At their core, atmosphere furnaces are specialized heat treatment systems designed to precisely control the chemical environment around a material. They function by introducing a specific, artificially prepared gas mixture into a sealed heating chamber. This enables a range of thermal processes like gas carburizing, carbonitriding, bright quenching, annealing, and normalizing that are impossible to achieve in open-air furnaces.
An atmosphere furnace moves beyond simple heating to become an active tool for material engineering. By replacing ambient air with a controlled gas mixture, it prevents unwanted reactions like oxidation and enables precise surface modifications, leading to superior material properties and process efficiency.
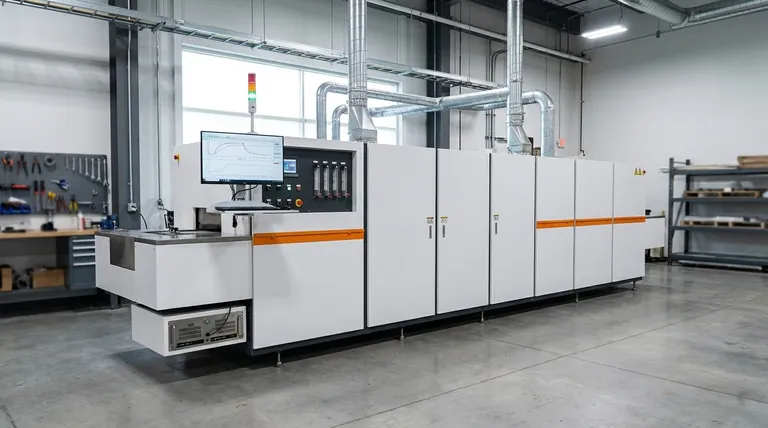

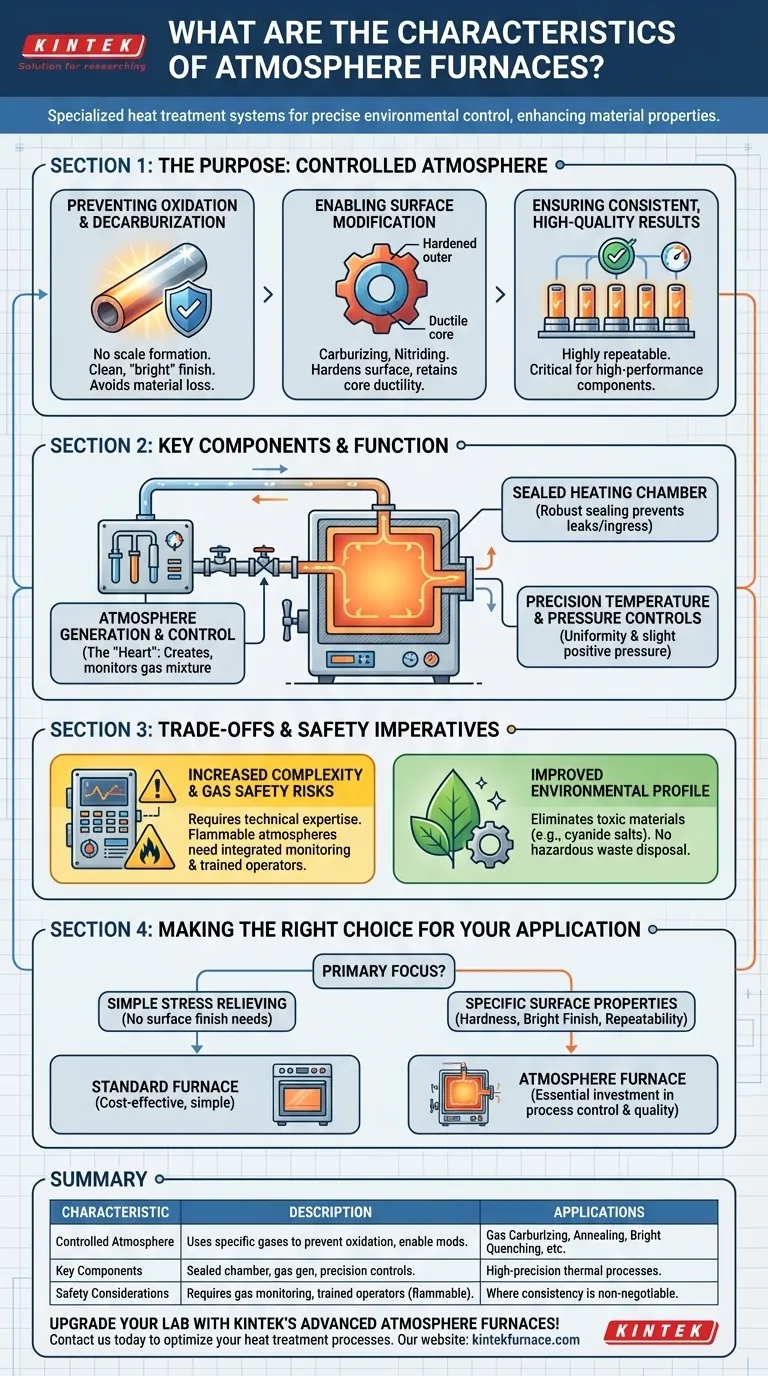
The Purpose of a Controlled Atmosphere
The primary function of an atmosphere furnace is to create a predictable and non-reactive (or selectively reactive) environment at high temperatures. This control is fundamental to modern metallurgy.
