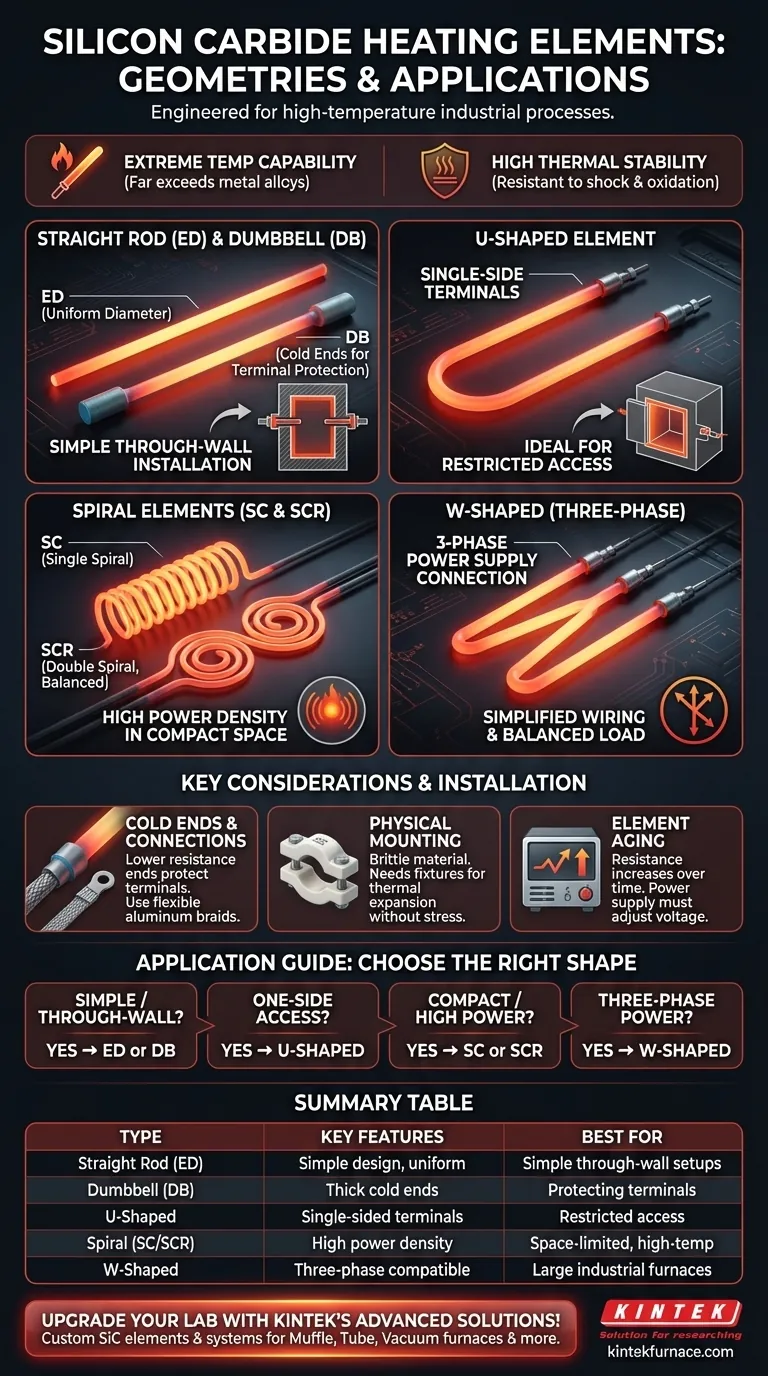
In high-temperature industrial processes, silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements are available in several distinct geometries, each designed for specific furnace layouts and electrical configurations. The primary types include straight rod (ED) and dumbbell (DB) shapes, U-shaped elements, single (SC) and double (SCR) spiral elements, and three-phase (W) elements. Each design addresses a different set of engineering requirements for heat distribution and installation.
The various shapes of SiC heating elements are not arbitrary choices. They are engineered solutions to common challenges in furnace design, such as terminal access, power distribution, and maximizing heating density within a confined space.
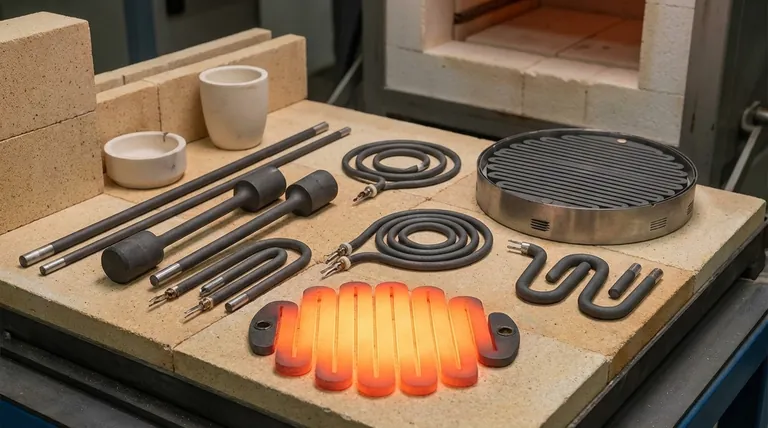

The Foundation: Why Choose Silicon Carbide?
