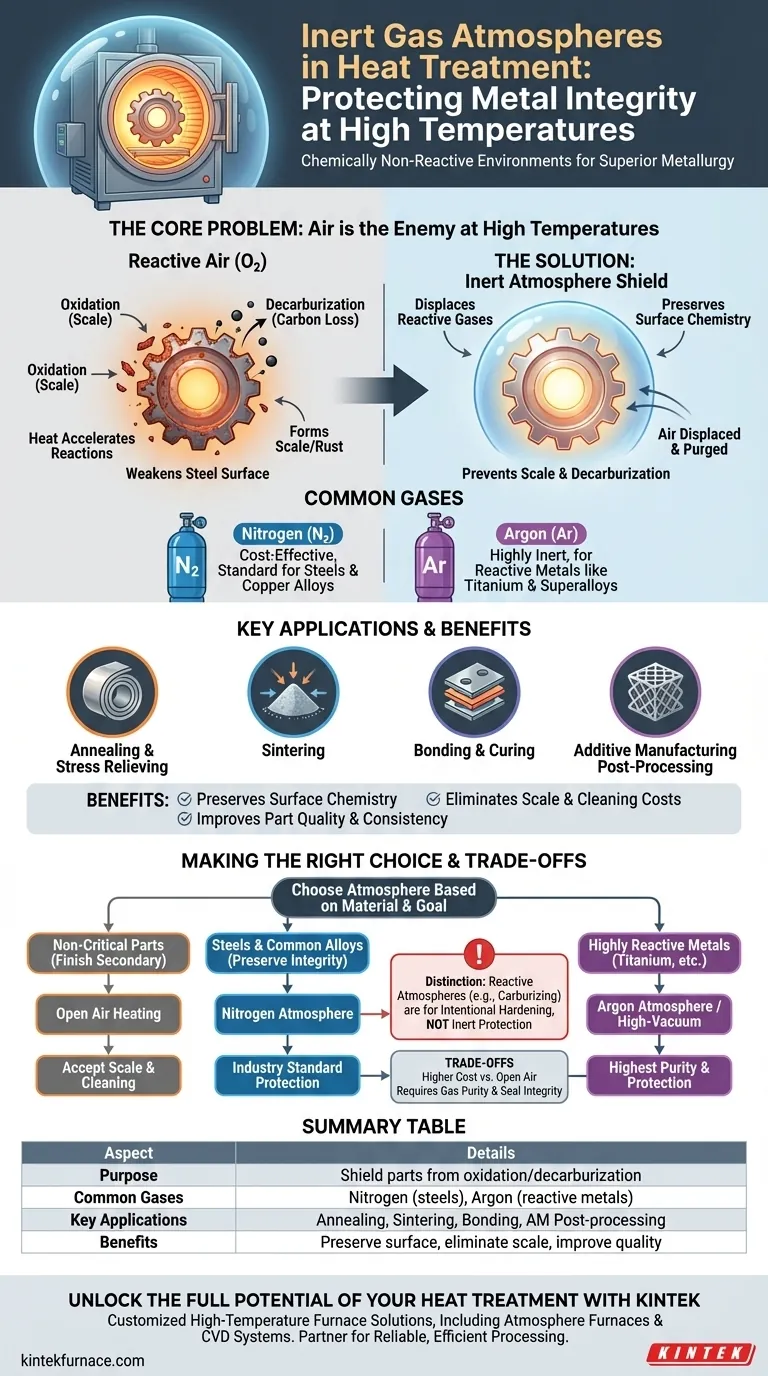
In the world of metallurgy, an inert gas atmosphere is a chemically non-reactive environment used inside a heat treatment furnace. These atmospheres, typically composed of nitrogen or argon, are used to shield metal parts from the damaging effects of air at high temperatures, preventing unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation.
The fundamental purpose of heat treatment is to alter a material's physical properties, not its chemical composition. Inert atmospheres solve the core problem of high-temperature processing: they replace reactive air with a neutral gas, preserving the material's intended surface chemistry and structural integrity.

The Core Problem: Why Air is the Enemy at High Temperatures
Heat is a catalyst. While it is essential for altering a metal's microstructure, it also dramatically accelerates chemical reactions between the metal's surface and the surrounding air.
Understanding Oxidation
At elevated temperatures, the oxygen in the air aggressively reacts with most metals. This process, known as oxidation, forms a layer of metallic oxides, or "scale," on the part's surface.