Preventing Oxidation and Decarburization
When steel is heated in air, the oxygen causes a layer of scale (oxidation) to form, which damages the surface finish and can lead to material loss. The controlled, low-oxygen atmosphere in these furnaces prevents this, resulting in a clean, "bright" surface finish.
Enabling Surface Modification
These furnaces are used for thermochemical treatments that change the chemistry of a part's surface. By introducing gases rich in carbon (carburizing) or nitrogen (nitriding), the surface can be hardened significantly while the core remains ductile.
Ensuring Consistent, High-Quality Results
Because the furnace atmosphere, temperature, and pressure are all tightly controlled, the results of the heat treatment process are highly repeatable. This is critical for manufacturing high-performance components where consistency is non-negotiable.
Key Components of an Atmosphere Furnace
Achieving such precise environmental control requires a more complex design than a standard furnace. The main components work in concert to maintain the integrity of the process.
The Sealed Heating Chamber
The furnace body and door must be engineered with robust sealing mechanisms. This is critical to prevent the controlled atmosphere from leaking out and, more importantly, to prevent ambient air from leaking in and contaminating the process.
Atmosphere Generation and Control Systems
This is the heart of the furnace. It includes the systems that generate the required gas mixture (e.g., endothermic, exothermic, or nitrogen-based) and the instruments that monitor and adjust its composition, flow rate, and pressure.
Precision Temperature and Pressure Controls
Thermocouples and advanced controllers ensure the temperature is uniform and follows the prescribed heating and cooling cycles. Pressure controls work with the sealing system to maintain a slight positive pressure inside the furnace, further preventing air ingress.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Safety Imperatives
While powerful, the capabilities of an atmosphere furnace come with significant operational considerations that distinguish them from simpler heat treatment equipment.
Increased Complexity vs. Standard Furnaces
A simple box furnace requires little more than high-temperature protection and is easy to operate. An atmosphere furnace is a complex system of interconnected gas, heating, and safety controls that demands a higher level of technical expertise.
The Critical Role of Gas Safety
Many process atmospheres are flammable or explosive (e.g., hydrogen, carbon monoxide). This necessitates integrated gas monitoring, leak detection, and explosion-proof devices. Only professionally trained operators should manage these systems due to the inherent safety risks.
Improved Environmental Profile
A major advantage is the elimination of toxic materials used in older methods. Atmosphere furnaces replace processes that relied on hazardous cyanide salts, removing the significant challenge and cost of disposing of contaminated salts, jigs, and waste.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace technology depends entirely on your material, process requirements, and operational capabilities.
- If your primary focus is simple stress relieving or tempering without surface finish requirements: A standard, non-atmosphere furnace is likely more cost-effective and simpler to operate.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific surface hardness or wear resistance: An atmosphere furnace is essential for processes like gas carburizing or carbonitriding.
- If your primary focus is producing bright, oxide-free parts after annealing or brazing: The controlled, inert environment of an atmosphere furnace is necessary to protect the material's surface.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability for high-value components: The precise control offered by an atmosphere furnace justifies the investment in equipment and operator training.
Ultimately, choosing an atmosphere furnace is an investment in process control and final material quality.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Controlled Atmosphere | Uses specific gas mixtures to prevent oxidation and enable surface modifications. |
| Key Components | Includes sealed heating chamber, atmosphere control systems, and precision temperature/pressure controls. |
| Applications | Ideal for gas carburizing, annealing, bright quenching, and other high-precision thermal processes. |
| Safety Considerations | Requires gas monitoring and trained operators due to flammable atmospheres. |
Upgrade your lab with KINTEK's advanced atmosphere furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing process control and material quality. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can optimize your heat treatment processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the two main types of atmosphere furnaces and their characteristics? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- Why is moisture control critical in inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Integrity
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity



















