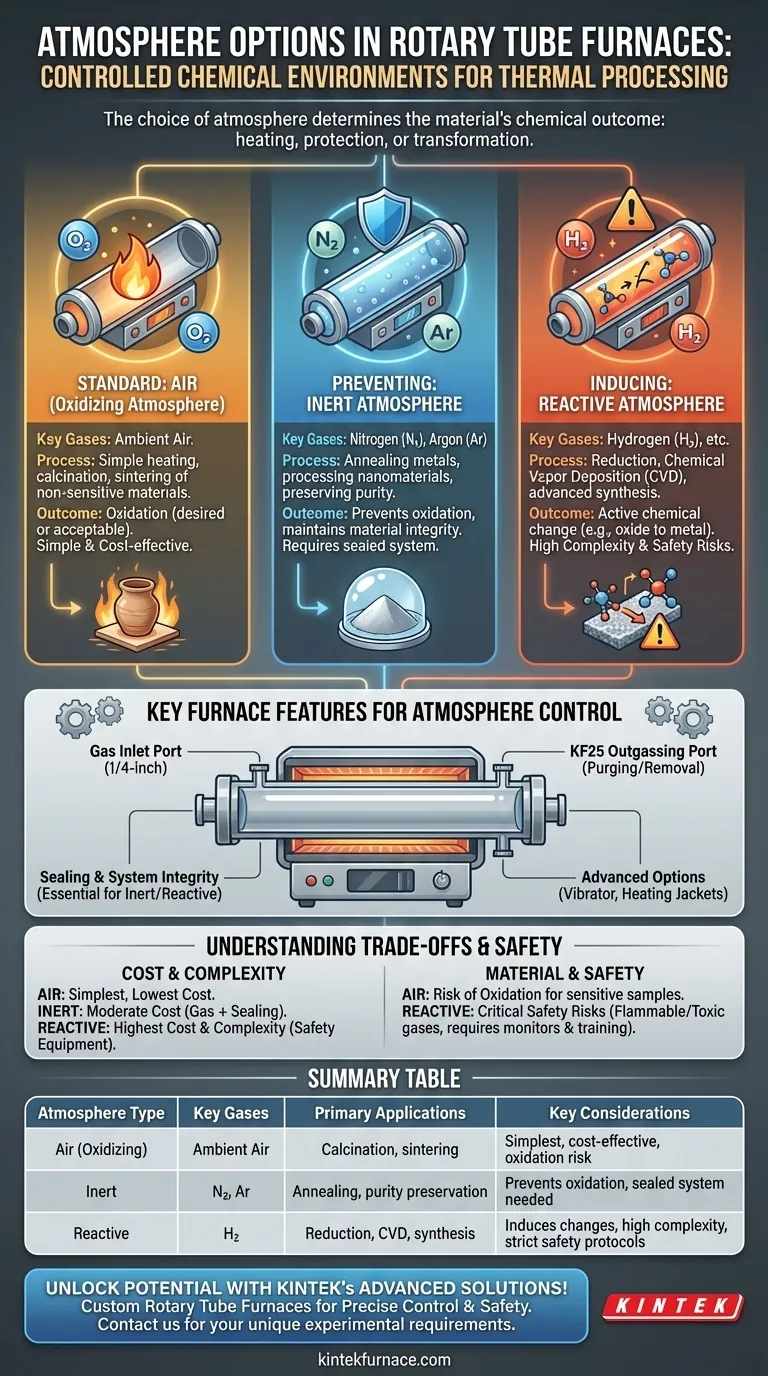
At its core, a rotary tube furnace can operate under three distinct atmosphere types to control the chemical environment during processing. These are standard air for simple heating, an inert gas like nitrogen or argon to prevent unwanted oxidation, and a reactive gas such as hydrogen to actively induce specific chemical changes in the material.
The choice of atmosphere is not merely an operational setting; it is a critical process variable. The decision directly dictates the chemical outcome of your material, determining whether it is simply heated, protected from oxidation, or fundamentally transformed by a chemical reaction.

The Role of Atmosphere in Thermal Processing
The atmosphere inside the furnace interacts directly with your material at high temperatures. Controlling this environment is fundamental to achieving the desired physical and chemical properties in the final product.
Standard Operation: Air (Oxidizing Atmosphere)
The simplest and most common mode of operation is using ambient air as the furnace atmosphere. This is suitable for processes where oxidation is either desired or has no negative effect on the material.
