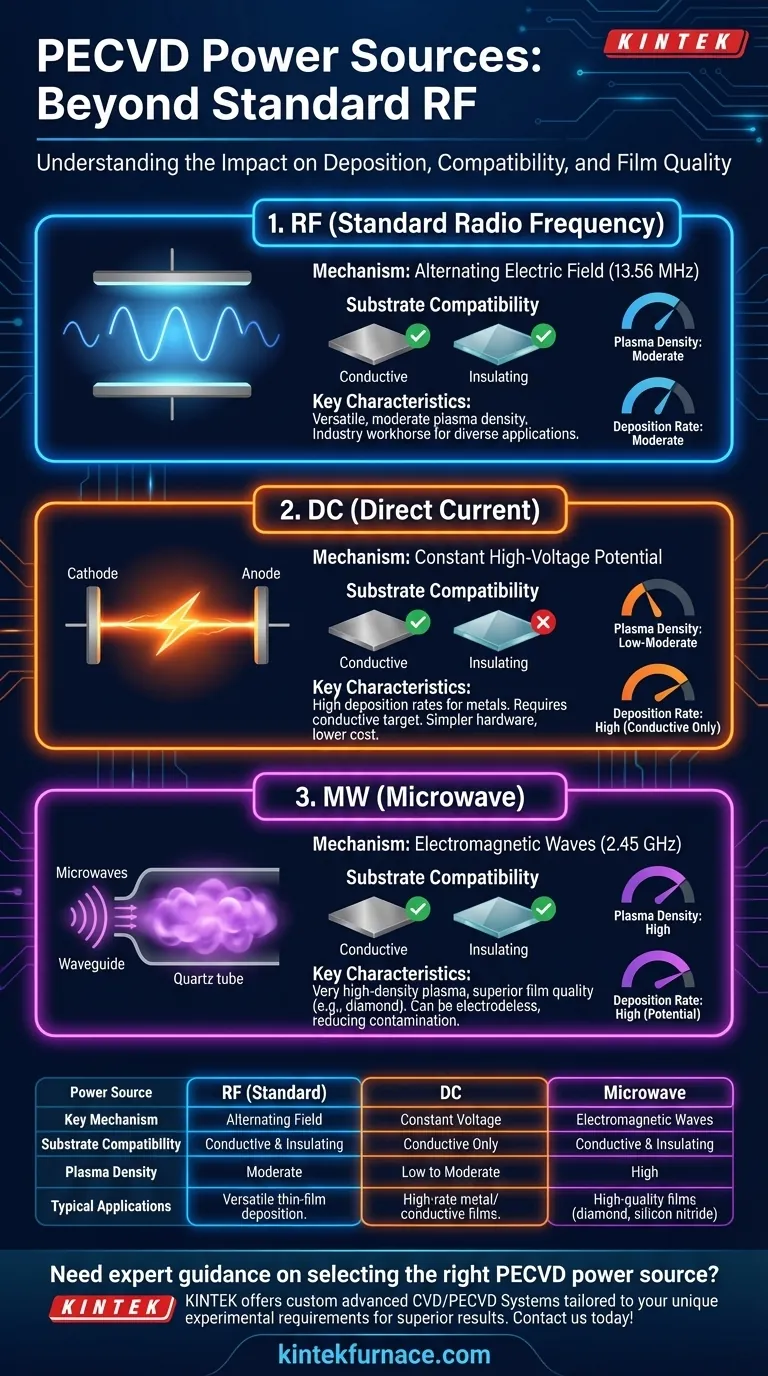
Beyond standard RF sources, Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) reactors can also be powered by Direct Current (DC) and microwave energy. While Radio Frequency (RF) is the most common method, each power source generates plasma through a distinct physical mechanism. This choice fundamentally impacts the deposition process, its suitability for different materials, and the final properties of the deposited film.
The choice of a power source for PECVD—be it RF, DC, or microwave—is a critical process decision. It directly dictates the plasma's characteristics, which in turn determines its suitability for depositing on conductive versus insulating substrates and influences final film properties like density and uniformity.

