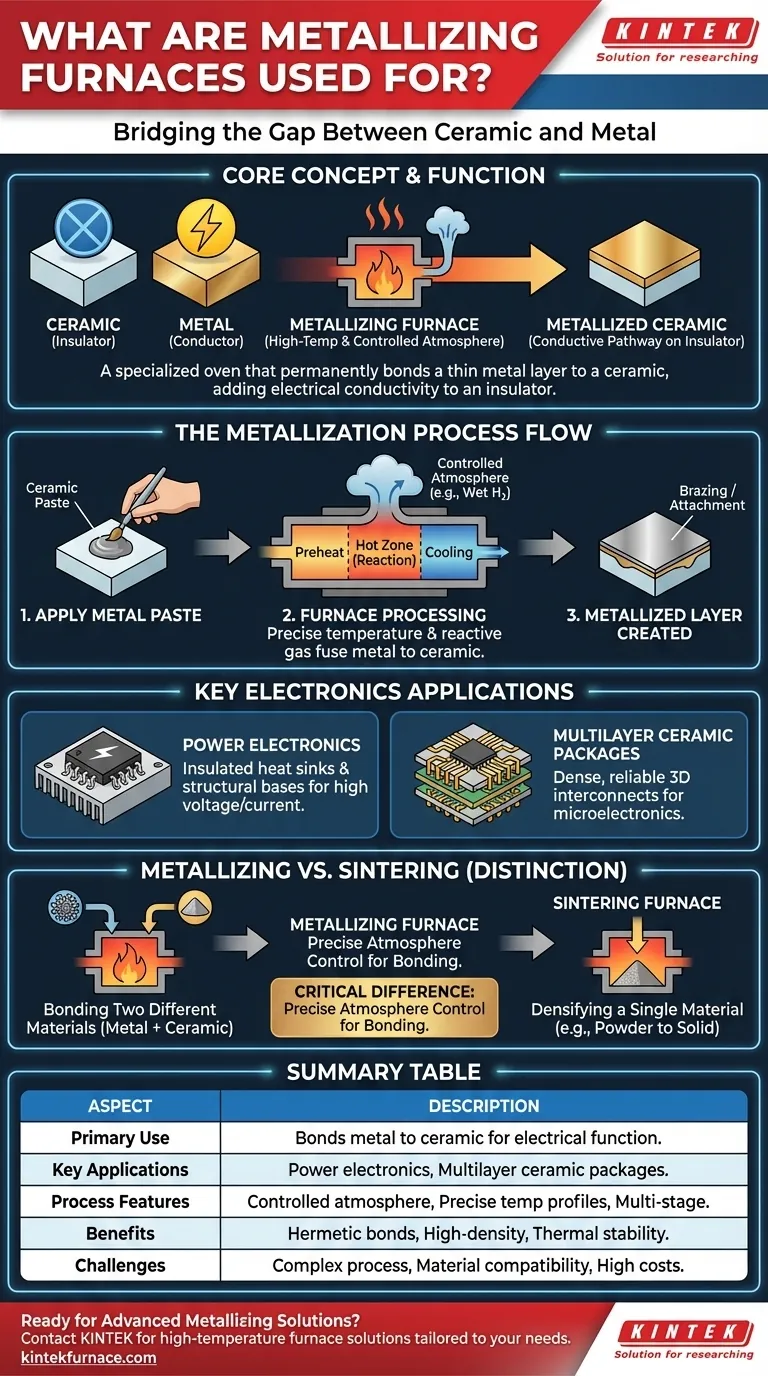
In essence, a metallizing furnace is a specialized high-temperature oven designed to permanently bond a thin layer of metal onto a ceramic surface. This process is critical for manufacturing robust components used in demanding power and electronic applications, such as multilayer ceramic packages. The furnace creates a precisely controlled atmosphere and temperature profile, which is essential for the chemical reactions that fuse the metal and ceramic together.
The core challenge in advanced electronics is joining materials with vastly different properties, like conductive metals and insulating ceramics. A metallizing furnace solves this by creating a strong, hermetic bond, enabling the production of complex components that require the best of both worlds: electrical conductivity and structural insulation.

The Core Function: Bridging the Gap Between Ceramic and Metal
The primary purpose of metallizing a ceramic is to add electrical functionality to a material that is, by its nature, an excellent electrical insulator.
