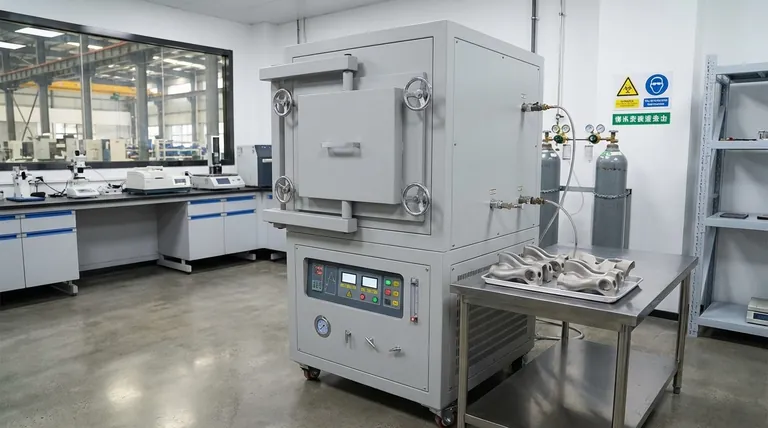
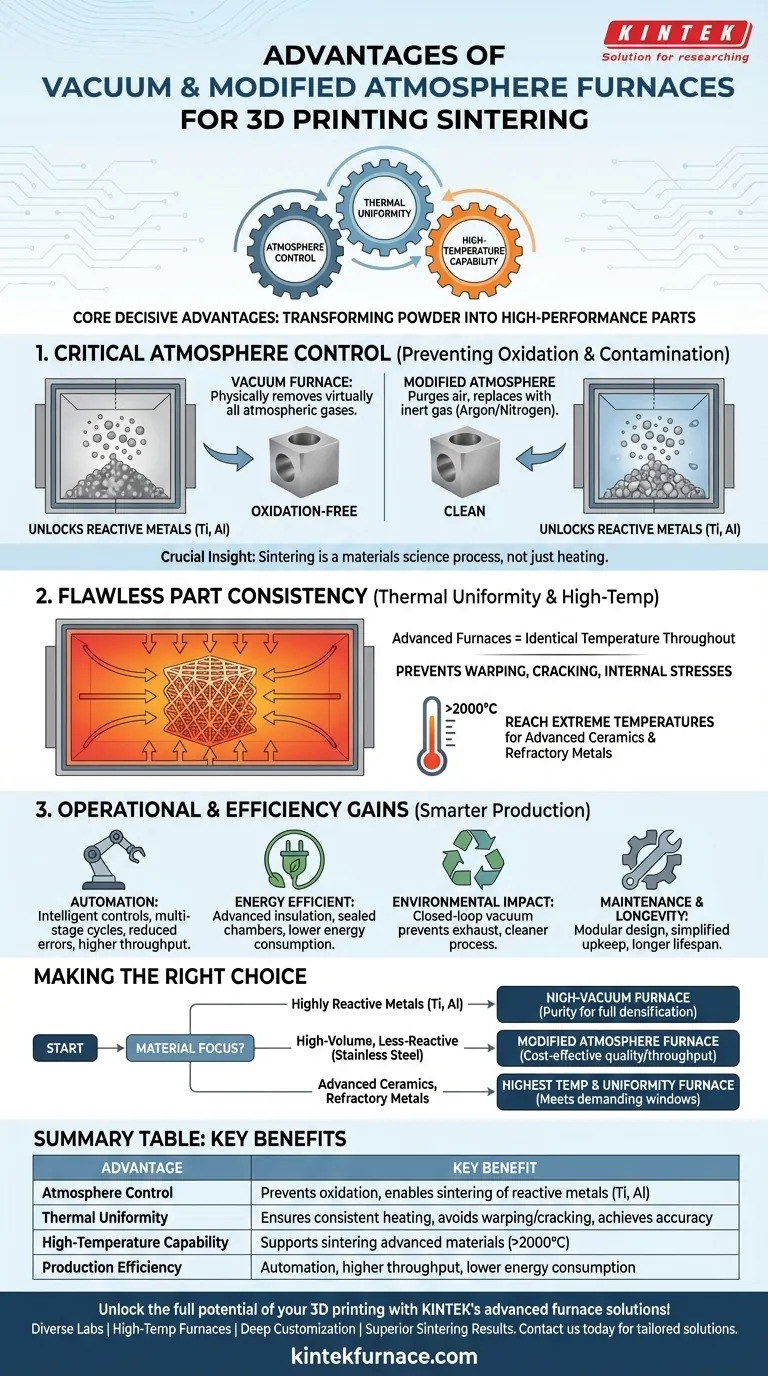
At its core, vacuum and modified atmosphere furnaces offer three decisive advantages for sintering 3D printed parts: absolute control over the processing atmosphere, exceptional thermal uniformity, and the ability to reach the extreme temperatures required for advanced materials. This combination allows for the transformation of metal or ceramic powder into a dense, high-performance solid part, free from the defects and inconsistencies caused by uncontrolled environments.
