In high-temperature vacuum furnaces, graphite heating elements are the standard for demanding metallurgical processes. Their use is most common in applications like the hardening of steel, the brazing of metals with nickel or copper filler, and the production of sintered metals from powder.
Graphite is chosen not just for its ability to reach extreme temperatures, but specifically for its unique property of getting stronger as it heats up, making it the superior choice for processes that must occur within a controlled, non-oxidizing (vacuum or inert) environment.
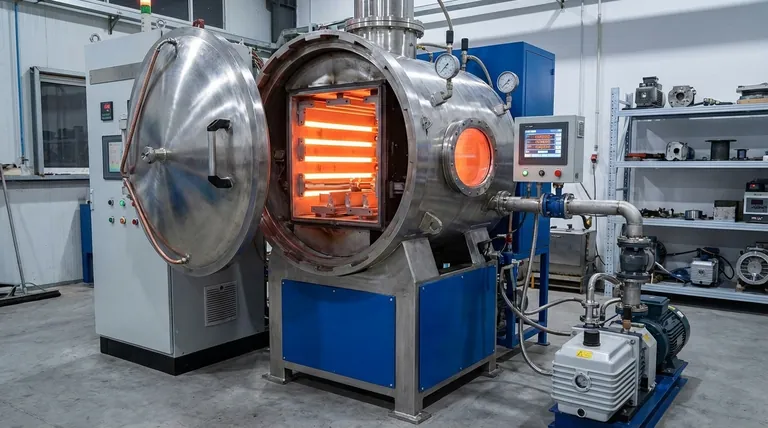

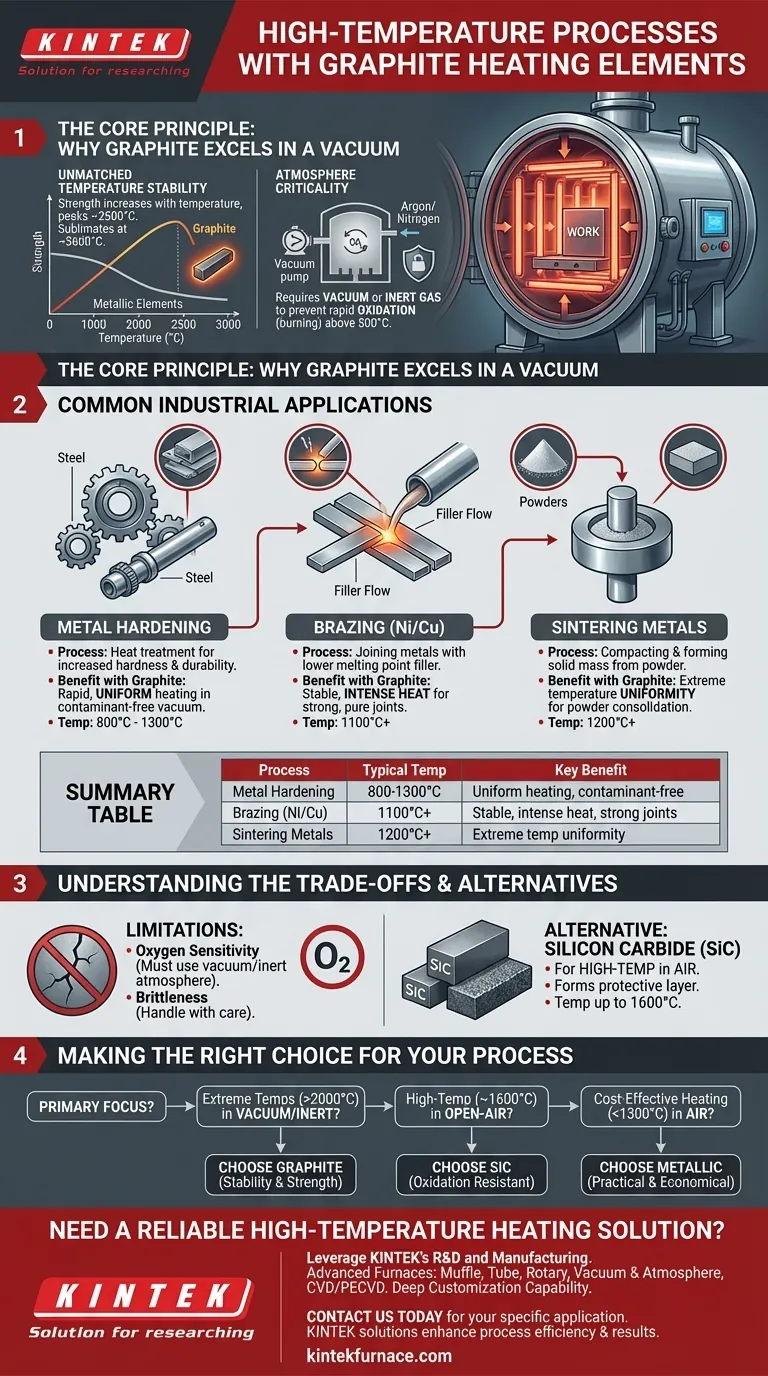
The Core Principle: Why Graphite Excels in a Vacuum
The decision to use a graphite heating element is fundamentally about managing extreme heat in a specific type of atmosphere. Its properties make it uniquely suited for these environments.