Applications like the calcination of certain ceramics or the sintering of non-sensitive powders can often be performed effectively in air.
Preventing Reactions: Inert Atmospheres
To process materials that are sensitive to oxygen, an inert atmosphere is required. Gases like nitrogen (N₂) or argon (Ar) are used to purge the air from the furnace tube.
This creates a neutral environment that prevents oxidation and other unwanted reactions. It is essential for applications such as annealing metal powders, processing sensitive nanomaterials, or any thermal treatment where the material's purity must be preserved.
Inducing Reactions: Reactive Atmospheres
For processes that require a specific chemical transformation, a reactive atmosphere is used. A gas is introduced that actively participates in a reaction with the material.
A common example is using hydrogen (H₂) for reduction processes, such as converting a metal oxide powder back into its pure metallic form. This method enables advanced material synthesis and chemical vapor deposition (CVD) but demands rigorous safety protocols.
Key Furnace Features for Atmosphere Control
Your ability to manage the furnace atmosphere depends directly on the furnace's design and features. A basic furnace may only run in air, while advanced models offer precise control over complex gas environments.
Gas Inlet and Outlet Ports
Effective atmosphere control requires a sealed system with dedicated ports. Furnaces are often equipped with a 1/4-inch gas inlet port to introduce the desired gas and a KF25 outgassing port to allow for efficient purging of air and removal of reaction byproducts.
Sealing and System Integrity
To maintain a pure inert or reactive atmosphere, the work tube must be properly sealed at both ends. Any leaks will allow ambient air to contaminate the process, compromising the results by introducing oxygen and moisture.
Advanced Options for Specific Processes
For challenging materials, specialized features are available. A hammer vibrator can be used to ensure continuous flow for high-viscosity or sticky powders, while heating jackets on the exhaust lines can prevent condensation of byproducts like tar when processing organic materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Safety
Choosing an atmosphere involves balancing process requirements against complexity, cost, and safety. Each option presents a different set of considerations.
Cost and Complexity
Operating in air is the simplest and most cost-effective method. Using an inert gas adds the cost of the gas itself and the need for a sealed system. Reactive atmospheres are the most complex and expensive, requiring not only gas but also significant investment in safety monitoring and handling equipment.
Material Compatibility
The most critical trade-off is its effect on your material. While running a process in air may be cheaper, it can lead to the complete oxidation and ruin of a sensitive sample. The added cost of an inert atmosphere is justified when it is the only way to achieve the desired outcome.
Critical Safety for Reactive Gases
Using flammable or toxic reactive gases like hydrogen introduces significant safety risks. These operations demand proper ventilation, gas leak detectors, emergency shut-offs, and comprehensive operator training. Never use reactive gases without a thorough safety review and appropriate engineering controls.
Selecting the Right Atmosphere for Your Application
Your choice should be driven entirely by the goal of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is calcination or heating stable oxide materials: Operating in an air atmosphere is typically sufficient and the most economical choice.
- If your primary focus is annealing metals or processing oxygen-sensitive powders: An inert atmosphere of nitrogen or argon is essential to prevent oxidation and preserve material integrity.
- If your primary focus is chemical reduction or advanced synthesis (CVD): A reactive atmosphere, such as hydrogen, is necessary, but requires investment in a properly equipped furnace and stringent safety protocols.
- If your primary focus is processing challenging organic or viscous materials: Look for a furnace with specialized options like vibrators or heated jackets to ensure consistent material flow and prevent system clogging.
Ultimately, matching the furnace atmosphere to your material's chemistry is the defining factor for successful and repeatable thermal processing.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Key Gases | Primary Applications | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air (Oxidizing) | Ambient Air | Calcination, sintering of non-sensitive materials | Simplest, cost-effective, may cause oxidation |
| Inert | Nitrogen (N₂), Argon (Ar) | Annealing metals, processing nanomaterials, preserving purity | Prevents oxidation, requires sealed system, moderate cost |
| Reactive | Hydrogen (H₂) | Reduction processes, chemical vapor deposition (CVD), advanced synthesis | Induces chemical changes, high complexity, requires safety protocols |
Unlock the full potential of your thermal processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with rotary tube furnaces and other systems like Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you need precise atmosphere control, enhanced safety features, or tailored designs for challenging materials. Don't let atmosphere limitations hold back your research—contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your setup and drive innovation in your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
People Also Ask
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules



















