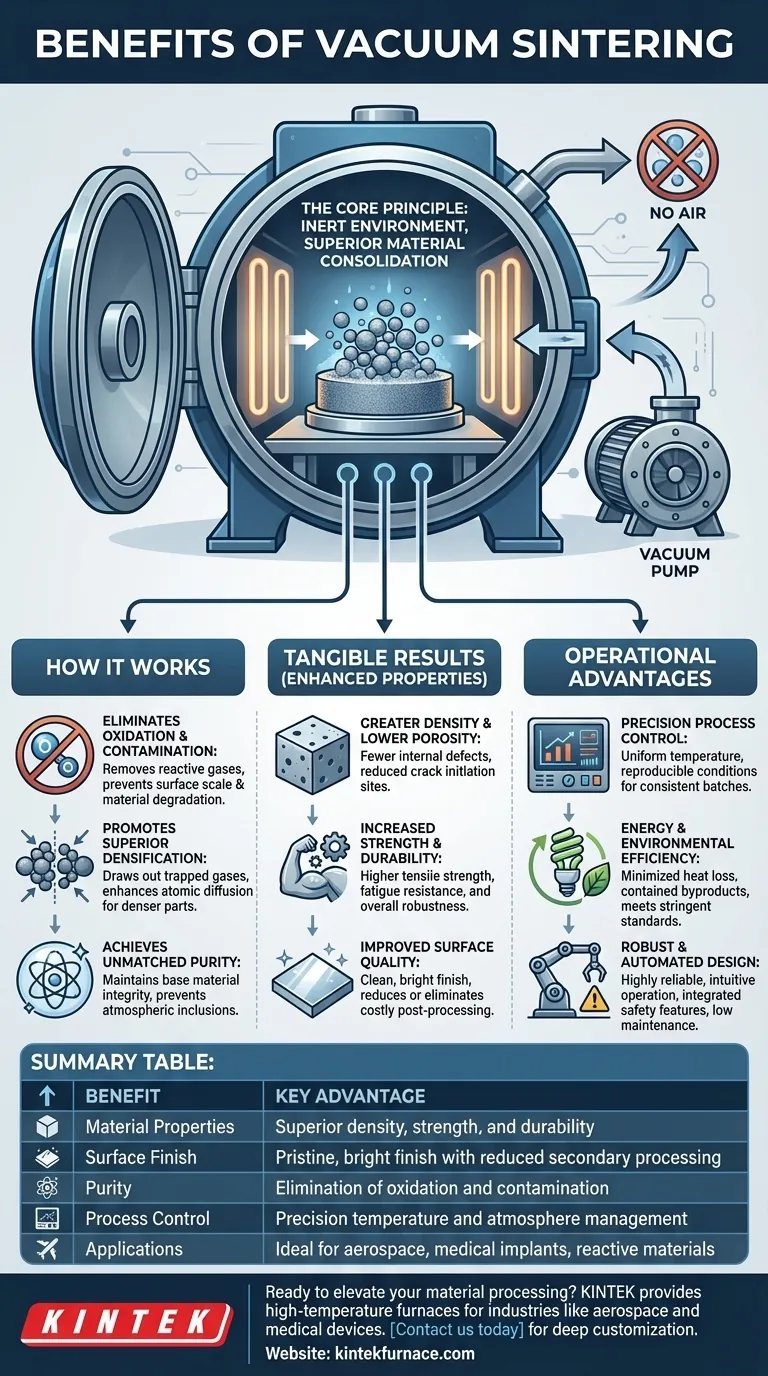
At its core, vacuum sintering delivers parts with superior material properties, pristine surface finishes, and exceptional purity. By conducting the process in a controlled, oxygen-free environment, it eliminates the risk of oxidation and contamination that plagues conventional methods, resulting in components with greater density, higher strength, and reduced need for secondary finishing.
The fundamental advantage of vacuum sintering is not simply the removal of air, but the creation of an active environment that promotes ideal material consolidation while preventing the unwanted chemical reactions that degrade a component's final integrity and performance.

The Core Principle: How a Vacuum Transforms Sintering
To understand the benefits, you must first understand the physics. A vacuum fundamentally alters the sintering environment, shifting it from a reactive atmosphere to a controlled, inert state that actively improves the material.
Eliminating Oxidation and Contamination
Atmospheric air is rich in oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor, all of which can react with materials at high temperatures. This leads to the formation of oxides and other compounds that compromise the material's properties.