Understanding the Role of the Power Source
The sole purpose of the power source in a PECVD system is to provide the energy needed to transform neutral reactant gases into a chemically reactive plasma. The way this energy is delivered defines the process.
The Standard: Radio Frequency (RF) PECVD
RF PECVD is the industry workhorse for its versatility. It uses an RF power supply, typically at 13.56 MHz, to create an oscillating electric field between two electrodes.
This alternating field energizes free electrons, which then collide with and ionize the gas molecules. Because the field is alternating, it does not require a conductive path, making it effective for depositing films on both conductive and insulating substrates.
The Primary Alternatives to RF
When the standard RF approach is not ideal, DC and microwave sources offer specialized capabilities.
Direct Current (DC) PECVD
In a DC system, a constant, high-voltage potential is applied between a cathode and an anode. This creates a continuous "glow discharge" plasma.
This method is simpler and can achieve very high deposition rates. However, it has a significant limitation: it requires a conductive substrate or target to complete the electrical circuit. It is therefore unsuitable for depositing films directly onto insulators like glass or silicon dioxide.
Microwave (MW) PECVD
Microwave PECVD uses electromagnetic waves, typically at 2.45 GHz, to energize the gas. This is often done without internal electrodes, with the microwaves guided into a quartz chamber containing the gases.
This technique creates a very high-density plasma, meaning a higher fraction of the gas is ionized. The result is often higher-quality, denser films deposited at high rates and potentially lower substrate temperatures.
Choosing Your Power Source: A Comparison of Trade-offs
Selecting the right power source involves balancing the requirements of your material, desired film quality, and process complexity.
Substrate Material Compatibility
RF PECVD is the most flexible choice, working equally well on conducting and insulating substrates.
DC PECVD is fundamentally restricted to applications involving conductive substrates.
Microwave PECVD is also highly flexible. Because it can be electrodeless, it is excellent for both conductive and insulating materials and eliminates a potential source of contamination.
Plasma Density and Film Quality
The plasma in RF and DC systems is generally less dense than in a microwave system. This is sufficient for a vast range of applications.
Microwave PECVD generates a uniquely dense and highly dissociated plasma. This is a key advantage for depositing difficult, high-purity materials like synthetic diamond films or high-quality silicon nitride.
Deposition Rate and System Cost
DC PECVD can offer very high deposition rates for specific metal or conductive films and generally relies on simpler, lower-cost power delivery hardware.
RF PECVD provides moderate deposition rates and represents the industry standard for cost and complexity.
Microwave PECVD can also achieve high deposition rates, but the system components (magnetron, waveguides, tuners) can be more complex and expensive to implement and maintain.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your process goal is the ultimate guide for selecting a power source.
- If your primary focus is versatility across all material types: RF PECVD is the established, flexible standard for both conductive and insulating substrates.
- If your primary focus is high-rate deposition on conductive substrates: DC PECVD offers a simpler, often faster, and more cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest film quality and density: Microwave PECVD generates a high-density plasma ideal for demanding applications like diamond films or advanced dielectrics.
Understanding these core differences empowers you to select the power source that directly aligns with your material requirements and desired film outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Power Source | Key Mechanism | Substrate Compatibility | Plasma Density | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF (Standard) | Alternating electric field at 13.56 MHz | Conductive and insulating substrates | Moderate | Versatile thin-film deposition |
| DC | Constant high-voltage potential | Conductive substrates only | Low to moderate | High-rate metal/conductive films |
| Microwave | Electromagnetic waves at 2.45 GHz | Conductive and insulating substrates | High | High-quality films like diamond or silicon nitride |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right PECVD power source for your lab? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you're working with conductive or insulating substrates and aiming for high deposition rates or superior film quality. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored PECVD solutions can enhance your research and production outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is the second benefit of deposition within a discharge in PECVD? Enhance Film Quality with Ion Bombardment
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What role does PECVD play in optical coatings? Essential for Low-Temp, High-Precision Film Deposition
- How is silicon dioxide (SiO2) used in PECVD applications? Key Roles in Microfabrication
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition application? Enable High-Performance Thin Films at Lower Temperatures



















