At its core, an atmosphere protection muffle furnace uses two primary heating methods: electric resistance heating and indirect gas heating. While both can achieve high temperatures, the choice between them is critical as it directly impacts the purity of the controlled atmosphere, temperature precision, and operational complexity. For most laboratory and high-purity applications, electric resistance is the standard due to its superior control and non-contaminating nature.
The central challenge in an atmosphere furnace isn't just reaching a target temperature, but doing so without compromising the protective atmosphere. The heating method you choose is the single most important factor in maintaining the integrity of your process environment.

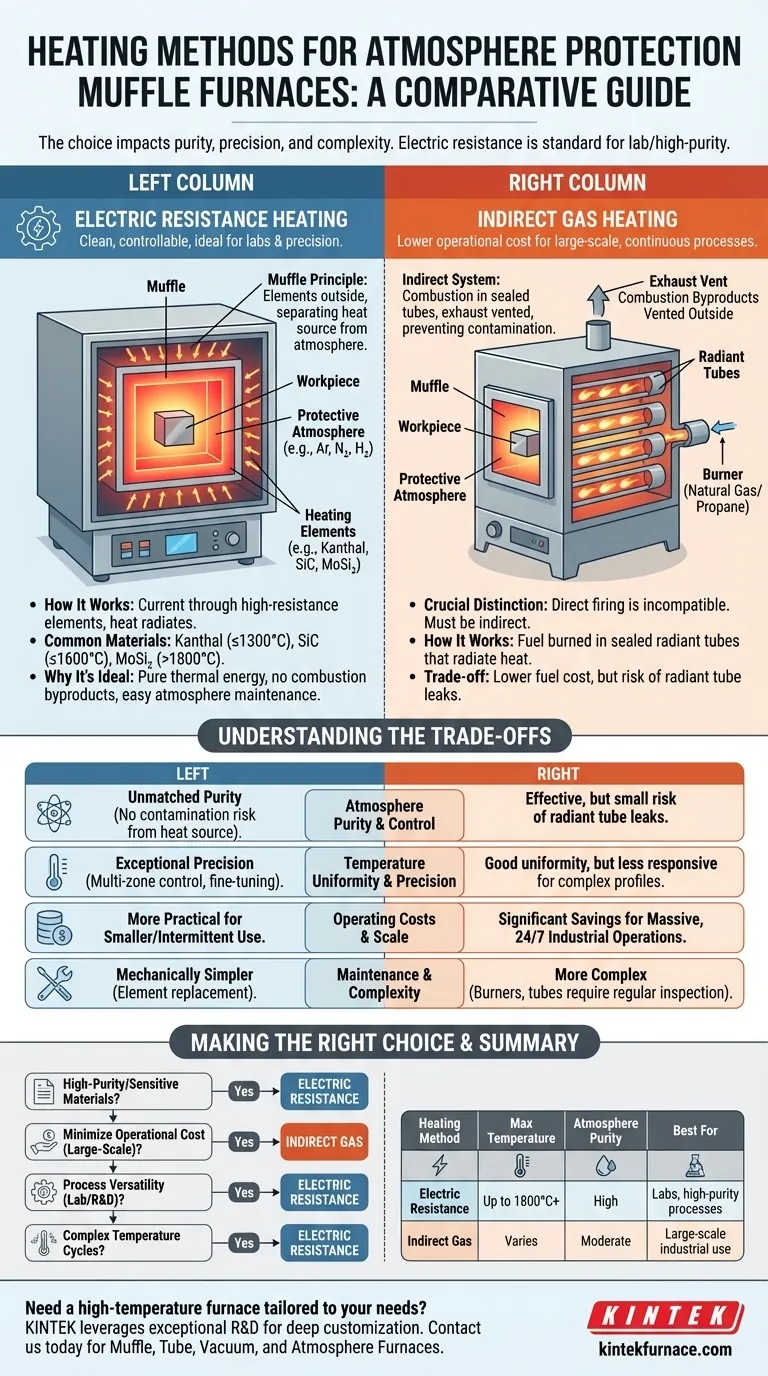
The Dominant Method: Electric Resistance Heating
Electric resistance is the most common heating method for atmosphere muffle furnaces, especially in laboratory and precision manufacturing settings. Its popularity stems from its inherent cleanliness and controllability.
