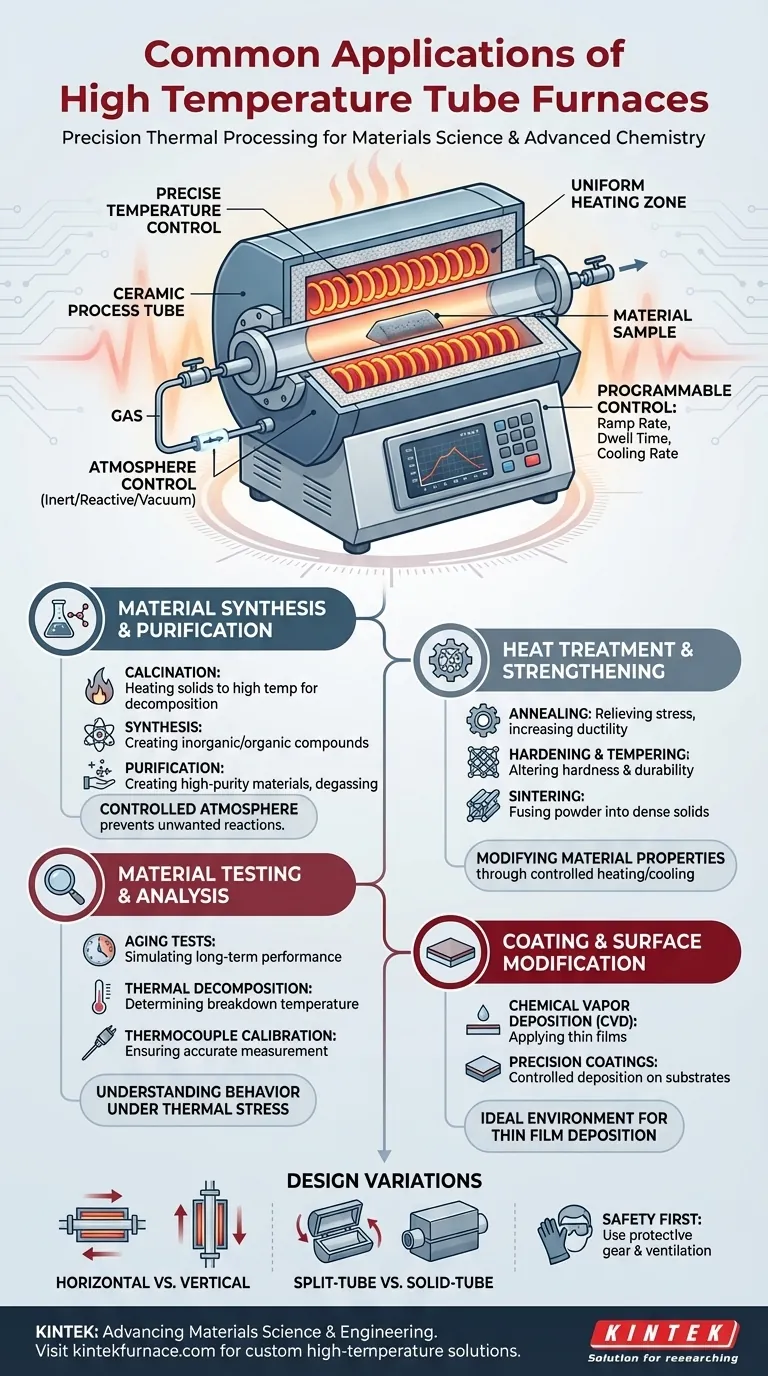
In short, a high-temperature tube furnace is a cornerstone of modern materials science and advanced chemistry. Its primary applications involve the precise thermal processing of materials, including the synthesis and purification of chemical compounds, strengthening metals through annealing, applying specialized coatings, and testing the long-term durability of materials under extreme heat.
The true value of a tube furnace is not just its ability to get hot, but its capacity to create a highly uniform and controllable thermal environment. This precision allows researchers and engineers to manipulate a material's fundamental properties in a repeatable and predictable way.

What is a Tube Furnace and Why is it Used?
A high-temperature tube furnace is a specialized piece of laboratory equipment designed for creating exceptionally precise and uniform heat within a confined, cylindrical space. This control is what makes it so indispensable across various scientific and industrial fields.
The Core Principle: Precision Heating in a Controlled Environment
At its heart, a tube furnace is an electric heater with heating coils wrapped around a ceramic tube. When electricity passes through the coils, they generate radiant heat that is focused on the material placed inside the tube.
