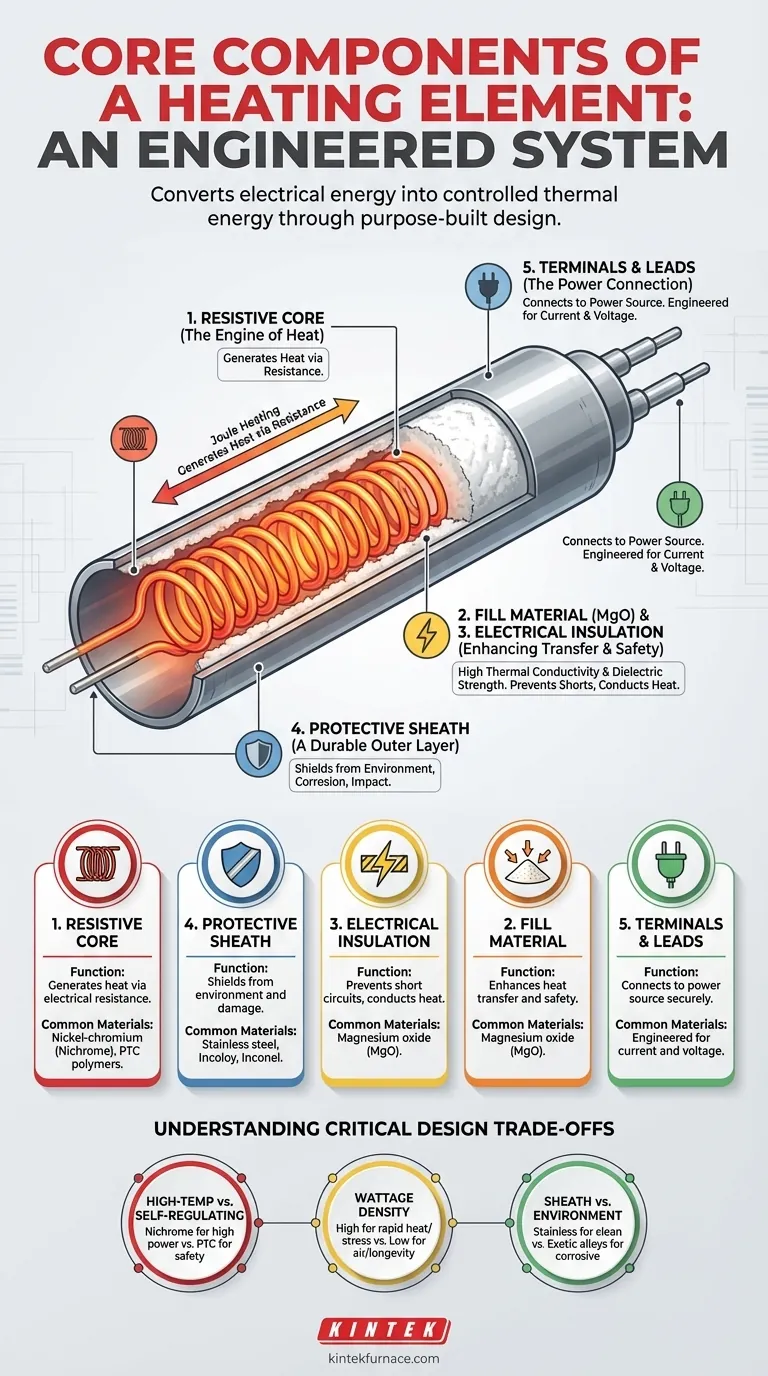
At its core, a heating element is an engineered system composed of a resistive material that generates heat, a protective outer sheath, internal electrical insulation to ensure safety, and terminals to connect it to a power source. These components work in concert to convert electrical energy into precisely controlled thermal energy for a specific application.
A heating element is not merely a wire that gets hot. It is a purpose-built component where a resistive core creates heat, while carefully selected sheath and insulating materials direct that energy safely and efficiently. The choice of each component is dictated entirely by the final application.
The Anatomy of a Heating Element
To understand how a heating element functions, we must examine each part and its specific role in the system. The interplay between these components defines the element's performance, lifespan, and safety.
