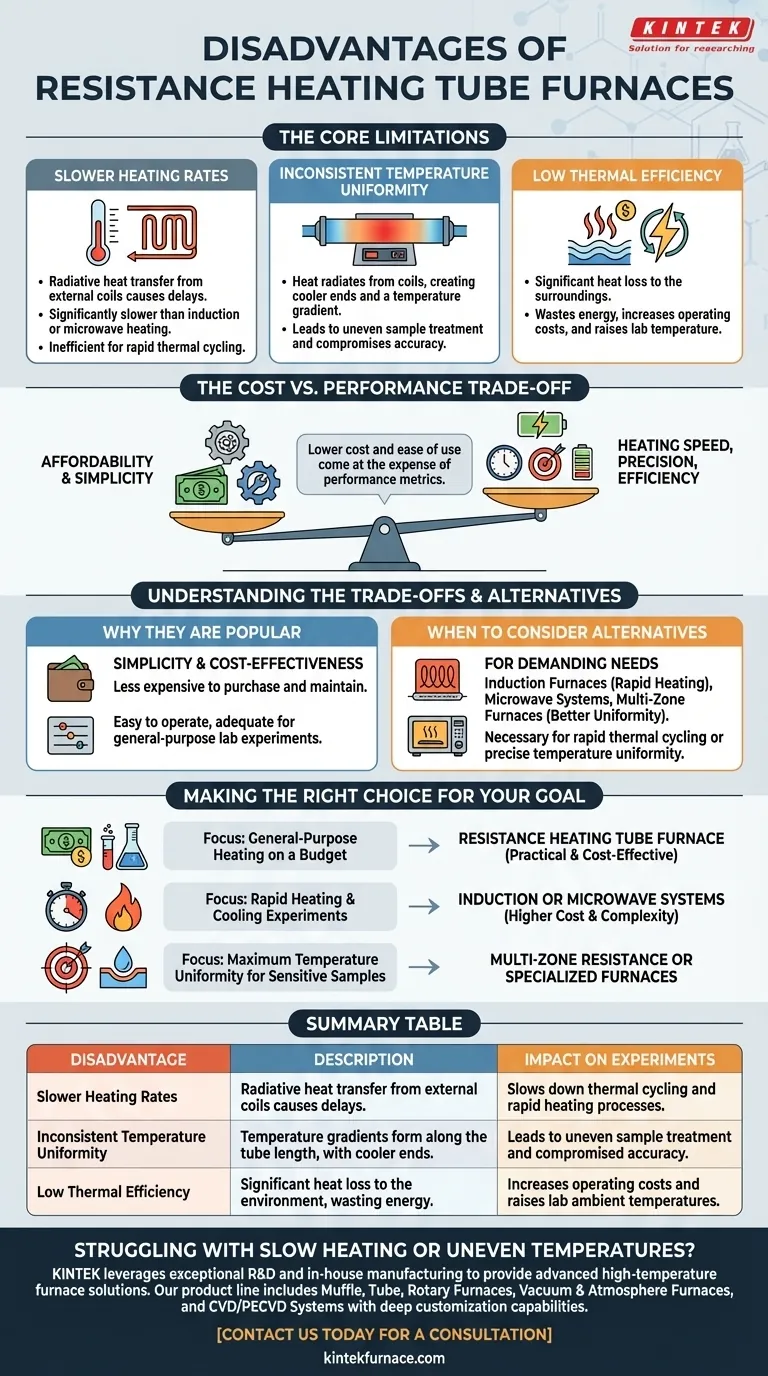
At their core, resistance heating tube furnaces have three primary disadvantages: they heat up relatively slowly, struggle to maintain perfectly even temperatures across the sample, and are not very energy efficient. These limitations stem directly from their simple design, where an external electric coil generates heat that radiates inward.
The central trade-off with a resistance heating tube furnace is one of cost versus performance. Its affordability and simplicity come at the expense of heating speed, temperature precision, and energy efficiency, making it ideal for some tasks but unsuitable for others.

The Core Limitations of Resistance Heating
The design of a resistance furnace—passing a current through an external heating element—is straightforward and cost-effective, but it introduces inherent performance constraints.
Slower Heating Rates
A resistance element needs time to heat up and then transfer that heat radiatively to the furnace tube and the sample inside.
This process is significantly slower than methods like induction or microwave heating, where energy is transferred more directly and rapidly to the sample or a metallic tube. For experiments requiring quick thermal cycling or rapid heating, this delay can be a critical drawback.
Inconsistent Temperature Uniformity
Because heat radiates from coils wound around the outside of the tube, the ends of the tube are often cooler than the center.
This creates a temperature gradient along the length of the furnace. For larger furnaces or sensitive materials, this lack of uniformity can lead to uneven sample treatment and compromise the accuracy of your results.
Low Thermal Efficiency
A significant portion of the heat generated by the resistance coils dissipates into the surrounding environment rather than heating the sample.
This not only wastes energy and increases long-term operating costs but can also raise the ambient temperature of the lab space. While insulation helps, the fundamental design is less efficient than more advanced heating methods.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single furnace technology is universally superior. The disadvantages of resistance heating must be weighed against its significant advantages in specific contexts.
The Advantage of Simplicity and Cost
Resistance furnaces are popular for a reason. Their simple structure makes them far less expensive to manufacture, purchase, and maintain compared to complex induction or corundum tube systems.
They are also easy to operate and provide a level of temperature control that is perfectly adequate for the vast majority of conventional laboratory experiments. This makes them an excellent choice for general-purpose applications and labs with budget constraints.
The Impact of Physical Orientation
The common horizontal tube furnace design can exacerbate temperature uniformity issues, as natural convection patterns can shift the hottest zone slightly.
While vertical furnaces can offer better uniformity, they may present challenges in sample handling. This is a practical consideration that adds another layer to the performance trade-offs.
When to Consider Alternatives
If your experiment cannot tolerate the limitations of a resistance furnace, alternatives become necessary.
Induction furnaces are a clear choice for rapid heating but are expensive and require a metallic tube. Opaque materials like corundum tubes can handle very high temperatures but are costly and prevent direct visual observation of the sample.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace requires matching the technology's capabilities to your experimental or process needs.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating on a budget: A resistance heating tube furnace is almost always the most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is experiments requiring rapid heating and cooling: You should investigate induction or microwave furnace systems, despite their higher cost and complexity.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum temperature uniformity for sensitive samples: Consider a multi-zone resistance furnace or other specialized heating technologies to mitigate temperature gradients.
Understanding these fundamental trade-offs ensures you select a furnace that serves as a reliable tool, not a source of experimental error.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Description | Impact on Experiments |
|---|---|---|
| Slower Heating Rates | Heat transfer is radiative from external coils, causing delays. | Slows down thermal cycling and rapid heating processes. |
| Inconsistent Temperature Uniformity | Temperature gradients form along the tube length, with cooler ends. | Leads to uneven sample treatment and compromised accuracy. |
| Low Thermal Efficiency | Significant heat loss to the environment, wasting energy. | Increases operating costs and raises lab ambient temperatures. |
Struggling with slow heating or uneven temperatures in your lab? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Enhance your lab's efficiency and accuracy—contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety



