Unmatched Temperature Stability
Unlike metallic elements that soften and weaken as they approach their melting point, graphite exhibits the opposite behavior. Its mechanical strength actually increases with temperature, peaking around 2500°C.
Graphite does not melt at atmospheric pressure but instead sublimates (turns from a solid directly to a gas) at approximately 3600°C, allowing it to operate reliably at temperatures far beyond the limits of most other materials.
The Critical Role of the Atmosphere
The primary limitation of graphite is its reaction with oxygen at high temperatures. Above approximately 500°C, graphite will rapidly oxidize in the presence of air, essentially burning away.
For this reason, graphite heating elements are used almost exclusively inside vacuum furnaces or furnaces filled with an inert gas, such as argon or nitrogen. This controlled atmosphere protects the element from degradation, enabling its high-performance capabilities.
Common Industrial Applications
Graphite's properties make it the ideal heating source for several precise, high-temperature manufacturing processes.
Metal Hardening
Hardening is a heat treatment process that alters the microstructure of metals like steel to increase their hardness and durability. Using a vacuum furnace with graphite elements ensures rapid, uniform heating and a clean environment free from contaminants that could affect the metal's surface.
Brazing (Nickel and Copper)
Brazing joins two pieces of metal using a filler material that has a lower melting point. For high-strength joints using nickel or copper-based fillers, temperatures can exceed 1100°C. Graphite elements provide the intense, stable heat required in a clean vacuum, ensuring a strong, pure braze joint.
Sintering Metals
Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material from powder using heat below its melting point. This is used to create specialized metal parts. The process requires extremely uniform and high temperatures, which graphite elements in a vacuum furnace provide perfectly.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, graphite is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is tied directly to its operating environment and physical characteristics.
The Oxygen Limitation
The absolute need for a vacuum or inert atmosphere is graphite's main trade-off. This adds significant cost and complexity to furnace design and operation compared to systems that can run in ambient air.
Brittleness and Handling
Graphite is a brittle ceramic material. Heating elements made from it must be handled with more care than robust metallic elements to avoid mechanical shock or fracture during installation and maintenance.
When to Consider Alternatives (like SiC)
For high-temperature processes that must occur in an air atmosphere, other materials are required. Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements, for example, can operate at high temperatures in air because they form a protective glassy layer of silicon dioxide that prevents further oxidation. They are often used for applications like drying or certain melting processes in air.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct heating element requires matching the material's properties to the specific goals and environment of your application.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme temperatures (>2000°C) in a vacuum or inert atmosphere: Graphite is the definitive and superior choice due to its stability and strength.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature heating (up to 1600°C) in an open-air environment: An oxidation-resistant material like Silicon Carbide (SiC) is the necessary solution.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective heating below ~1300°C in air: Traditional metallic elements (like FeCrAl alloys) are often the most practical and economical option.
Ultimately, your choice of heating element is dictated by the required temperature, the process atmosphere, and the material being heated.
Summary Table:
| Process | Typical Temperature Range | Key Benefit with Graphite |
|---|---|---|
| Metal Hardening | 800°C - 1300°C | Uniform heating in a contaminant-free vacuum |
| Brazing (Ni/Cu) | 1100°C+ | Stable, intense heat for strong, pure joints |
| Sintering Metals | 1200°C+ | Extreme temperature uniformity for powder consolidation |
Need a Reliable High-Temperature Heating Solution for Your Lab?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Whether your process requires the extreme temperature stability of graphite in a vacuum or an alternative for air atmospheres, our experts can help you select and customize the ideal system.
Contact us today to discuss your specific high-temperature application and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your process efficiency and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does vacuum heat treatment reduce workpiece deformation? Achieve Superior Dimensional Stability
- What is the primary application of vacuum heat treating furnaces in aerospace? Enhance Component Performance with Precision
- How does graphite contribute to energy efficiency in vacuum furnaces? Achieve Faster, More Uniform Heating
- What is the mechanism and effect of post-annealing NiTi thin films in a vacuum furnace? Unlock Superelasticity
- Why are graphite fixtures and holders important in vacuum furnaces? Unlock Precision & Durability



