The Resistive Core: The Engine of Heat
The heart of the element is a material, often a wire or ribbon, with high electrical resistance. When an electric current flows through this core, it encounters resistance, which forces the electrical energy to convert into heat.
This phenomenon is known as Joule heating. The amount of heat generated is a product of the current and the material's resistance, making resistance the most critical property for designers to control. Common materials include nickel-chromium (Nichrome) alloys, prized for their high-temperature performance.
The Protective Sheath: A Durable Outer Layer
The resistive core is fragile and must be protected from its operating environment. The sheath is a metallic tube or casing that encloses the core and other internal components.
This outer layer shields the element from moisture, corrosion, physical impact, and chemical exposure, ensuring its longevity and reliability. The sheath material, such as stainless steel or Incoloy, is chosen based on the specific environmental challenges it will face.
Electrical Insulation: Directing Current and Ensuring Safety
To prevent the electric current from shorting to the protective sheath, a layer of electrical insulation is essential. This material must be a poor conductor of electricity but an excellent conductor of heat.
This dual property is critical. It ensures the current flows only through the resistive core while allowing the generated heat to escape efficiently to the element's surface.
The Fill Material: Enhancing Thermal Transfer
In many high-performance tubular elements, the space between the resistive core and the sheath is filled with a compacted powder. Magnesium oxide (MgO) is the industry standard for this purpose.
MgO is an exceptional material because it exhibits high thermal conductivity (transferring heat well) and high dielectric strength (resisting electricity). It holds the resistive core in place, prevents short circuits, and ensures uniform heat transfer to the sheath.
Terminals and Leads: The Power Connection
Terminals, pins, or flexible leads provide the connection points to the external power supply. They are engineered to handle the required current and voltage safely without overheating. The design of these connections is critical for a secure and reliable electrical circuit.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The effectiveness of a heating element is determined by the material choices made during its design. There is no single "best" configuration; instead, engineers must balance performance, cost, and safety by making critical trade-offs.
High-Temperature vs. Self-Regulating Materials
The choice of resistive material dictates the element's operating range. Nichrome and similar alloys are ideal for high-power, high-temperature applications like industrial furnaces and ovens.
Conversely, materials like polymer PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) are designed for lower-temperature, self-regulating applications. Their resistance increases dramatically as they heat up, causing them to naturally limit their own temperature, which is ideal for applications where safety is paramount.
Wattage Density and Its Implications
Wattage density—the amount of power generated per square inch of the element's surface—is a critical design factor. High wattage density allows for rapid heating in a compact form but places immense stress on the sheath and insulation.
An element designed for heating air will have a low wattage density, while an element for immersion in water can have a much higher density because the liquid is more effective at drawing heat away. Mismatching this can lead to premature failure.
Sheath Material vs. Environment
The protective sheath must be chemically compatible with its surroundings. A stainless steel sheath might be sufficient for heating air or clean water, but a corrosive fluid may require a more exotic alloy like Inconel or titanium to prevent rapid degradation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heating element requires aligning its components with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature industrial processing: Prioritize elements with Nichrome cores and robust stainless steel or Incoloy sheaths designed for high wattage densities.
- If your primary focus is safety in a consumer product: Choose self-regulating PTC elements or designs that include integrated thermal cutoffs and low wattage densities.
- If your primary focus is efficiency in a liquid: Select an immersion element whose sheath material is resistant to the liquid and whose shape maximizes surface contact for rapid heat transfer.
Understanding these components transforms a heating element from a simple part into a solvable engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Resistive Core | Generates heat via electrical resistance | Nickel-chromium (Nichrome), PTC polymers |
| Protective Sheath | Shields from environment and damage | Stainless steel, Incoloy, Inconel |
| Electrical Insulation | Prevents short circuits, conducts heat | Magnesium oxide (MgO) |
| Fill Material | Enhances heat transfer and safety | Magnesium oxide (MgO) |
| Terminals and Leads | Connects to power source securely | Engineered for current and voltage |
Struggling to find the right heating element for your lab's high-temperature needs? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely match your unique experimental requirements, ensuring safety, efficiency, and durability. Let us help you optimize your thermal processes—contact us today for a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production



