A vacuum removes these reactive gases. This is not merely a passive benefit; it is an absolute requirement for processing oxidation-sensitive materials like titanium, refractory metals, and certain advanced ceramics.
Promoting Superior Densification
Sintering works by bonding material particles together, and a key goal is to eliminate the empty spaces, or pores, between them. A vacuum environment actively aids this process.
By reducing the external pressure, a vacuum helps draw out gases trapped within the material's pores. This facilitates the collapse of these voids and enhances atomic diffusion, allowing the particles to bond more completely and form a denser, more solid final part.
Achieving Unmatched Purity
Beyond preventing oxidation, the vacuum maintains the chemical purity of the base material. It prevents harmful components in the atmosphere from being incorporated into the final part, ensuring that its performance characteristics match the material's design specifications.
The Tangible Results: Enhanced Mechanical Properties
The controlled environment of a vacuum furnace translates directly into measurable improvements in the final product. These are not marginal gains; they are often transformative.
Greater Density and Lower Porosity
As a direct result of enhanced gas removal from pores, vacuum-sintered parts consistently achieve higher final densities. Lower porosity means fewer internal defect sites where cracks can initiate, which is a critical factor for performance.
Increased Strength and Durability
Higher density and purity directly correlate to improved mechanical properties. Vacuum-sintered components exhibit greater tensile strength, fatigue resistance, and overall durability compared to those sintered in a conventional atmosphere.
Improved Surface Quality
Oxidation on the surface of a part creates a rough, discolored scale that must often be removed through costly and time-consuming secondary operations like grinding or machining.
Because vacuum sintering prevents this surface oxidation, parts emerge from the furnace with a clean, bright finish, significantly reducing or even eliminating the need for mechanical rework.
Understanding the Operational Advantages
Beyond the part itself, modern vacuum furnaces offer significant process and operational benefits that contribute to efficiency and reliability.
Precision Process Control
Vacuum furnaces provide an unparalleled level of control. Temperature uniformity is optimized through strategic heating element placement, and thermocouples allow for precise monitoring and adjustment. This ensures every batch is processed under the exact same ideal conditions.
Energy and Environmental Efficiency
Advanced insulation materials, such as graphite felt, minimize heat loss and reduce overall energy consumption. Furthermore, the sealed vacuum chamber contains all process byproducts, preventing the release of exhaust gases and meeting stringent environmental standards without requiring expensive secondary treatment systems.
Robust and Automated Design
Modern systems are highly automated for intuitive, reliable operation. Integrated safety features, such as alarms for over-temperature or cooling water loss, protect both the equipment and the product. This robust design leads to high reliability and low ongoing maintenance costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a sintering method depends entirely on your material and performance requirements. Vacuum sintering is not always necessary, but for demanding applications, it is often the only viable path.
- If your primary focus is performance-critical components: Vacuum sintering is essential for achieving the highest density, purity, and strength required in fields like aerospace, medical implants, and high-performance tooling.
- If you are working with reactive materials: For materials like titanium, niobium, or specialized stainless steels, a vacuum environment is non-negotiable to prevent catastrophic oxidation.
- If your goal is a pristine surface finish: To minimize post-processing costs and achieve a clean, bright surface directly from the furnace, vacuum sintering is the superior choice.
Ultimately, adopting vacuum sintering is a strategic decision to prioritize the absolute highest level of material integrity and performance.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Advantage |
|---|---|
| Material Properties | Superior density, strength, and durability |
| Surface Finish | Pristine, bright finish with reduced secondary processing |
| Purity | Elimination of oxidation and contamination |
| Process Control | Precision temperature and atmosphere management |
| Applications | Ideal for aerospace, medical implants, and reactive materials |
Ready to elevate your material processing with advanced vacuum sintering solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnaces like Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, tailored for industries such as aerospace and medical devices. Our deep customization capabilities ensure your unique experimental needs are met precisely. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your lab's efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do vacuum sintering and annealing furnaces contribute to the densification of NdFeB magnets?
- How does pressure application in a vacuum hot press furnace facilitate sintering of copper composites? Optimize Density
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in CoNiCrAlY coatings? Repairing Cold-Sprayed Microstructures
- What is the mechanism of a vacuum sintering furnace for AlCoCrFeNi2.1 + Y2O3? Optimize Your High-Entropy Alloy Processing



















