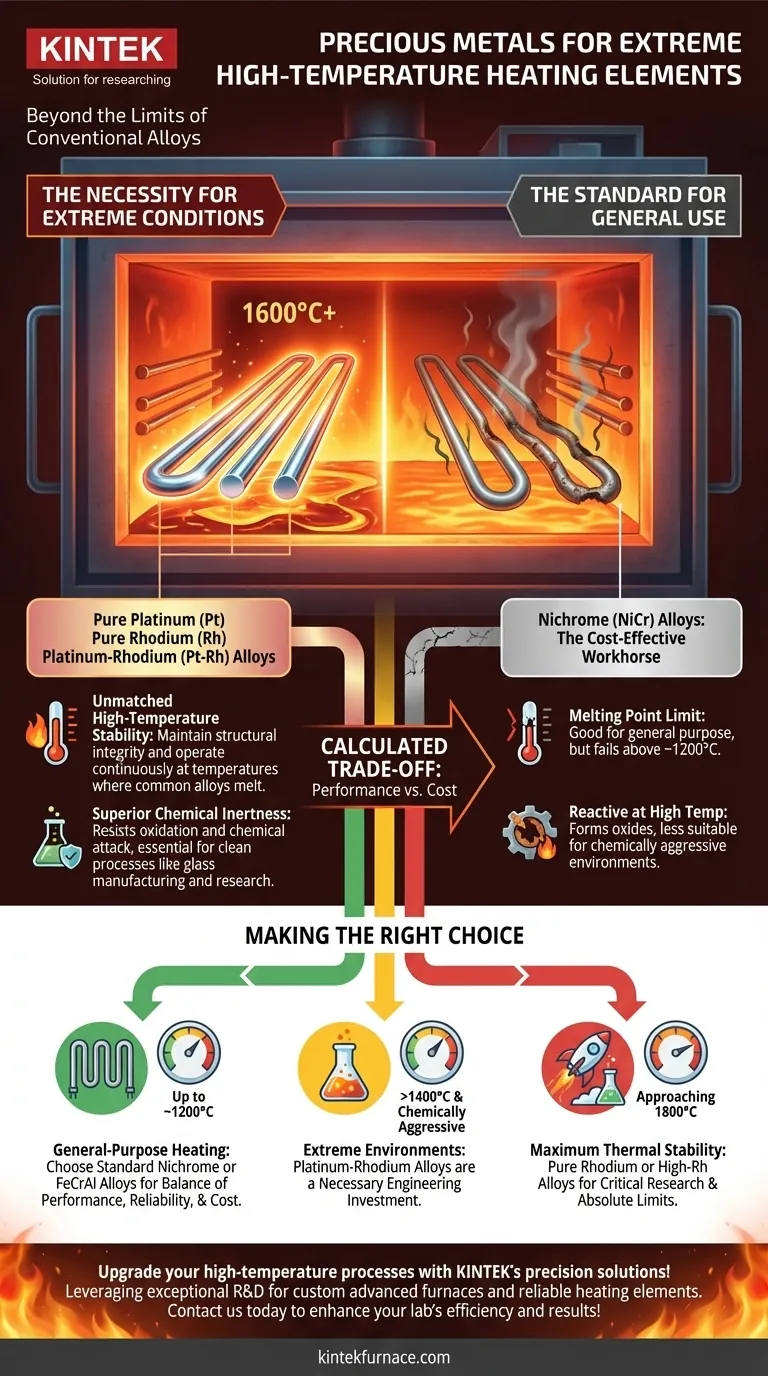
For extreme thermal applications, the primary precious metals used as high-temperature heating elements are pure platinum, pure rhodium, and specialized platinum-rhodium alloys. These materials are selected for their unique ability to maintain stability and resist degradation at temperatures that would cause more common alloys to fail, making them essential for highly specialized industrial and research settings.
While standard nickel-chromium (nichrome) alloys are the workhorse for most heating applications, precious metals are not just a luxury—they are a necessity for environments defined by ultra-high temperatures and chemical inertness. The decision to use them is a calculated trade-off between extreme performance requirements and significant material cost.
The Case for Precious Metal Elements
Precious metal heating elements solve problems that conventional materials cannot. Their use is dictated by environments where reliability and performance under extreme duress are non-negotiable.
Unmatched High-Temperature Stability
The most significant advantage of precious metals is their exceptionally high melting point. Pure rhodium, for example, melts at 1960°C (3560°F), far exceeding the approximate 1400°C (2550°F) melting point of standard nichrome.
This allows for stable, continuous operation in furnaces and processing equipment running at temperatures that are simply out of reach for nickel-based alloys.
Superior Chemical Inertness
At high temperatures, materials become much more reactive. Precious metals, particularly those in the platinum group, exhibit outstanding resistance to oxidation and chemical attack.
This inertness is critical in applications like glass manufacturing, where the element must not contaminate the product, or in laboratory furnaces where a clean, controlled atmosphere is required. Their favorable oxide evaporation rates mean they do not shed material that could compromise a process.
Key Materials and Their Properties
The choice among precious metals depends on the specific temperature and strength requirements.
- Pure Platinum (Pt): A common choice known for its excellent resistance to oxidation and chemical corrosion. It is a benchmark for high-temperature stability.
- Pure Rhodium (Rh): Used for the most demanding applications due to its higher melting point, superior hot strength, and low vapor pressure compared to platinum.
- Platinum-Rhodium (Pt-Rh) Alloys: These are the most frequently used option. Adding rhodium to platinum significantly increases its mechanical strength at high temperatures and raises its melting point, creating a robust element that balances performance and cost more effectively than pure rhodium.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a precious metal element is a decision driven by necessity, not preference. Understanding their limitations is key to making an informed choice.
The Prohibitive Cost Factor
This is the single greatest barrier to their widespread use. Platinum and rhodium are orders of magnitude more expensive than nickel and chromium, restricting their use to applications where no other material will suffice.
The Dominance of Conventional Alloys
For the vast majority of heating needs, nickel-based alloys like nichrome (80% nickel, 20% chromium) are the superior choice.
Nichrome offers a high melting point, excellent resistance to oxidation (it forms a protective, adherent layer of chromium oxide), and a stable electrical resistance over a wide temperature range—all at a fraction of the cost. This makes it the default, cost-effective solution for applications up to about 1200°C.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The selection process is an engineering decision that hinges on the operating environment and budget.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating up to ~1200°C: Standard nichrome or FeCrAl alloys provide the best possible balance of performance, reliability, and cost.
- If your application involves temperatures above 1400°C or a chemically aggressive environment (e.g., molten glass): Precious metal elements, specifically platinum-rhodium alloys, become a necessary engineering investment.
- If you require maximum thermal stability and strength for critical research approaching 1800°C: Pure rhodium or alloys with a high rhodium content are the definitive, albeit most expensive, solution.
Ultimately, selecting the right heating element is a critical decision that balances the absolute limits of material science against economic reality.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Pure Platinum | High oxidation resistance, stable at high temperatures | Laboratory furnaces, glass manufacturing |
| Pure Rhodium | Highest melting point (~1960°C), superior strength | Critical research up to 1800°C |
| Platinum-Rhodium Alloys | Enhanced strength and higher melting point than pure platinum | High-temperature industrial processes |
| Nichrome (Standard Alloy) | Cost-effective, good oxidation resistance up to ~1200°C | General-purpose heating applications |
Upgrade your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's precision solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure your unique experimental needs are met with reliable, high-performance heating elements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability



















