In technical applications, three-zone furnaces are primarily used for material testing, advanced heat treatment processes like annealing and hardening, semiconductor manufacturing, and sophisticated research and development. Their defining feature is the ability to create exceptionally precise and uniform thermal environments required for sensitive, high-stakes processes.
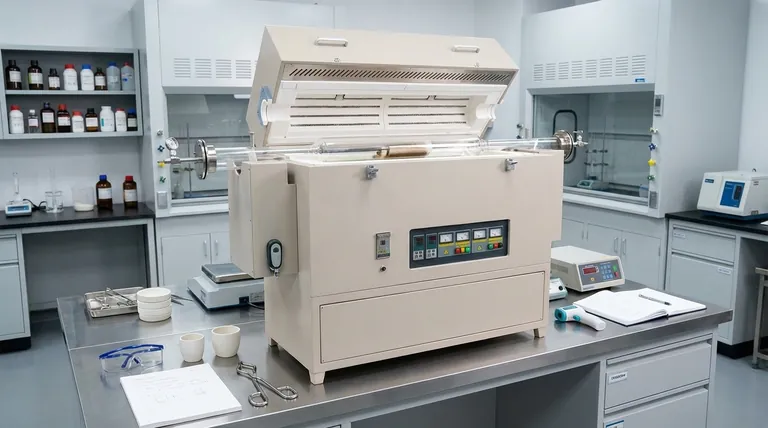
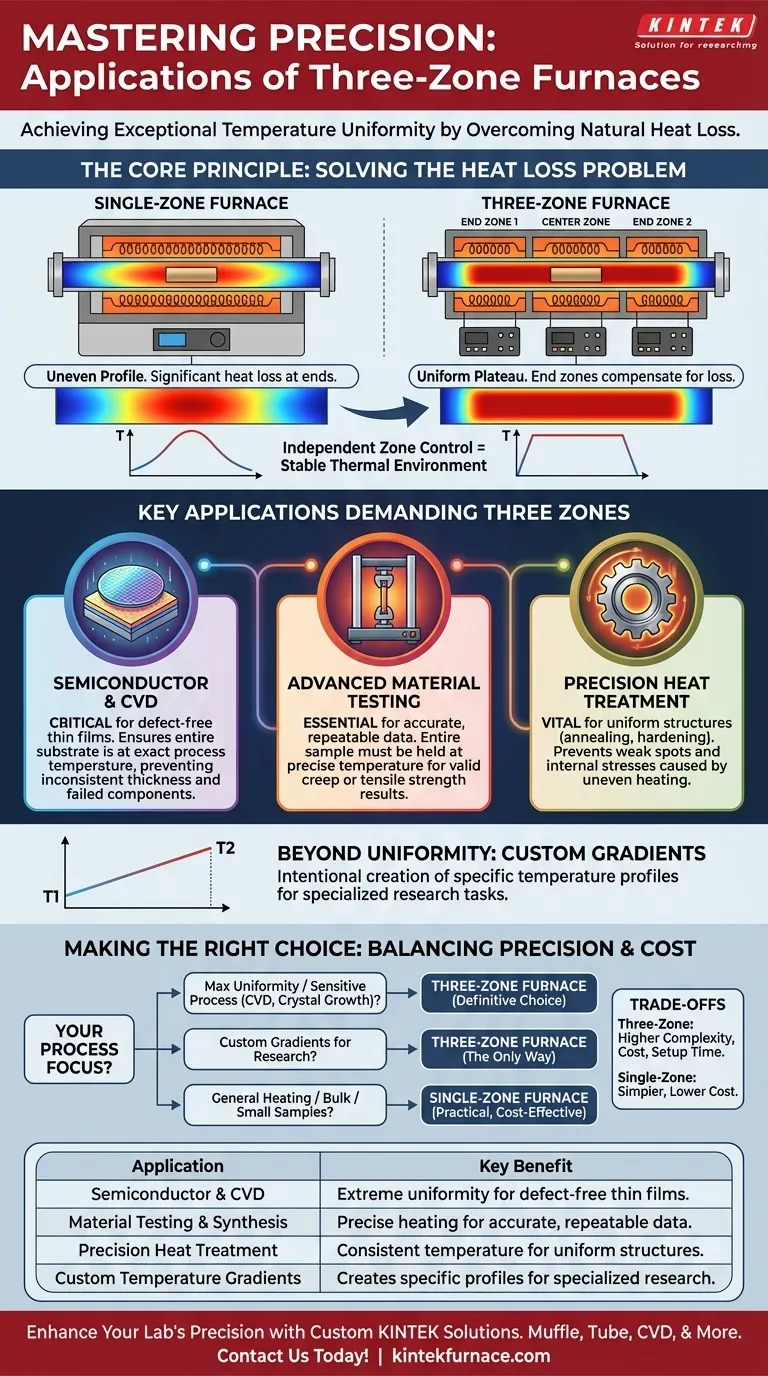
The fundamental advantage of a three-zone furnace is not just heating, but achieving exceptional temperature uniformity across a sample. By independently controlling end zones to compensate for natural heat loss, these furnaces create a stable, precise thermal environment that single-zone models cannot match.

