The fundamental advantage of a vacuum heat treatment furnace is its ability to create an exceptionally clean and controlled environment for processing materials. By removing atmospheric gases, these furnaces prevent unwanted surface reactions like oxidation and decarburization, resulting in parts that are not only stronger but also maintain a bright, unaltered surface finish straight out of the furnace.
The critical takeaway is that a vacuum furnace changes the nature of heat treatment itself. Instead of merely managing the negative effects of a heated atmosphere, it removes the atmosphere entirely, giving you precise control over the material’s final properties and surface quality.

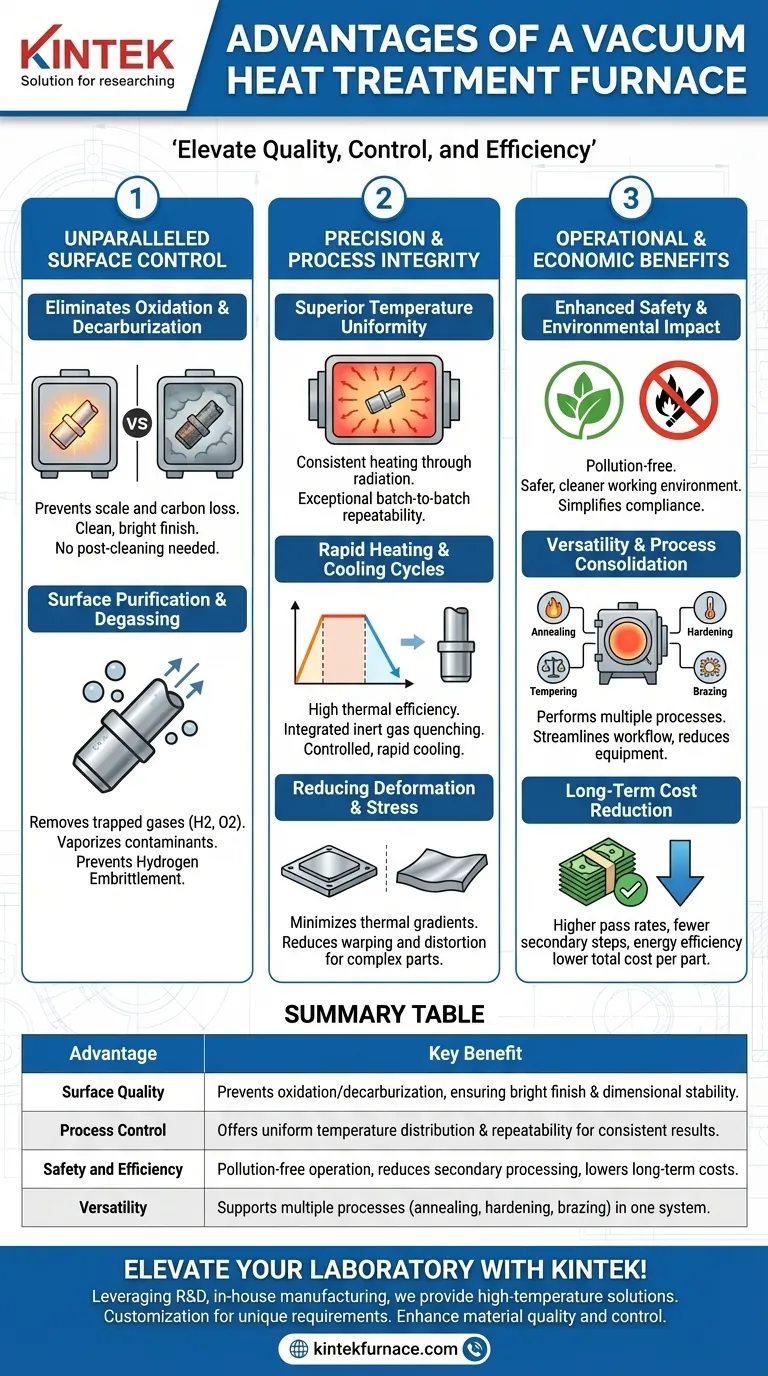
Unparalleled Control Over the Material's Surface
The most significant benefit of vacuum processing is the elimination of atmospheric interference. This has profound effects on the workpiece's final condition.
Eliminating Oxidation and Decarburization
In a conventional furnace, the oxygen present in the air reacts with the hot metal surface, forming a layer of oxide scale. A vacuum furnace removes virtually all the oxygen, completely preventing oxidation.