Why Metallize a Ceramic?
Most advanced electronic systems require conductive pathways (circuits) to be placed on stable, insulating substrates. Ceramics offer superior thermal stability and electrical insulation compared to typical plastic circuit boards.
Metallization creates these conductive pathways directly on the ceramic base, allowing it to function as part of an integrated electronic or power component.
The Metallization Process Explained
Think of the process as applying a special "primer" to the ceramic that allows metal to stick. A paste, often containing metals like molybdenum and manganese, is applied to the ceramic part.
The part is then processed through the metallizing furnace. The furnace's high heat and controlled, reactive atmosphere (typically wet hydrogen) cause the metallic particles to fuse into the ceramic's surface structure.
This creates a new, metallized layer that is ready for subsequent processes, such as brazing, where other metal components (like pins or leads) are attached.
Key Applications in Electronics
The references point to two main areas: power electronics and multilayer ceramic packages.
- Power Electronics: These components handle high voltage and current. Metallized ceramics act as insulated heat sinks and structural bases for power transistors and diodes.
- Multilayer Ceramic Packages: These are like complex, three-dimensional circuit boards built from stacked layers of ceramic. Metallization creates the vertical and horizontal connections between layers, allowing for incredibly dense and reliable microelectronics.
How Metallizing Differs from Other Furnaces
While many furnaces use heat, their intended purpose varies dramatically. A metallizing furnace is a highly specialized tool, distinct from more general-purpose equipment.
Metallizing vs. Sintering
The goals are fundamentally different. A sintering furnace is used to densify and harden a single, powdered material (like zirconia for dental crowns) into a solid object. Its main job is to reduce porosity.
A metallizing furnace, by contrast, is designed to bond two different types of material—a metal and a ceramic—together.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere
Unlike a simple oven, a metallizing furnace's most critical feature is its precise atmosphere control. The process will fail without the correct gas mixture.
The reactive gas atmosphere prevents the metal from oxidizing at high temperatures and actively promotes the chemical bonding between the metal paste and the ceramic substrate.
Process Flow and Configuration
As noted in the references, these furnaces are often complex systems with multiple stages:
- Preheat Section: Slowly brings the parts up to temperature to prevent thermal shock and cracking.
- Hot Zone: The main section where the high-heat metallization reaction occurs.
- Cooling Section: Gradually cools the parts under a controlled atmosphere to ensure a stress-free final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
Metallization is a powerful but demanding industrial process with specific challenges.
Process Complexity
Success requires a deep understanding of material science and chemistry. Controlling the furnace's temperature profile and gas atmosphere is a technical discipline in itself. Small deviations can lead to weak bonds or component failure.
Material Compatibility
Not all metals can be bonded to all ceramics. The selection of the metallizing paste, the ceramic material, and the furnace's operational parameters are all interdependent. Extensive testing is often required to develop a reliable process.
Equipment and Operating Cost
From lab-scale units to fully automated production lines, metallizing furnaces represent a significant capital investment. Furthermore, the consumption of specialized gases like hydrogen adds to the operational cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of furnace depends entirely on the material transformation you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is creating a conductive layer on an insulating base: A metallizing furnace is the specific tool required for bonding metal to ceramic.
- If your primary focus is hardening and densifying a single powdered material: A sintering furnace is the correct choice, designed for high-temperature material consolidation.
- If your primary focus is altering the bulk properties of a metal (like softening or hardening): A general-purpose heat-treating furnace for processes like annealing or tempering is what you need.
Ultimately, selecting the right thermal process is about matching the equipment's unique capabilities to your specific material engineering goal.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Permanently bonds a thin metal layer onto ceramic surfaces for electrical functionality. |
| Key Applications | Power electronics (e.g., insulated heat sinks), multilayer ceramic packages (e.g., 3D circuit boards). |
| Process Features | Controlled atmosphere (e.g., wet hydrogen), precise temperature profiles, multi-stage heating and cooling. |
| Benefits | Enables hermetic bonds, supports high-density electronics, provides thermal stability and insulation. |
| Challenges | High process complexity, material compatibility requirements, significant equipment and operating costs. |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with advanced metallizing solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for electronics and power applications. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our metallizing furnaces can drive your innovations forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling



















