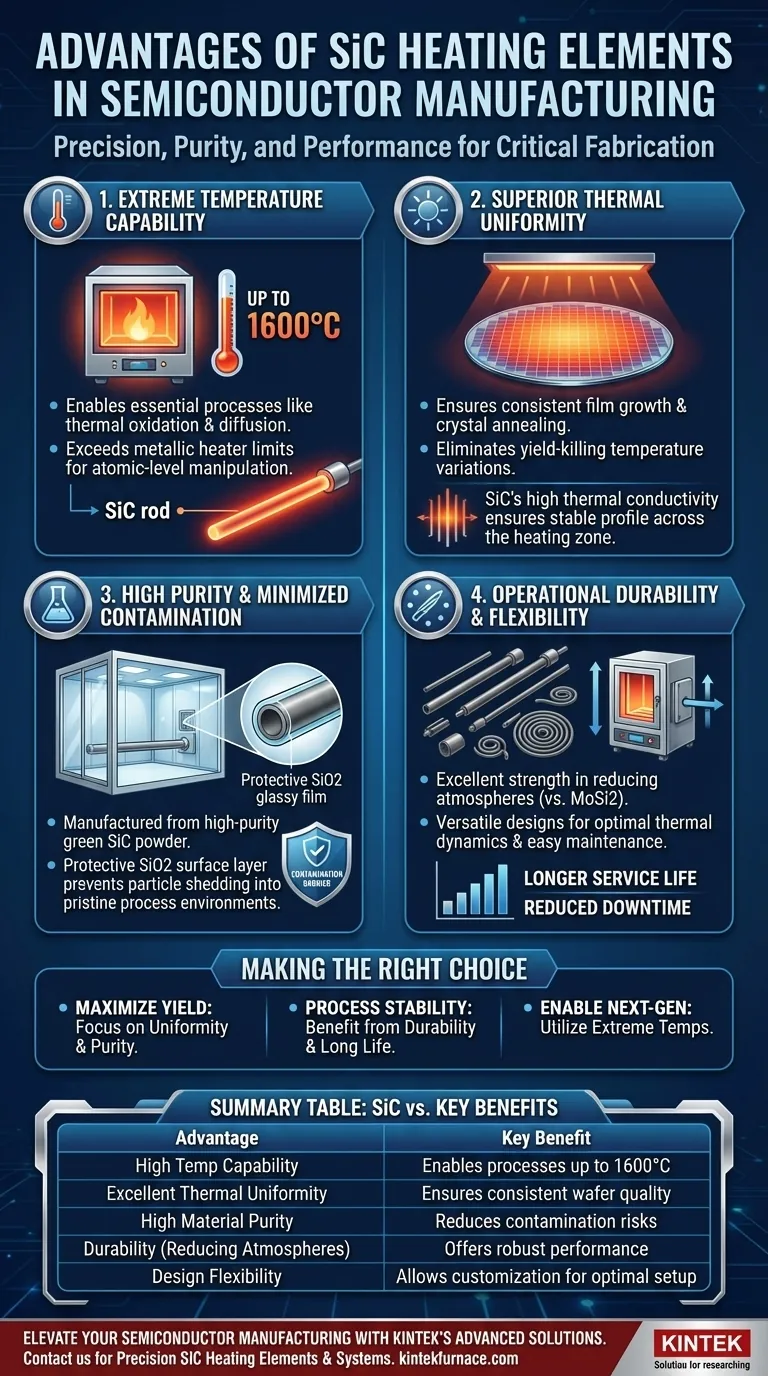
In short, silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements provide the exceptionally high temperatures, thermal uniformity, and material purity required for critical semiconductor fabrication steps. Processes like doping, diffusion, and annealing demand precise thermal control that SiC elements are uniquely positioned to deliver, ensuring consistent quality and high yields for silicon wafers.
The core advantage of silicon carbide is not just its ability to get hot, but its capacity to create an extremely stable, uniform, and clean thermal environment. This transforms the furnace from a simple oven into a precision instrument for manipulating materials at the atomic level.

