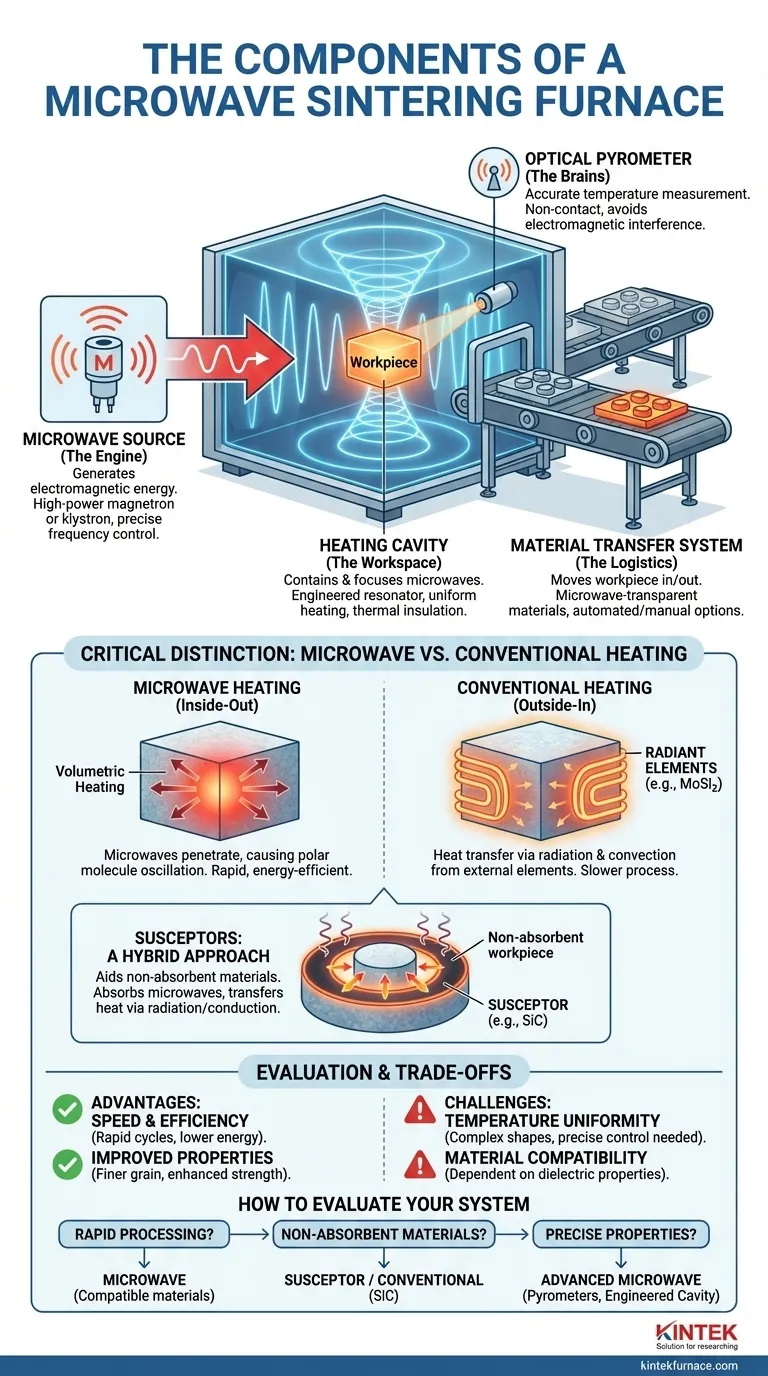
At its core, a microwave sintering furnace is composed of three primary systems: a microwave source to generate the energy, a heating cavity to contain and focus that energy, and a material transfer system to move the workpiece. These components work together to heat materials from the inside out, which is fundamentally different from how conventional furnaces operate.
The crucial distinction to understand is that microwave furnaces use electromagnetic energy to directly heat the material volumetrically, while conventional furnaces rely on external heating elements to transfer heat from the outside in. This difference in mechanism dictates the furnace's design, capabilities, and limitations.

The Core Components and Their Function
To understand how a microwave furnace achieves its unique results, we must look at the role of each key component.
The Microwave Source (The Engine)
The microwave source is the heart of the system. It is typically a high-power magnetron or klystron—a specialized vacuum tube that converts electrical energy into high-frequency electromagnetic waves (microwaves).
The power and frequency of this source are critical parameters that determine the heating rate and efficiency for a given material.
The Heating Cavity (The Workspace)
The heating cavity is a precisely engineered metal chamber, often called a resonator, designed to contain the microwaves. Its geometry is optimized to create a standing wave pattern, focusing the microwave energy onto the material being sintered.
