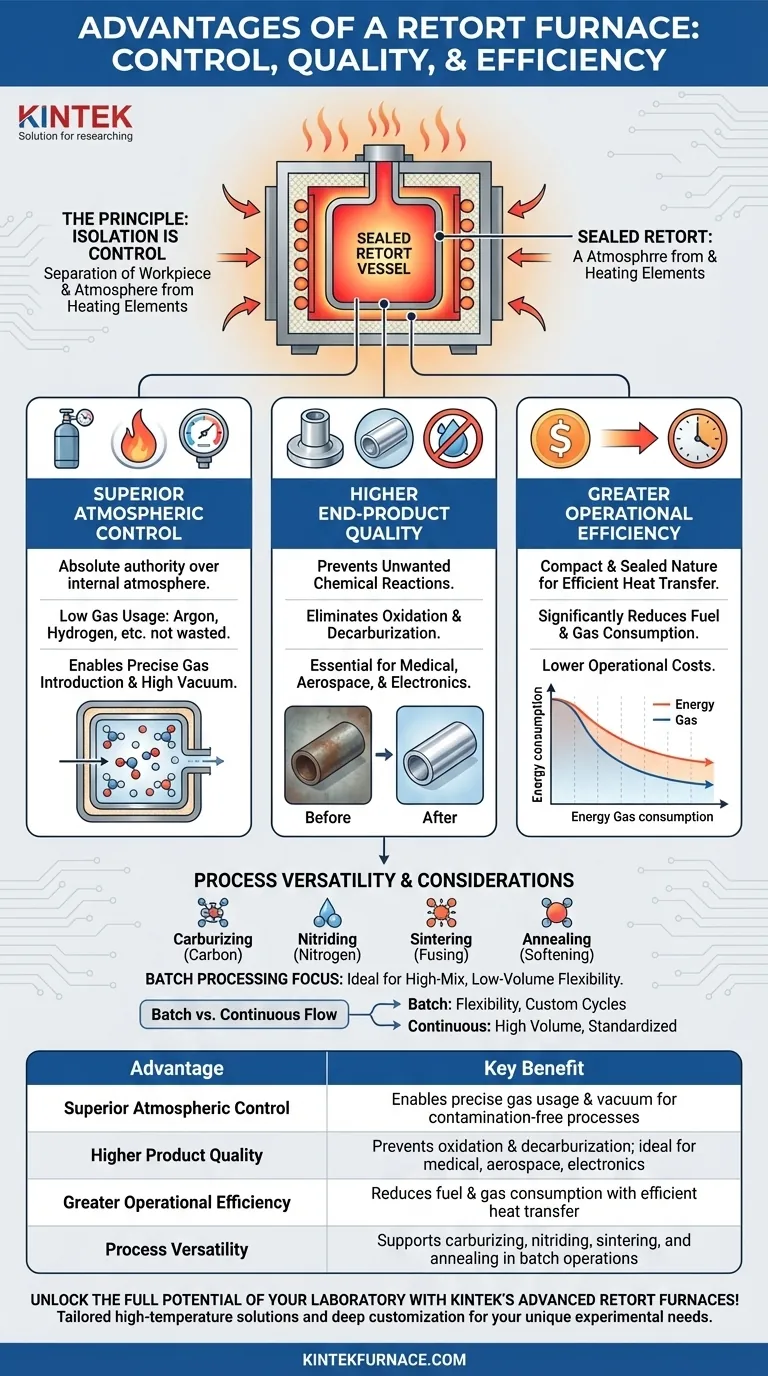
At its core, a retort furnace offers three primary advantages: superior atmospheric control, higher end-product quality, and greater operational efficiency. These benefits stem directly from its unique design, which uses a sealed internal chamber to isolate the material being processed from the furnace's heating elements and the outside environment.
The defining feature of a retort furnace is its sealed vessel. This design element is not just a component; it is the source of all its advantages, enabling a level of process control and product purity that is difficult to achieve in other furnace types.