The Foundation of Precision: Thermal Performance
In semiconductor manufacturing, heat is not a brute force tool; it is a precision scalpel. The electrical properties of a finished chip are a direct result of the thermal profiles it was subjected to during fabrication.
Achieving Extreme Process Temperatures
Many essential semiconductor processes, such as thermal oxidation and dopant diffusion, require temperatures well above 1000°C. SiC elements can reliably operate at up to 1600°C, far exceeding the capabilities of traditional metallic heaters. This high-temperature range enables the necessary atomic motion and chemical reactions within the silicon wafer.
Ensuring Absolute Uniformity
Even minor temperature variations across a single wafer can lead to inconsistent electrical characteristics, rendering entire sections of the wafer useless. SiC’s excellent thermal conductivity ensures a highly uniform temperature profile across the entire heating zone. This stability is critical for achieving consistent film growth, dopant concentration, and crystal annealing, which directly impacts chip performance and yield.
The Purity Imperative: Minimizing Contamination
The smallest foreign particle or chemical impurity can destroy a microchip. The materials used inside a process chamber are a primary concern for contamination control.
Starting with High-Purity Materials
High-quality SiC elements are manufactured from high-purity green silicon carbide powder. This minimizes the risk of the element itself introducing contaminants into the furnace atmosphere, which could then diffuse into the silicon wafers and alter their sensitive electronic properties.
A Stable and Protective Surface
During operation, SiC elements form a protective glassy film of silicon dioxide on their surface. This layer not only enhances the element's antioxidant properties and service life but also acts as a barrier, preventing particles from shedding into the pristine process environment.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
While SiC offers clear advantages, selecting the right heating element requires understanding its specific characteristics in context.
Atmospheric Considerations
SiC elements show excellent strength and durability in reducing atmospheres. This makes them a more robust choice than alternatives like Molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) elements, which can be more susceptible to degradation in such environments. The choice depends entirely on the specific process gas chemistry being used.
Design and Maintenance Flexibility
SiC heaters can be manufactured in various shapes (rods, spirals) and can be mounted vertically or horizontally. This versatility allows engineers to design or retrofit furnaces for optimal thermal dynamics and easy maintenance, minimizing costly equipment downtime.
Element Aging
It is important to note that silicon carbide elements age over their operational life, meaning their electrical resistance gradually increases. This is a predictable characteristic that must be managed by a power control system capable of adjusting its output voltage to maintain consistent power delivery and temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your choice of heating element should be directly tied to your primary process goals within the fabrication plant.
- If your primary focus is maximizing wafer yield: The exceptional thermal uniformity and material purity of SiC are your greatest assets for ensuring consistent results across every wafer.
- If your primary focus is process stability and uptime: The long service life and durability of SiC, particularly in specific chemical atmospheres, reduce maintenance cycles and improve equipment reliability.
- If your primary focus is enabling next-generation processes: The ability of SiC to reach extreme temperatures opens the door for advanced annealing, diffusion, and deposition techniques required for smaller and more complex chip designs.
Ultimately, adopting silicon carbide heating elements is a strategic decision to enhance process control, safeguard against contamination, and ensure the reliability of your most critical thermal operations.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit for Semiconductor Manufacturing |
|---|---|
| High Temperature Capability | Enables processes up to 1600°C, such as thermal oxidation and diffusion |
| Excellent Thermal Uniformity | Ensures consistent wafer quality and high yields by minimizing temperature variations |
| High Material Purity | Reduces contamination risks for sensitive electronic properties |
| Durability in Reducing Atmospheres | Offers robust performance and longer service life in specific process gases |
| Design Flexibility | Allows customization for optimal furnace setup and easy maintenance |
Elevate your semiconductor manufacturing with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with precision heating elements and systems tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our SiC heating elements can enhance your process control, boost yields, and ensure reliability in critical thermal operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan



