This scale is essentially a form of rapid, high-temperature rust. It can alter a component's dimensions, ruin its surface finish, and must often be removed through costly secondary operations like sandblasting or acid pickling.
The Threat of Decarburization
For steels, there is another significant threat: decarburization. At high temperatures, the carbon near the surface of the steel can react with oxygen from the air and be "stolen" from the material.
Since carbon is the primary hardening element in steel, its removal leaves a soft, weak outer layer. This compromises the part's wear resistance and fatigue life, making it unsuitable for its intended application.
How Inert Atmospheres Provide a Solution
An inert atmosphere creates a protective shield, isolating the hot component from the reactive gases in the air. This is achieved by displacing the air inside the furnace.
The Principle of Displacement
Before and during the heating cycle, a continuous flow of inert gas is pumped into the sealed furnace chamber. This purges the oxygen and moisture, replacing it with a stable, non-reactive environment that will not interact with the metal surface, even at extreme temperatures.
The result is a bright, clean part that exits the furnace with the same surface chemistry it had when it went in.
Common Gases: Nitrogen vs. Argon
Nitrogen (N2) is the workhorse of inert atmospheres. It is effective for most common metals, including steels and copper alloys, and is relatively inexpensive.
Argon (Ar) is a more truly inert gas and is used for highly reactive materials like titanium, certain stainless steels, and superalloys. It provides a higher degree of protection where even nitrogen could potentially form undesirable nitrides.
Key Applications
Inert atmospheres are critical for any process where surface chemistry and finish are important.
- Annealing & Stress Relieving: Softens metal or removes internal stresses without creating surface scale.
- Sintering: Fuses powdered metal parts together in a process where oxidation would prevent proper bonding.
- Bonding & Curing: Protects a part or an adhesive layer during a thermal curing process.
- Additive Manufacturing: Crucial for post-processing 3D-printed metal parts, such as in Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), to consolidate the part without compromising the material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, using an inert atmosphere involves practical considerations and is not a universal solution.
Cost vs. Benefit
The primary trade-off is cost. Operating a furnace with an inert gas supply is more expensive than heating in open air. However, this cost is often justified by eliminating scrap and the expense of secondary cleaning operations.
Purity is Paramount
The effectiveness of the process depends entirely on the purity of the gas and the integrity of the furnace seal. Any air that leaks into the chamber can contaminate the atmosphere and undermine its protective function.
Inert vs. Reactive Atmospheres
It is critical to distinguish inert atmospheres from reactive atmospheres. Inert gases are used solely for protection. Reactive atmospheres, such as those used for carburizing or nitriding, are intentionally designed to introduce elements like carbon or nitrogen into the metal's surface to harden it.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your choice of furnace atmosphere depends directly on the material, process, and required quality of the final component.
- If your primary focus is on non-critical parts where surface finish is secondary: Heating in open air may be sufficient, but be prepared for scale formation and cleaning.
- If your primary focus is preserving the surface integrity of steels and common alloys: A nitrogen-based inert atmosphere is the industry standard for preventing both oxidation and decarburization.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive metals like titanium or superalloys: A purer argon atmosphere or a high-vacuum furnace is necessary for complete protection.
- If your primary focus is intentionally changing the surface chemistry for hardening: You need a specific reactive atmosphere (e.g., carburizing or nitriding), not an inert one.
By controlling the atmosphere, you gain precise control over the final properties and quality of your heat-treated components.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Shield metal parts from air to prevent oxidation and decarburization during high-temperature processes. |
| Common Gases | Nitrogen (cost-effective for steels, copper alloys), Argon (for reactive metals like titanium, superalloys). |
| Key Applications | Annealing, sintering, bonding, curing, additive manufacturing post-processing. |
| Benefits | Preserves surface chemistry, eliminates scale, reduces secondary cleaning costs, improves part quality. |
| Considerations | Higher cost than open air, requires high gas purity and furnace seal integrity, not for reactive treatments. |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Heat Treatment with KINTEK
Struggling with oxidation, decarburization, or inconsistent results in your metal processing? KINTEK has the solution. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all supported by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Whether you're working with steels, copper alloys, or highly reactive metals like titanium, our inert atmosphere systems ensure your parts emerge bright, clean, and free from defects. Don't let air compromise your quality—partner with KINTEK for reliable, efficient heat treatment.
Contact us today to discuss how our customized furnace solutions can enhance your process and deliver superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity



