This means parts emerge with a clean, bright finish, preserving their precise dimensions and eliminating the need for costly and time-consuming secondary operations like sandblasting or acid cleaning. Similarly, the absence of reactive gases prevents decarburization (the loss of carbon from the surface of steel), ensuring the material's surface hardness and fatigue strength are not compromised.
Achieving Surface Purification and Degassing
The vacuum environment actively works to clean the part. It provides a powerful degassing function, pulling trapped gases like hydrogen and oxygen out from within the material itself.
This process also removes residual surface oils and other contaminants through vaporization, resulting in a state of surface purification that is impossible to achieve in an atmospheric furnace.
Preventing Hydrogen Embrittlement
For certain high-strength steels and alloys, the absorption of hydrogen during processing can lead to a dangerous phenomenon called hydrogen embrittlement, which can cause catastrophic failure under load.
Because a vacuum furnace actively removes gases from the workpiece, it effectively prevents hydrogen from permeating the material, safeguarding its structural integrity.
Precision, Consistency, and Process Integrity
Beyond surface quality, vacuum furnaces offer a superior level of process control that directly translates to higher quality and more reliable parts.
Superior Temperature Uniformity and Control
Heating in a vacuum primarily occurs through radiation, which provides exceptionally uniform temperature distribution across the entire workload.
Combined with advanced, computer-controlled systems, this ensures every part in the batch, and every batch over time, experiences the exact same thermal cycle. This repeatability is critical for high-stakes applications in aerospace, medical, and tool manufacturing.
Rapid Heating and Cooling Cycles
Modern vacuum furnaces are designed for high thermal efficiency. They can heat up quickly and, more importantly, are often equipped with integrated inert gas quenching systems.
This allows for rapid, controlled cooling at rates necessary to achieve specific metallurgical properties (hardness) without ever exposing the part to air. The entire heat-treat-quench cycle can be performed in a single, sealed chamber.
Reducing Deformation and Thermal Stress
The uniform heating and controlled, even cooling minimize the thermal gradients that cause internal stress in a workpiece. This significantly reduces the risk of warping and distortion, which is especially important for complex geometries, thin sections, or high-precision components.
Understanding the Operational and Economic Benefits
The technical advantages of vacuum furnaces create tangible benefits in safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Enhanced Safety and Environmental Impact
Vacuum furnaces are inherently safer and more environmentally friendly than alternatives like salt bath or atmosphere furnaces. They do not involve open flames, flammable gases, or the disposal of hazardous waste products.
This pollution-free operation simplifies regulatory compliance and creates a cleaner, safer working environment.
Versatility and Process Consolidation
A single vacuum furnace can be programmed to run numerous different processes, such as annealing, hardening, tempering, brazing, and sintering. This all-in-one capability offers incredible flexibility.
It allows a facility to consolidate its heat treatment services, reducing the need for multiple pieces of specialized equipment and streamlining workflow.
Long-Term Cost Reduction
While the initial investment may be higher, vacuum furnaces often lead to a lower total cost per part. Costs are reduced through a high product pass rate, the elimination of post-treatment finishing steps, and higher energy efficiency.
The improved mechanical properties and extended service life of vacuum-treated parts also add significant value that lowers long-term ownership costs for the end-user.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right heat treatment method depends entirely on your project's specific requirements for quality, consistency, and cost.
- If your primary focus is a pristine surface finish: A vacuum furnace is essential to avoid post-treatment cleaning and preserve the part's final dimensions without scaling.
- If your primary focus is dimensional stability for complex parts: The uniform heating and controlled cooling of a vacuum process dramatically reduce warping and distortion.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability for high-value components: The automated, computer-controlled nature of vacuum heat treatment ensures every batch meets the exact same metallurgical specifications.
- If your primary focus is treating reactive or exotic materials: A vacuum provides the necessary inert environment to process metals like titanium and superalloys without contamination.
Ultimately, adopting vacuum heat treatment is a strategic decision to prioritize quality, control, and process integrity from the inside out.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Surface Quality | Prevents oxidation and decarburization, ensuring bright finish and dimensional stability |
| Process Control | Offers uniform temperature distribution and repeatability for consistent results |
| Safety and Efficiency | Pollution-free operation, reduces secondary processing, and lowers long-term costs |
| Versatility | Supports multiple processes like annealing, hardening, and brazing in one system |
Elevate your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced vacuum heat treatment furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet unique experimental requirements. Experience enhanced material quality, precise control, and cost savings—contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your heat treatment processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance



















