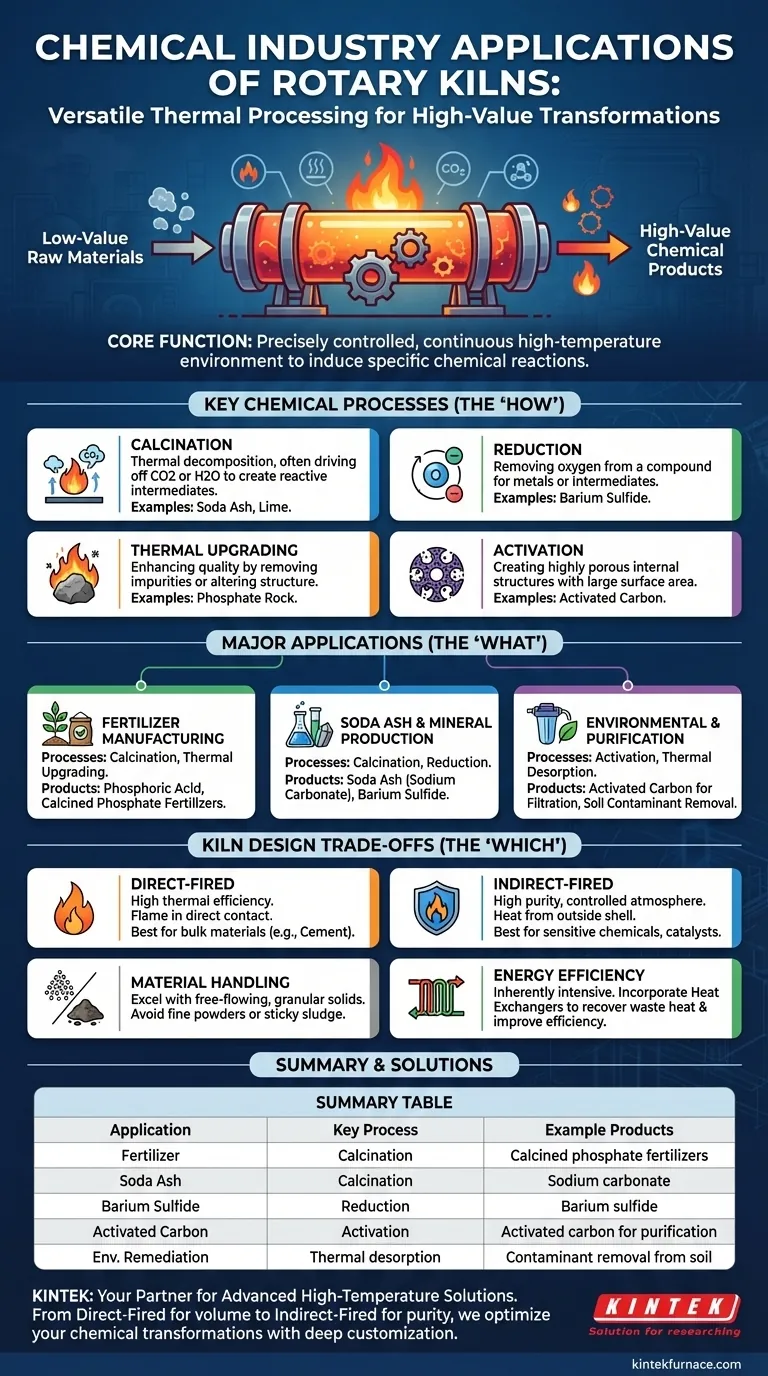
In the chemical industry, a rotary kiln is a versatile thermal processing tool used to produce a wide range of essential products. Key applications include the manufacturing of soda ash, calcined phosphate fertilizers, barium sulfide, and the activation of catalysts and carbon materials for purification processes. They are fundamental for any high-temperature chemical transformation involving granular solids.
At its core, the rotary kiln's value lies in its ability to create a precisely controlled, continuous, high-temperature environment. This allows engineers to induce specific chemical reactions—like calcination or reduction—to transform low-value raw materials into high-value, purified, or reactive chemical products.

The Core Functions of a Rotary Kiln in Chemical Processing
A rotary kiln is not just a furnace; it is a dynamic reactor. Its gentle rotation and controlled temperature profile enable several critical chemical processes.
Calcination: Creating Reactive Intermediates
Calcination is a thermal decomposition process used to create more reactive materials, often by driving off carbon dioxide (CO2) or water.
In the production of soda ash or lime, for example, the kiln heats the raw material to a specific temperature, causing a chemical change that releases gases and leaves behind a solid product like sodium oxide or calcium oxide.
Reduction: Removing Oxygen
Reduction is a chemical reaction that involves removing oxygen from a compound. This is crucial for producing certain metals or chemical intermediates.
