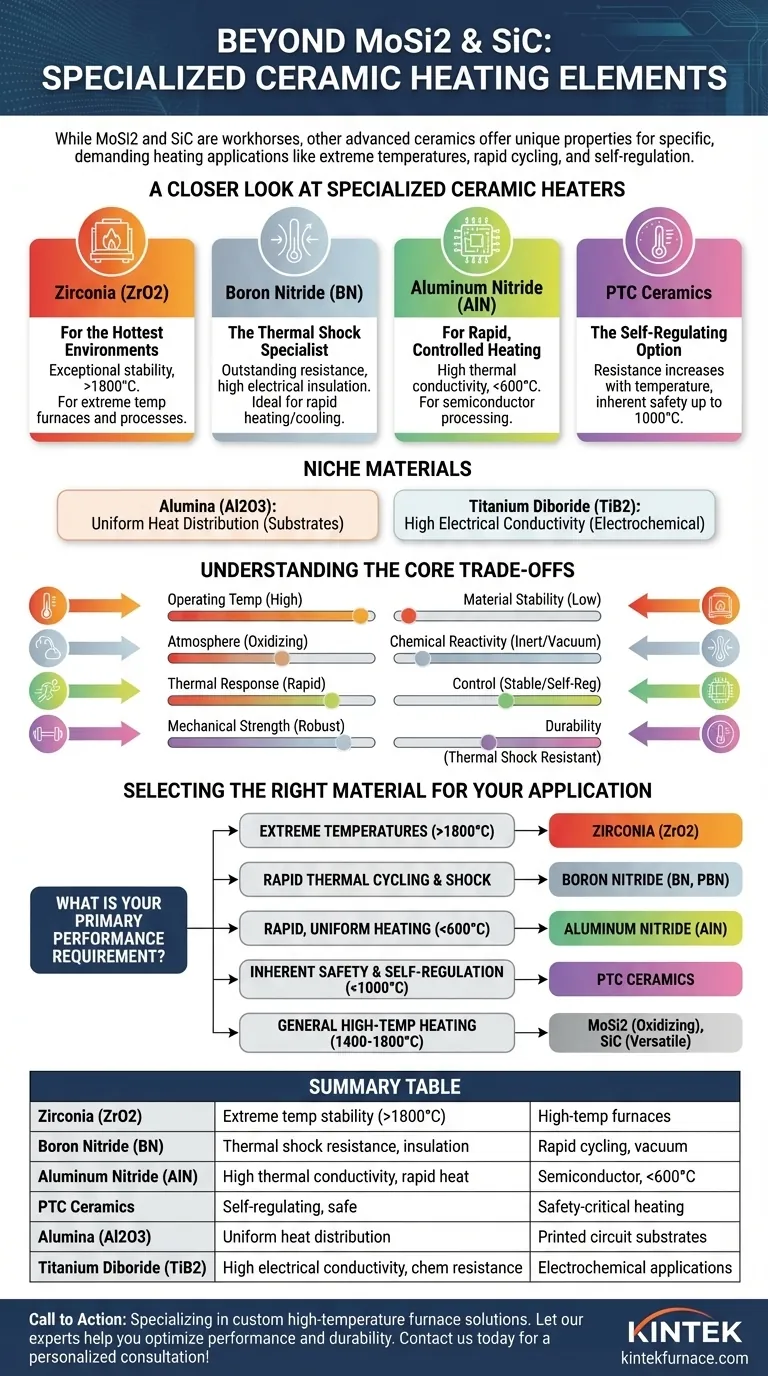
Beyond the workhorses of MoSi2 and SiC, a range of advanced ceramic materials offer specialized performance for unique heating applications. These alternatives are chosen when specific properties like extreme temperature resistance, thermal shock immunity, or self-regulation are more critical than the general-purpose capabilities of Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) and Silicon Carbide (SiC). Key examples include Zirconia (ZrO2), Boron Nitride (BN), Aluminum Nitride (AlN), and PTC ceramics.
The choice of a ceramic heating element is a precise engineering decision. While MoSi2 and SiC cover most high-temperature needs, understanding the unique properties of specialized ceramics is essential for optimizing performance, safety, and lifespan in demanding or niche applications.
A Closer Look at Specialized Ceramic Heaters
While MoSi2 and SiC are valued for their high-temperature performance in a variety of atmospheres, certain applications demand a different set of material characteristics.
Zirconia (ZrO2): For the Hottest Environments
Zirconia stands out for its exceptional stability at extreme temperatures, often operating where even MoSi2 elements would fail. It is the material of choice for furnaces and processes pushing the upper limits of material science, well above 1800°C.