Proper cavity design is essential for achieving uniform heating. Poor design can lead to "hot spots" and "cold spots," resulting in inconsistent material properties. The cavity also includes insulation to minimize thermal loss.
The Material Transfer System (The Logistics)
This system is responsible for moving the material, or "workpiece," into and out of the heating cavity. It can be as simple as a manual door for batch processing or a more complex automated conveyor for continuous production.
The materials used in this system must be transparent to microwaves to avoid interfering with the heating process.
Temperature Measurement and Control (The Brains)
Accurately measuring temperature inside a high-energy microwave field is a significant challenge. Traditional thermocouples (metal probes) can act like antennas, absorbing microwave energy and providing false readings.
For this reason, high-performance systems use non-contact optical pyrometers. These devices measure temperature by detecting the thermal radiation emitted by the hot material, providing accurate data without interfering with the electromagnetic field.
The Critical Distinction: Microwave vs. Conventional Heating
The reference to heating elements like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) highlights a common point of confusion. Those components belong to conventional, not microwave, furnaces.
How Microwave Heating Works
Microwave sintering relies on volumetric heating. The microwaves penetrate the material and cause its polar molecules or ions to oscillate rapidly, generating friction and thus heat. This process occurs simultaneously throughout the entire volume of the material.
This "inside-out" heating is why microwave sintering can be significantly faster and more energy-efficient than conventional methods.
The Role of Conventional Heating Elements
In a traditional resistance furnace, electrical current is passed through heating elements made of materials like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) or Silicon Carbide (SiC). These elements become extremely hot and transfer heat to the workpiece via radiation and convection.
This is an "outside-in" process, where the surface of the material heats first, and the core heats last through thermal conduction.
Susceptors: A Hybrid Approach
Sometimes, the material being sintered does not absorb microwaves well. In these cases, a susceptor can be used. A susceptor is a material (often Silicon Carbide) that strongly absorbs microwave energy.
It is placed in the cavity next to the target material. The susceptor heats up via microwaves and then transfers its heat to the workpiece through conventional radiation and conduction, effectively acting as a microwave-powered heating element.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any technology, microwave sintering has clear advantages and specific challenges that must be considered.
Advantage: Speed and Energy Efficiency
Because volumetric heating is so direct, sintering cycles can be reduced from many hours to just minutes. This drastically increases throughput and can lower energy consumption.
Advantage: Improved Material Properties
The rapid, uniform heating can produce materials with a finer, more homogenous grain structure. This often leads to enhanced mechanical properties like greater strength and hardness.
Challenge: Temperature Uniformity
While volumetric heating is theoretically uniform, achieving it in practice with complex shapes or large parts can be difficult. It requires sophisticated cavity design and precise control.
Challenge: Material Compatibility
The effectiveness of microwave sintering is highly dependent on the dielectric properties of the material—its ability to absorb microwave energy. Materials that do not couple well with microwaves will not heat efficiently without the use of a susceptor.
How to Evaluate a Microwave Sintering System
Your choice of technology should be driven by your material and your final goal.
- If your primary focus is rapid processing and energy savings: Microwave sintering is a strong candidate, provided your materials are compatible and absorb microwave energy effectively.
- If you are working with non-microwave-absorbent materials: You must either plan to use a susceptor-based system or investigate a conventional furnace with radiant heating elements like SiC.
- If achieving precise final material properties is critical: Prioritize a microwave system with advanced, non-contact temperature monitoring (pyrometers) and a well-engineered cavity designed for maximum heating uniformity.
Ultimately, understanding the function of each component empowers you to select the right heating technology for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Microwave Source | Generates electromagnetic energy for heating | High-power magnetron or klystron, precise frequency control |
| Heating Cavity | Contains and focuses microwaves on the material | Engineered resonator, uniform heating, insulation for thermal efficiency |
| Material Transfer System | Moves workpiece into and out of the cavity | Microwave-transparent materials, manual or automated options |
| Temperature Control | Measures and regulates temperature accurately | Non-contact optical pyrometers, avoids interference with microwaves |
| Susceptor (Optional) | Aids heating for non-absorbent materials | Absorbs microwaves and transfers heat via radiation/conduction |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's capabilities with tailored high-temperature solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnace systems, including Microwave Sintering Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, boosting efficiency and material quality. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What are the two main types of atmosphere furnaces and their characteristics? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- What industries commonly use inert atmosphere heat treating? Key Applications in Military, Automotive, and More
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality



