The key advantage is the ability to control the atmosphere inside the tube. By connecting gas lines or a vacuum pump, operators can remove reactive gases like oxygen or introduce specific inert or reactive gases, which is critical for many chemical synthesis and purification processes.
Key Features That Enable Advanced Processes
Modern tube furnaces are not simple ovens. Their utility comes from a suite of advanced features that enable complex thermal processing.
- Programmable Control: Operators can set precise temperature profiles, including the rate of heating (ramp rate), how long the temperature is held (dwell time), and the rate of cooling.
- Uniform Temperature Zones: High-quality furnaces ensure the temperature is consistent across the entire length of the sample. Some models offer multi-zone control to create specific temperature gradients.
- High-Resolution Measurement: Sensitive thermocouples provide accurate, real-time temperature feedback, ensuring the process runs exactly as programmed.
A Breakdown of Key Applications by Process
The applications of a tube furnace are vast, but they can be grouped into a few primary categories based on the intended outcome of the thermal process.
Material Synthesis and Purification
This is a core application in chemistry and materials science. Processes like calcination (heating solids to high temperatures to cause decomposition) and synthesis of inorganic or organic compounds are common.
By controlling the atmosphere, researchers can prevent unwanted side reactions or use a specific gas as a reactant, allowing for the creation and purification of high-purity materials used in electronics and pharmaceuticals.
Heat Treatment and Material Strengthening
In metallurgy and engineering, a tube furnace is used to alter a material's physical and mechanical properties.
- Annealing: Heating a metal or glass and allowing it to cool slowly removes internal stresses and increases its ductility.
- Hardening & Tempering: These processes involve specific heating and cooling cycles to increase the hardness and durability of metals.
- Sintering: This involves heating a compressed powder to just below its melting point, causing the particles to fuse together to form a solid, dense object.
Material Testing and Analysis
Understanding how a material behaves under thermal stress is critical for engineering and quality control.
Tube furnaces are used for aging tests, where a material is held at a high temperature for a prolonged period to simulate its lifespan. They are also used for thermal decomposition studies to determine the temperature at which a material breaks down, and for the precise calibration of thermocouples.
Coating and Surface Modification
The controlled environment of a tube furnace is ideal for applying thin films and coatings. Processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) often use a tube furnace to heat a substrate while precursor gases are introduced, which then react and deposit a thin, solid film onto the substrate's surface.
Understanding the Design Variations and Trade-offs
Not all tube furnaces are the same. The design is chosen based on the specific application, and each comes with its own set of considerations.
Horizontal vs. Vertical Furnaces
A horizontal furnace is the most common design, allowing for easy loading and observation of samples. A vertical furnace is used when it's critical to prevent the sample from touching the sides of the tube, such as when growing crystals or working with molten materials.
Split-Tube vs. Solid-Tube Furnaces
A split-tube furnace is hinged, allowing it to open like a clamshell. This design makes it easy to place and remove the process tube or quickly cool a sample. However, a solid, single-piece tube furnace often provides slightly better temperature uniformity.
The Critical Role of Safety
Working with extreme temperatures requires strict adherence to safety protocols. Users must always wear appropriate protective gear, including heat-resistant gloves and safety goggles.
It is essential that only trained personnel operate the furnace. The area must be well-ventilated, especially when processes may release gases, and the equipment must be properly maintained and cleaned before each use to prevent contamination or unexpected chemical reactions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right process, you must first define your objective. The versatility of a tube furnace allows you to pursue a wide range of outcomes by applying the correct thermal technique.
- If your primary focus is creating new materials or purifying compounds: You will rely on processes like synthesis, calcination, and degassing, often requiring precise atmospheric control.
- If your primary focus is improving the mechanical properties of a material: You will use heat treatments such as annealing, hardening, or sintering to modify its internal structure.
- If your primary focus is research and quality control: You will perform aging tests, thermal decomposition analysis, or thermocouple calibration to understand a material's behavior under thermal stress.
Ultimately, mastering the tube furnace means mastering the ability to precisely manipulate matter through controlled thermal energy.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Primary Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Material Synthesis & Purification | Calcination, Synthesis, Degassing | Chemistry, Electronics, Pharmaceuticals |
| Heat Treatment & Strengthening | Annealing, Hardening, Sintering | Metallurgy, Engineering |
| Material Testing & Analysis | Aging Tests, Thermal Decomposition, Thermocouple Calibration | Research, Quality Control |
| Coating & Surface Modification | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Electronics, Materials Science |
Ready to elevate your laboratory's capabilities with precision high-temperature solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnace systems tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in materials science, chemistry, or engineering, we can help you achieve superior thermal processing outcomes. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can drive your research and innovation forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