Boron Nitride (BN): The Thermal Shock Specialist
Boron Nitride is renowned for its outstanding thermal shock resistance and high electrical insulation. It can withstand rapid heating and cooling cycles that would fracture other ceramics.
Pyrolytic Boron Nitride (PBN) is an ultra-pure, non-porous version, making it ideal for high-vacuum and semiconductor applications where contamination is a critical concern.
Aluminum Nitride (AlN): For Rapid, Controlled Heating
Aluminum Nitride offers a combination of high thermal conductivity and excellent electrical insulation. This allows it to heat up and cool down very quickly while ensuring even heat distribution.
Its primary use is in moderate-temperature applications (typically below 600°C) where rapid thermal response is paramount, such as in semiconductor processing equipment.
PTC Ceramics: The Self-Regulating Option
Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) materials are not a single compound but a class of engineered ceramics. Their electrical resistance increases sharply at a specific, designed temperature.
This unique property makes them inherently self-regulating. As they reach their target temperature, their increasing resistance throttles the current, preventing overheating without external controls. This is ideal for applications requiring safety and stable temperatures up to around 1000°C.
Other Niche Materials
Specialized ceramics like Alumina (Al2O3) are often used for their ability to provide uniform heat distribution, frequently as a substrate for a printed heating circuit. Titanium Diboride (TiB2) is notable for its high electrical conductivity (unusual for a ceramic) and chemical resistance, suiting it for specific electrochemical applications.
Understanding the Core Trade-offs
Selecting the right material requires balancing competing factors. The "best" heater is simply the one whose properties most closely match the demands of the application.
Operating Temperature vs. Material Stability
The primary factor is always the required operating temperature. MoSi2 and Zirconia excel at the highest ranges, but this capability comes at a cost, often including brittleness at room temperature or higher material expense.
Atmosphere and Chemical Reactivity
The furnace atmosphere dictates material choice. MoSi2 thrives in oxidizing atmospheres where it forms a protective silica layer but can be unsuitable for other environments. SiC is more versatile, but materials like PBN are required for ultra-pure vacuum conditions.
Thermal Response and Control
An application needing rapid temperature cycling benefits from a material with high thermal conductivity like AlN. In contrast, applications needing inherent safety and stability over precise control are a perfect fit for PTC ceramics.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance are critical for longevity. SiC is known for its mechanical robustness, while BN is the superior choice for environments with extreme thermal cycling. This is a trade-off against materials like MoSi2, which can be brittle and require careful handling.
Selecting the Right Material for Your Application
Your choice should be guided by your single most important performance requirement.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme temperatures (above 1800°C): Zirconia (ZrO2) is your leading candidate, operating where most other materials fail.
- If your primary focus is resistance to rapid temperature changes and thermal shock: Boron Nitride (BN), particularly in its pyrolytic form (PBN), offers unmatched stability.
- If your primary focus is rapid, uniform heating at moderate temperatures (below 600°C): Aluminum Nitride (AlN) provides excellent thermal conductivity and response time.
- If your primary focus is inherent safety and self-regulation up to 1000°C: PTC ceramics are the ideal choice as they automatically limit their own temperature.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose high-temperature heating (1400-1800°C): MoSi2 (in oxidizing atmospheres) and SiC (for versatility and strength) remain the industry standards.
Ultimately, a successful design hinges on a clear understanding of the application's demands matched with the specific strengths of the chosen ceramic material.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Zirconia (ZrO2) | Extreme temperature stability (>1800°C) | High-temperature furnaces, material science |
| Boron Nitride (BN) | Excellent thermal shock resistance, high electrical insulation | Rapid thermal cycling, high-vacuum systems |
| Aluminum Nitride (AlN) | High thermal conductivity, rapid heating/cooling | Semiconductor processing, moderate temperatures (<600°C) |
| PTC Ceramics | Self-regulating, resistance increases with temperature | Safety-critical heating, stable temperatures up to 1000°C |
| Alumina (Al2O3) | Uniform heat distribution | Substrates for printed heating circuits |
| Titanium Diboride (TiB2) | High electrical conductivity, chemical resistance | Electrochemical applications |
Struggling to find the perfect ceramic heating element for your lab's unique needs? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature furnace solutions with deep customization capabilities. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, tailored to meet your specific experimental requirements. Let our experts help you optimize performance and durability—contact us today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions



