Before examining the different shapes, it's crucial to understand why silicon carbide is the material of choice for demanding heating applications. Its properties offer significant advantages over traditional metallic elements.
Exceptional Temperature Capability
SiC elements can operate reliably at extremely high temperatures, often far exceeding the limits of even the most robust metal alloys. This makes them indispensable for processes in metallurgy, ceramics, and materials science.
High Thermal Stability
The material is exceptionally resistant to thermal shock and oxidation, even in harsh furnace atmospheres. This translates to a longer service life and greater operational stability compared to many alternatives.
The Operating Principle
Like any resistance heater, a SiC element functions by passing an electric current through its body. The material's resistance converts this electrical energy into heat, which radiates outward to heat the furnace and its contents. The temperature is precisely managed by adjusting the voltage and current supplied to the element.
A Guide to SiC Element Geometries
The shape of a SiC element directly impacts its installation, wiring, and heating characteristics. The choice depends entirely on the design of the furnace.
The Straight Rod (ED) and Dumbbell (DB)
These are the simplest forms. The ED type is a straight rod of uniform diameter, while the DB type has thicker, less resistive ends (the "cold ends") where the electrical connections are made.
They are ideal for simple through-wall installations where the element passes completely through the furnace chamber, with terminals on opposite sides. The DB type is often preferred to minimize heat loss and protect the terminal connections.
The U-Shaped Element
This element solves a common access problem. By bending the rod into a "U" shape, both electrical terminals are located on the same side.
This design is invaluable for furnaces where access to the back or opposing side is restricted, allowing all wiring and maintenance to be performed from a single point of entry.
The Spiral Elements (SC and SCR)
Spiraling the element creates a much longer resistive path within a compact physical length. The SC (single spiral) and SCR (double spiral) designs are used to increase the heating surface area and overall resistance.
This allows for higher power density and is useful for achieving very high temperatures quickly or for applications where space is limited. The double-spiral (SCR) design, with two spirals wound in opposite directions, can help minimize electromagnetic fields.
The W-Shaped (Three-Phase) Element
As the name implies, the W-shaped element is specifically engineered for furnaces running on a three-phase power supply. It consists of three legs connected in a configuration that allows for direct connection to a three-phase system.
This design simplifies the electrical wiring significantly and helps ensure a balanced load across the power supply, which is critical for the stability of large industrial furnaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Installation
Selecting an element is only part of the process. Proper installation and understanding the material's behavior are key to a long service life.
Terminal Connections and Cold Ends
The connection points of a SiC element must remain cooler than the main heating section. This is why dumbbell (DB) and multi-leg elements feature thicker "cold ends." These ends have lower electrical resistance, generating less heat and protecting the clamps and wiring.
Physical Mounting and Support
SiC is a ceramic and is therefore brittle. Elements must be secured with appropriate fixtures, often made of stainless steel, that allow for thermal expansion without putting mechanical stress on the element body. These fixtures secure the rod and ensure proper alignment within the furnace.
Electrical Connectivity
High-purity aluminum braids or straps are typically used to connect the power supply to the element terminals. These flexible connectors ensure excellent conductivity while accommodating minor shifts or vibrations during operation.
A Critical Factor: Element Aging
All silicon carbide elements "age" during use. Over time and exposure to high temperatures, their electrical resistance gradually increases. Your power control system must be able to increase the voltage supplied to the elements over their lifespan to maintain the required power output and temperature.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice should be dictated by your equipment's physical design and electrical system.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and through-wall mounting: Straight rod (ED) or dumbbell (DB) elements are the most direct and cost-effective solution.
- If you only have access to one side of the furnace: U-shaped elements provide a single-sided terminal connection, dramatically simplifying installation and maintenance.
- If you need high power density in a compact space: Spiraled elements (SC or SCR) offer increased heating surface area and resistance for more concentrated power output.
- If your furnace uses a three-phase power supply: W-shaped elements are specifically designed to simplify wiring and ensure a balanced electrical load.
Ultimately, selecting the correct SiC element geometry is a critical step in optimizing your furnace's performance, efficiency, and long-term reliability.
Summary Table:
| Type | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Straight Rod (ED) | Simple design, uniform diameter | Simple through-wall installations |
| Dumbbell (DB) | Thick cold ends, reduced heat loss | Protecting terminals in through-wall setups |
| U-Shaped | Single-sided terminals | Restricted access furnaces |
| Spiral (SC/SCR) | High power density, compact | Space-limited, high-temperature needs |
| W-Shaped | Three-phase power compatibility | Large industrial furnaces with balanced loads |
Upgrade your lab's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored silicon carbide heating elements and systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your high-temperature processes and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions



















