At its core, a heating element is a specialized transducer designed to convert electrical energy into thermal energy. This conversion happens through a physical principle known as Joule heating, where the material's inherent resistance to the flow of electric current generates heat. This simple yet powerful function is the cornerstone of countless devices, from everyday household appliances to critical industrial furnaces.
The true value of a heating element lies not just in its ability to get hot, but in its material science. Its effectiveness is defined by high electrical resistance, the ability to withstand extreme temperatures without degrading, and long-term stability, which collectively determine the efficiency and reliability of any heating system.
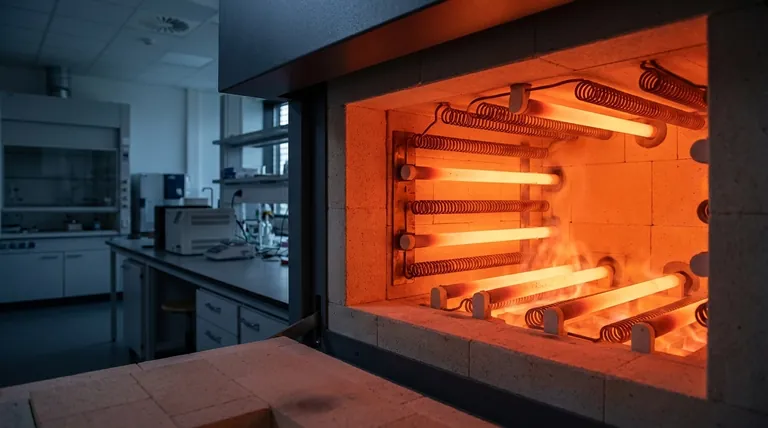
The Fundamental Principle: How Joule Heating Works
At the heart of every heating element is a simple process that turns electricity into controlled, usable heat. Understanding this principle is key to appreciating why different elements are designed for different tasks.
Electricity Meets Resistance
When an electric current flows through a conductor, the moving electrons collide with the atoms of the material. In a highly conductive material like copper, these collisions are minimal, allowing electricity to pass with little energy loss.
The Transfer of Energy
Heating elements, however, are made from materials with high electrical resistance. This high resistance causes frequent and intense collisions between electrons and atoms. Each collision transfers kinetic energy, forcing the material's atoms to vibrate more vigorously.
Heat as a Byproduct
This increased atomic vibration is what we perceive and measure as heat. The more resistance a material has, the more efficiently it converts electrical energy into thermal energy, making it a suitable candidate for a heating element.
Key Characteristics of an Effective Heating Element
Not all resistive materials make good heating elements. They must possess a specific set of properties to perform reliably and safely, especially under demanding conditions.
High Electrical Resistivity
This is the primary property that enables efficient heat generation. The material must actively resist the flow of electricity to convert it into heat effectively.
High-Temperature Tolerance
The element must be able to operate at its target temperature without melting, deforming, or breaking down. Its melting point must be significantly higher than its maximum operating temperature.
Resistance to Oxidation and Corrosion
Heating elements often operate at high temperatures in the presence of air, which promotes oxidation. A protective oxide layer or inherent resistance to chemical degradation is crucial for a long service life.
Stable Performance Over Time
A quality heating element maintains a relatively constant electrical resistance throughout its lifespan. This ensures consistent, predictable, and controllable heat output.
Common Types and Their Applications
Heating elements come in various forms, each engineered for a specific set of applications, environments, and temperature ranges.
Wire and Coil Elements
These are the simplest forms, often made from alloys like Nichrome (nickel-chromium). The wire is typically wound into a coil to fit a large amount of resistive material into a compact space. They are common in devices like toasters and portable space heaters.
Tubular (Sheathed) Elements
These elements consist of a resistive coil housed inside a protective metal tube (the sheath), insulated by a ceramic powder like magnesium oxide. This design protects the element from moisture and mechanical damage, making it ideal for ovens, water heaters, and cooktops.
Cartridge and Band Heaters
Designed for industrial process heating, cartridge heaters are inserted into drilled holes to heat metal blocks (like molds and dies). Band heaters wrap around cylindrical objects like pipes or nozzles on injection molding machines to provide direct, uniform heat.
Advanced Ceramic and Infrared Elements
For very high temperatures or non-contact heating, specialized elements are used. Materials like silicon carbide and molybdenum disilicide can operate in furnaces up to 1800°C. Infrared elements, often using quartz tubes, radiate heat directly onto a target without heating the air in between.
Understanding the Trade-offs in Material Selection
The choice of material is a critical engineering decision that balances cost, performance, and lifespan.
The Cost vs. Performance Balance
Common alloys like Nichrome are the workhorses of the industry. They are cost-effective, durable, and reliable for most applications up to approximately 1200°C (2200°F).
The Need for Extreme Temperatures
For specialized applications like laboratory furnaces or semiconductor processing, temperatures can exceed 1200°C. Here, more exotic and expensive materials like platinum, molybdenum disilicide, or silicon carbide are required due to their superior heat tolerance.
Environmental Demands
The operating environment dictates the material choice. An element submerged in water requires a corrosion-resistant sheath. An element in a vacuum furnace has different requirements than one exposed to open air, which must resist high-temperature oxidation.
Choosing the Right Element for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating element requires matching the component's capabilities to the system's specific demands for heat, durability, and safety.
- If your primary focus is household or commercial appliances: Sheathed tubular elements offer the best balance of safety, durability, and cost-effectiveness for applications like ovens and water heaters.
- If your primary focus is direct, open-air heating: Simple wire or coil elements are highly efficient and economical for devices like toasters and space heaters where the element is exposed.
- If your primary focus is industrial process heating: Cartridge, band, or strip heaters provide the form factor and precision required for manufacturing applications like molding and sealing.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature furnaces (>1200°C): You must use specialized elements made from materials like silicon carbide or molybdenum disilicide to ensure operational stability and safety.
Understanding these fundamental types and trade-offs empowers you to select or design systems that are efficient, reliable, and perfectly suited to their task.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Converts electrical energy into thermal energy via Joule heating |
| Key Properties | High electrical resistivity, high-temperature tolerance, oxidation resistance, stable performance |
| Common Types | Wire/coil, tubular, cartridge/band, ceramic/infrared |
| Applications | Household appliances, industrial processes, high-temperature furnaces |
Need a Custom High-Temperature Furnace Solution? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and reliability with tailored heating elements and systems!
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure



