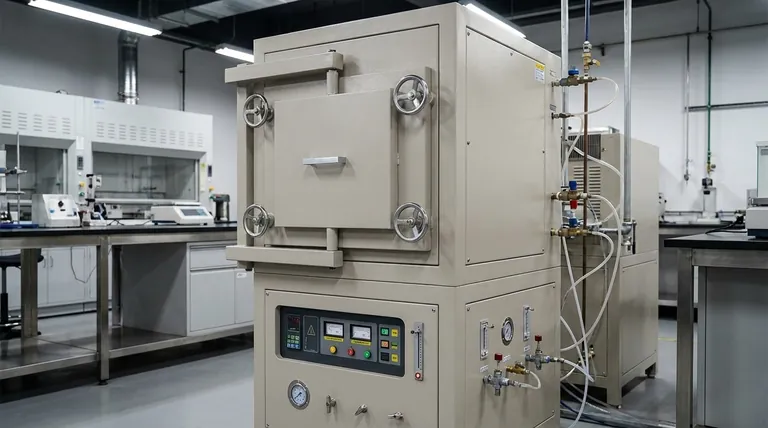

The Principle: Isolation is Control
A standard furnace heats materials in a chamber where the atmosphere is often influenced by the heating method and external air. A retort furnace fundamentally changes this relationship by introducing a critical barrier.
What is a Retort?
A retort is a sealed vessel, typically made of metal alloys or ceramics, that sits inside the main furnace body. The materials you are treating are placed inside this retort, not in the main furnace chamber.
The Power of Separation
This design separates the workpiece and its immediate atmosphere from the heating elements and insulation. The furnace heats the retort from the outside, and the retort, in turn, heats the material inside it. This separation is the key to all its benefits.
Key Advantages Explained
By isolating the process, a retort furnace provides specific, measurable advantages that are critical for advanced material treatments.
Unmatched Atmosphere Control
Because the retort is a sealed, contained space, you have absolute authority over the atmosphere within it. This allows for extremely low atmosphere usage, as gases like argon or hydrogen are not wasted filling a large, leaky chamber.
You can also precisely introduce specialized gases or create a near-perfect vacuum, which is essential for processes sensitive to oxygen or other contaminants.
Superior Product Quality
Directly resulting from atmospheric control, retort furnaces excel at preventing unwanted chemical reactions. By eliminating oxygen, you can prevent oxidation and decarburization on metal surfaces, leading to a cleaner, higher-quality final product.
This purity is essential for applications in medical, aerospace, and electronics manufacturing, where material integrity is non-negotiable.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency
The compact and sealed nature of the retort allows for very efficient heat transfer to the workload, which can lead to quicker heating times.
Furthermore, because you are only consuming the precise amount of atmospheric gas needed for the small retort volume, you significantly reduce fuel and gas consumption, lowering operational costs over time.
Process Versatility
The precise control over temperature and atmosphere makes retort furnaces incredibly versatile. They are the ideal choice for a range of specialized heat treatments.
Common processes include carburizing (adding carbon), nitriding (adding nitrogen), sintering (fusing powdered material), and annealing (softening metal), among many other advanced treatments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the retort furnace design is not universally superior. Its advantages come with specific considerations that make it ideal for some applications but less so for others.
Batch Processing vs. Continuous Flow
Most retort furnaces are batch furnaces. They are loaded, run through a cycle, and then unloaded. This provides immense flexibility for customizing cycles for different low-to-medium volume parts.
However, they are inherently less suited for high-volume, continuous production lines where parts are constantly moving through a furnace.
Upfront Cost and Complexity
The specialized components, such as the retort itself and the sophisticated atmosphere control systems, can lead to a higher initial investment compared to simpler, non-atmospheric furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be driven by the specific requirements of your material and production goals.
- If your primary focus is product purity: A retort furnace is the definitive choice for preventing oxidation and contamination.
- If your primary focus is specialized material treatment: Processes requiring specific atmospheres like hydrogen or nitrogen are only possible in a sealed retort.
- If your primary focus is flexibility for varied, smaller runs: The batch-style operation of a retort furnace offers superior control for high-mix, low-volume production.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, standardized production: A continuous belt furnace may be a more efficient choice, provided your process does not require strict atmospheric control.
Ultimately, choosing a retort furnace is a commitment to achieving the highest degree of process control and product quality.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Superior Atmospheric Control | Enables precise gas usage and vacuum creation for contamination-free processes |
| Higher Product Quality | Prevents oxidation and decarburization, ideal for medical, aerospace, and electronics |
| Greater Operational Efficiency | Reduces fuel and gas consumption with efficient heat transfer |
| Process Versatility | Supports carburizing, nitriding, sintering, and annealing in batch operations |
Unlock the full potential of your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced retort furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide tailored high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and product quality. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can transform your processes and deliver superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling



