The Core Principle: Overcoming Heat Loss for Uniformity
To understand the applications, you must first understand the problem these furnaces solve. Any furnace naturally loses heat at its ends, creating an uneven temperature profile inside.
The Problem with Single-Zone Furnaces
In a standard single-zone furnace, the temperature is highest at the very center and drops off significantly toward the openings. This means a long sample placed inside will not be heated evenly, leading to inconsistent results.
The Three-Zone Solution
A three-zone furnace divides the heating chamber into a large central zone and two smaller end zones. Each zone has its own independent thermocouple and controller.
Operators can set the end zones to a slightly higher temperature than the center. This extra heat counteracts the natural thermal loss, creating a much larger, more stable, and highly uniform temperature plateau across the central zone.
Beyond Uniformity: Creating Custom Profiles
This independent control also allows for the intentional creation of temperature gradients. For certain research applications, you can program the zones to create a specific, linear temperature change across the sample, a task impossible with a single-zone furnace.
Key Applications and Why They Demand Three Zones
The need for superior temperature control dictates where these furnaces are deployed.
Semiconductor Manufacturing & CVD
Processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), where thin films are grown on wafers, demand extreme temperature uniformity. Even a slight variation across the wafer can result in defects, inconsistent film thickness, and failed components. A three-zone furnace ensures the entire substrate is at the exact same process temperature.
Advanced Material Testing & Synthesis
When testing the properties of materials at high temperatures (e.g., creep, tensile strength), the entire sample must be held at a precise, uniform temperature. If one part of the sample is hotter than another, the test data is invalid. Three-zone furnaces are essential for generating accurate and repeatable material data.
Precision Heat Treatment
Critical heat treatments like annealing, tempering, and hardening require holding a material at a specific temperature for a set duration to achieve the desired crystalline structure. The uniformity of a three-zone furnace ensures the entire component receives the exact same treatment, preventing weak spots or internal stresses caused by uneven heating.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a three-zone furnace is not always the necessary choice. Understanding its trade-offs is key to making a sound investment.
Increased Complexity and Cost
A three-zone furnace is inherently more complex, containing three sets of controllers, thermocouples, and heating elements. This leads to a higher initial purchase price compared to a simpler single-zone model.
More Involved Setup and Programming
Achieving a perfectly flat temperature profile requires careful setup and tuning. While modern controllers automate much of this, it is a more involved process than setting a single temperature point on a one-zone furnace.
When a Single Zone Is Sufficient
For heating very small samples placed directly in the thermal center, or for applications where absolute temperature uniformity is not the most critical parameter, a single-zone furnace is often a more practical and cost-effective solution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be driven by the precision your process demands.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature uniformity for sensitive processes like CVD, crystal growth, or certification-grade material testing: A three-zone furnace is the definitive and necessary choice.
- If your primary focus is creating a specific temperature gradient across a sample for specialized research: The independent control of a three-zone furnace is the only way to achieve this.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating, bulk processing, or testing where slight temperature variations are acceptable: A simpler, more cost-effective single-zone furnace is likely the more practical option.
Ultimately, selecting a three-zone furnace is a strategic decision to prioritize process precision and repeatability over initial equipment cost.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Semiconductor Manufacturing & CVD | Ensures extreme temperature uniformity for defect-free thin film deposition |
| Advanced Material Testing & Synthesis | Provides precise, uniform heating for accurate and repeatable test data |
| Precision Heat Treatment | Maintains consistent temperature for uniform annealing, tempering, and hardening |
| Custom Temperature Gradients | Allows intentional creation of specific temperature profiles for specialized research |
Ready to enhance your lab's precision with a custom three-zone furnace? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can deliver tailored solutions for your sensitive processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a multi-zone tube furnace achieve precise temperature gradient control? Master MoS2 Isotope Monolayer Synthesis
- How are multi zone tube furnaces used in ceramics, metallurgy and glass research? Unlock Precise Thermal Control for Advanced Materials
- What are the benefits of integrating multiple heating zones in a tube furnace? Unlock Precise Thermal Control
- How are multi zone tube furnaces applied in biomedical research? Unlock Advanced Biomaterial Engineering
- What are the advantages of individually temperature-controlled zones in multi-zone furnaces? Unlock Precision Thermal Gradients



















