).
Stage 2: Gas-Phase Reactions
As the precursors travel toward the hot substrate, some may react with each other in the gas phase before reaching the surface. This can create new, highly reactive chemical species that are essential for the final film formation.
Stage 3: Surface Adsorption and Reaction
This is the most critical stage where the film is actually built. The reactive species from the gas phase arrive at the substrate and stick to its surface, a process called adsorption. Once adsorbed, they migrate across the surface, find energetically favorable sites, and undergo chemical reactions that convert them into a solid, stable material.
Stage 4: By-product Desorption and Removal
The chemical reactions on the surface almost always produce volatile by-products (waste gases). These by-products must detach from the surface (desorption) and be transported away and purged from the chamber. If by-products are not removed efficiently, they can contaminate the film or inhibit further growth.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Controls
The quality, composition, and thickness of the final film are not accidental; they are the direct result of carefully balancing key process parameters.
Temperature: The Primary Driver
In thermal CVD, temperature is the most critical control knob. Higher temperatures generally increase reaction rates and can improve film crystallinity. However, the temperature is limited by the substrate's melting point or tolerance for heat.
Pressure: Controlling Molecular Interactions
The chamber pressure dictates the density of gas molecules and their mean free path (the average distance a molecule travels before hitting another). Lower pressures reduce unwanted gas-phase reactions and improve film uniformity, while higher pressures can increase the deposition rate.
The Thermal vs. Plasma Trade-off
A major limitation of traditional CVD is the requirement for very high temperatures, which can damage sensitive substrates like plastics or certain electronic components. Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) solves this by using an electric field to create a low-temperature plasma. This plasma energizes the precursor gases, allowing deposition to occur at significantly lower, safer temperatures.
Applying This to Your Project
Your choice of CVD parameters is dictated entirely by the properties you need in your final film and the constraints of your substrate.
- If your primary focus is high-purity, crystalline films (e.g., for semiconductors): A high-temperature thermal CVD process is often necessary to provide the energy for atoms to arrange into a perfect crystal lattice.
- If your primary focus is depositing on temperature-sensitive substrates (e.g., polymers): You must use a lower-temperature method like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) to avoid damaging the underlying material.
- If your primary focus is precise thickness control and uniformity: Meticulous, stable control over gas flow rates, chamber pressure, and temperature distribution across the substrate is paramount.
By mastering these steps and their controlling variables, you can engineer thin films with specific properties for nearly any application.
Summary Table:
| Step | Description | Key Actions |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Transport of Reactants | Gases move to substrate via convection and diffusion. | Introduce precursor gases into the chamber. |
| 2. Gas-Phase Reactions | Precursors react in gas phase before reaching substrate. | Form reactive species for deposition. |
| 3. Surface Adsorption and Reaction | Species stick to substrate and form solid film. | Adsorb, migrate, and react on surface. |
| 4. By-product Desorption and Removal | Waste gases detach and are purged from chamber. | Desorb by-products to prevent contamination. |
Ready to optimize your CVD process with tailored solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you're working with semiconductors, polymers, or other materials. Contact us today to discuss how our Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and more can enhance your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is resistance heating and how is it classified? Discover the Best Method for Your Thermal Needs
- How does chemical vapour deposition (CVD) differ from PVD? Key Differences in Thin-Film Coating Methods
- How is silicon dioxide deposited from tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) in PECVD? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality SiO2 Films
- What are the classifications of CVD based on vapor characteristics? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition Process
- What is PECVD specification? A Guide to Choosing the Right System for Your Lab



