How It Works: The Muffle Principle
An electric furnace generates heat by passing a current through high-resistance heating elements. These elements, often made of specialized alloys or ceramics, become extremely hot and radiate heat into the furnace chamber.
The "muffle" is a crucial component—it's a separated inner chamber that contains the workpiece and the protective atmosphere. The heating elements typically sit outside this muffle, heating it externally. This physical separation is key to preventing any outgassing from the elements from contaminating the process atmosphere.
Common Heating Element Materials
The maximum temperature of the furnace is determined by the material of its heating elements. Common types include:
- Kanthal (FeCrAl) alloys: Used for temperatures up to approximately 1300°C.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): For applications requiring temperatures up to 1600°C.
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂): Used for the highest temperature ranges, often exceeding 1800°C.
Why It’s Ideal for Atmosphere Control
Electric heating is purely thermal energy. It does not produce any byproducts of combustion like water vapor or carbon dioxide. This makes it exceptionally easy to maintain a pure, controlled atmosphere, whether it's an inert gas like nitrogen or argon, or a reactive gas like hydrogen for reduction processes.
The Industrial Alternative: Indirect Gas Heating
While less common in precision applications, indirect gas heating is a viable method for very large, continuous industrial furnaces where operating cost is a primary driver.
The Critical Distinction: Direct vs. Indirect Firing
It is crucial to understand that direct gas firing is incompatible with atmosphere control. A direct-fired furnace burns fuel inside the main chamber, flooding it with combustion byproducts that would destroy any protective atmosphere.
Instead, atmosphere-compatible gas furnaces must use indirect heating.
The Role of Radiant Tubes
In an indirect system, natural gas or propane is burned inside sealed pipes called radiant tubes. These tubes get very hot and radiate heat into the furnace chamber, much like electric elements do.
The exhaust from this combustion is vented directly outside and never comes into contact with the workpiece or the controlled atmosphere. This allows for the use of cheaper gas fuel while still maintaining a separated, clean process environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heating method involves balancing performance requirements with operational realities. The best choice depends entirely on the process goals.
Atmosphere Purity and Control
Electric resistance heating offers unmatched purity. There is virtually no risk of contamination from the heat source itself. Indirect gas heating, while effective, carries a small but persistent risk of a radiant tube leaking and contaminating the furnace atmosphere.
Temperature Uniformity and Precision
Modern electric furnaces with multiple heating zones provide exceptionally precise and uniform temperature control. While large gas furnaces can also achieve good uniformity, the fine-tuning and responsiveness of electric systems are generally superior for complex heat treatment profiles.
Operating Costs and Scale
For smaller furnaces or intermittent use, electricity is often more practical. For massive, 24/7 industrial operations, the lower cost of natural gas compared to electricity can result in significant long-term operational savings, making the complexity of an indirect gas system worthwhile.
Maintenance and Complexity
Electric furnaces are mechanically simpler. Maintenance typically involves the eventual replacement of heating elements. Indirect gas furnaces are more complex, with burners, fuel lines, and radiant tubes that require regular inspection and maintenance to ensure safe and leak-free operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your heating method should be selected based on the non-negotiable requirements of your material and process.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing or sensitive materials: Choose electric resistance heating for its cleanliness and precise control.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational cost for a large-scale, continuous process: Evaluate indirect gas heating, but carefully consider the maintenance and control trade-offs.
- If your primary focus is process versatility in a lab or R&D setting: Electric resistance is the clear choice for its adaptability to different atmospheres and temperature profiles.
- If your primary focus is achieving complex temperature cycles with high precision: An electric furnace with multi-zone control offers superior performance.
Ultimately, selecting the right heating system is the foundational decision that ensures the integrity and success of your controlled-atmosphere heat treatment.
Summary Table:
| Heating Method | Max Temperature | Atmosphere Purity | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Resistance | Up to 1800°C+ | High | Labs, high-purity processes |
| Indirect Gas | Varies | Moderate | Large-scale industrial use |
Need a high-temperature furnace tailored to your lab's unique needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your process efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance



