The production of barium sulfide, mentioned in chemical applications, often involves the reduction of barium sulfate (barite) with carbon in a rotary kiln. The controlled atmosphere and temperature are essential for this reaction to proceed efficiently.
Thermal Upgrading: Enhancing Value and Purity
Rotary kilns are frequently used to improve the quality of raw materials by removing impurities or altering their physical structure.
A prime example is the upgrading of low-grade phosphate rock. Heating the ore in a kiln can drive off organic impurities and moisture, concentrating the phosphate content and making it suitable for producing high-quality fertilizers.
Activation: Creating Porous Structures
Specialized applications include activation, where a material is heated to create a highly porous internal structure with a large surface area.
This is the principle behind producing activated carbon for water and air purification or activating catalysts used to accelerate reactions in other chemical manufacturing processes.
Key Chemical Products and Processes
The versatility of these core functions translates into several specific, high-impact applications across the chemical industry.
Fertilizer Manufacturing
The rotary kiln was central to a new process for producing phosphoric acid developed in the 1960s. This method offered significant advantages, including lower energy consumption and the ability to use low-grade phosphate rock without requiring sulfuric acid.
This makes kilns vital for producing calcined phosphate fertilizers, turning otherwise unusable raw materials into valuable agricultural products.
Soda Ash and Mineral Production
The production of soda ash (sodium carbonate), a foundational chemical used in glass, detergents, and other chemical processes, relies on calcination steps often performed in a rotary kiln.
Similarly, other inorganic chemicals like barium sulfide depend on the kiln's ability to facilitate high-temperature reduction reactions.
Environmental and Purification Materials
Kilns are essential for producing materials used in environmental protection. The production and reactivation of activated carbon for filtration systems are common applications.
They can also be used for thermal desorption, a process that uses heat to remove contaminants from soil or industrial waste, or for the safe combustion of organic waste materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Kiln Design
Choosing the right kiln technology is critical and involves clear trade-offs based on the specific chemical process.
Direct vs. Indirect Firing
A direct-fired kiln is highly efficient because the flame and combustion gases are in direct contact with the material. This is ideal for bulk materials like cement or lime where slight contamination is not a concern.
An indirect-fired kiln heats the material from outside a rotating shell. This prevents any contact between the material and combustion gases, making it essential for high-purity chemicals, sensitive catalysts, or processes requiring a specific controlled atmosphere.
Material Handling Limitations
Rotary kilns excel at processing free-flowing, granular, or small, lumpy solids. Their tumbling action ensures even heating.
They are not well-suited for very fine powders that can become entrained in the gas flow or for sticky, sludge-like materials that can build up inside the kiln shell.
Energy Consumption and Efficiency
While some modern processes are optimized for low energy use, rotary kilns are inherently energy-intensive.
To mitigate this, many modern designs incorporate heat exchangers. These systems recover waste heat from the hot exit gas or the discharged solid product and use it to preheat the incoming raw material, significantly improving overall thermal efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific goal determines the ideal kiln configuration.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost commodity production: A direct-fired kiln offers the best thermal efficiency and throughput for materials like lime or cement.
- If your primary focus is purity and controlled atmospheres: An indirect-fired kiln is non-negotiable for processing sensitive catalysts, specialty chemicals, or food-grade products.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and sustainability: Prioritize a modern kiln system equipped with heat exchangers to recover and reuse waste heat.
- If your primary focus is processing diverse or difficult materials: Consider specialized designs for waste management or remediation that can handle specific contaminants or material properties.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln serves as the adaptable workhorse of the chemical industry, enabling the transformation of raw earth into the building blocks of modern life.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Process | Example Products |
|---|---|---|
| Fertilizer Manufacturing | Calcination | Calcined phosphate fertilizers, Phosphoric acid |
| Soda Ash Production | Calcination | Sodium carbonate |
| Barium Sulfide Production | Reduction | Barium sulfide |
| Activated Carbon Production | Activation | Activated carbon for purification |
| Environmental Remediation | Thermal desorption | Contaminant removal from soil |
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need efficient direct-fired kilns for high-volume production or pure indirect-fired systems for sensitive processes, we can help optimize your chemical transformations. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your lab's productivity and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does customization benefit the use of rotary kilns? Boost Efficiency and Quality with Tailored Solutions
- What types of physical and chemical transformations occur in a rotary kiln? Master Material Processing for Superior Results
- How do vibrational feeder specifications impact rotary kiln efficiency? Optimize Your Lab's Material Flow & Stability
- What role does gas flow and combustion play in a rotary kiln? Optimize Heat Transfer for Efficiency and Quality
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency



