The crucial insight is that sintering is not merely a heating process; it is a materials science process. A vacuum or modified atmosphere furnace provides a perfectly controlled environment, ensuring the final part achieves its intended metallurgical and mechanical properties without compromise.

The Critical Role of Atmosphere Control
The single greatest challenge in high-temperature sintering is managing the part's interaction with the air around it. Standard atmosphere is reactive and detrimental to most high-performance materials.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
When heated, metal powders react aggressively with oxygen in the air, forming brittle oxides on the particle surfaces. This oxidation prevents the particles from properly bonding, resulting in a weak, porous, and ultimately failed part.
A vacuum furnace solves this by physically removing virtually all atmospheric gases. A modified atmosphere furnace achieves a similar result by purging the chamber of air and replacing it with a stable, non-reactive (inert) gas like argon or nitrogen. Both methods eliminate the risk of oxidation and other forms of atmospheric contamination.
Unlocking Advanced Material Properties
This precise atmospheric control is essential for processing reactive metals like titanium, aluminum, and certain specialty steels. Without a vacuum or inert gas shield, it is impossible to sinter these materials into a dense, high-strength final form suitable for aerospace, medical, or automotive applications.
The controlled environment ensures the material's intrinsic properties are preserved and enhanced during the sintering cycle.
Achieving Flawless Part Consistency
Beyond the atmosphere, the quality of the heat itself is paramount. Inconsistent heating leads to inconsistent parts.
The Importance of Thermal Uniformity
Advanced furnaces are engineered for high thermal uniformity, meaning the temperature is identical throughout the entire processing chamber. This ensures every part of the component—regardless of its geometry or position—is heated and cooled at the exact same rate.
This uniformity prevents internal stresses, warping, or cracking that can occur when different sections of a part heat unevenly. The result is superior dimensional accuracy and predictable, repeatable mechanical performance across an entire production run.
High-Temperature Capability
Many of the most valuable materials in 3D printing, such as technical ceramics and refractory metals, require sintering temperatures well above what conventional ovens can provide.
Vacuum and modified atmosphere furnaces are specifically designed to safely and efficiently reach these extreme temperatures (often exceeding 2000°C), making the production of wear-resistant and high-temperature-resistant components possible.
Understanding the Operational and Efficiency Gains
Modern sintering furnaces provide more than just a controlled environment; they are designed for efficient and reliable industrial production.
Production Efficiency and Automation
Equipped with intelligent control systems, these furnaces can run complex, multi-stage sintering cycles automatically. This automation reduces the need for manual oversight, minimizes the chance of human error, and significantly increases production throughput.
Energy and Environmental Impact
Vacuum furnaces, in particular, are highly efficient. Their advanced insulation and sealed chambers minimize heat loss, reducing overall energy consumption.
Furthermore, the closed-loop vacuum environment prevents the release of exhaust gases, making the process cleaner and often eliminating the need for costly secondary environmental treatments.
Maintenance and System Longevity
Many modern furnaces feature a modular design. This simplifies routine maintenance, troubleshooting, and repairs, leading to less downtime and a longer operational lifespan for the equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The choice between a vacuum and a modified atmosphere furnace depends entirely on the materials you process and your production goals.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive metals (e.g., titanium, aluminum): A high-vacuum furnace is non-negotiable to achieve the purity required for full densification and optimal material properties.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of less-reactive metals (e.g., stainless steel): A modified atmosphere furnace using an inert gas like argon often provides a cost-effective balance of quality control and throughput.
- If your primary focus is advanced ceramics or refractory metals: You must prioritize a furnace with the highest possible temperature range and validated thermal uniformity to meet the material's demanding processing window.
Ultimately, investing in the right furnace technology is what elevates a 3D printed object from a prototype into a reliable, high-performance engineering component.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Prevents oxidation and contamination, enabling sintering of reactive metals like titanium and aluminum |
| Thermal Uniformity | Ensures consistent heating to avoid warping, cracking, and achieve dimensional accuracy |
| High-Temperature Capability | Supports sintering of advanced materials (e.g., ceramics, refractory metals) at temperatures above 2000°C |
| Production Efficiency | Automation reduces errors, increases throughput, and lowers energy consumption |
Unlock the full potential of your 3D printing with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs, delivering superior sintering results for reactive metals, ceramics, and high-volume production. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your material properties and operational efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality



















