In short, Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements offer significant advantages over traditional materials like nickel-chromium alloys. They operate at much higher temperatures, heat up faster, use less energy, and last substantially longer. This combination leads to improved process efficiency and a lower total cost of ownership over the element's lifespan.
The decision to use SiC heating elements is about more than just a component upgrade. It represents a strategic shift towards precision thermal management, prioritizing long-term operational efficiency, process speed, and reliability over minimal upfront cost.
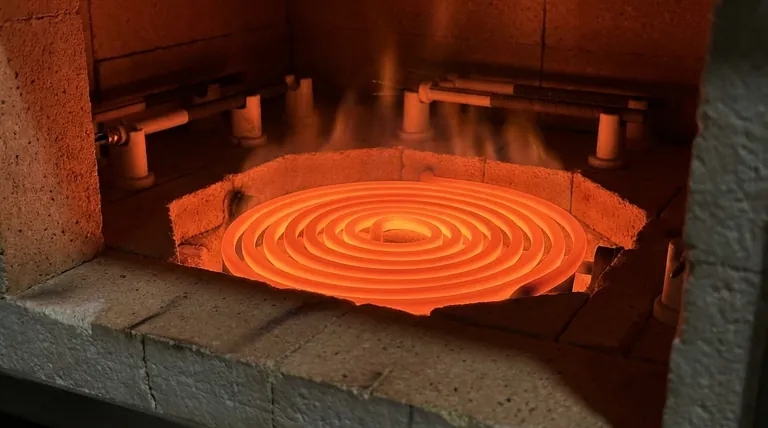

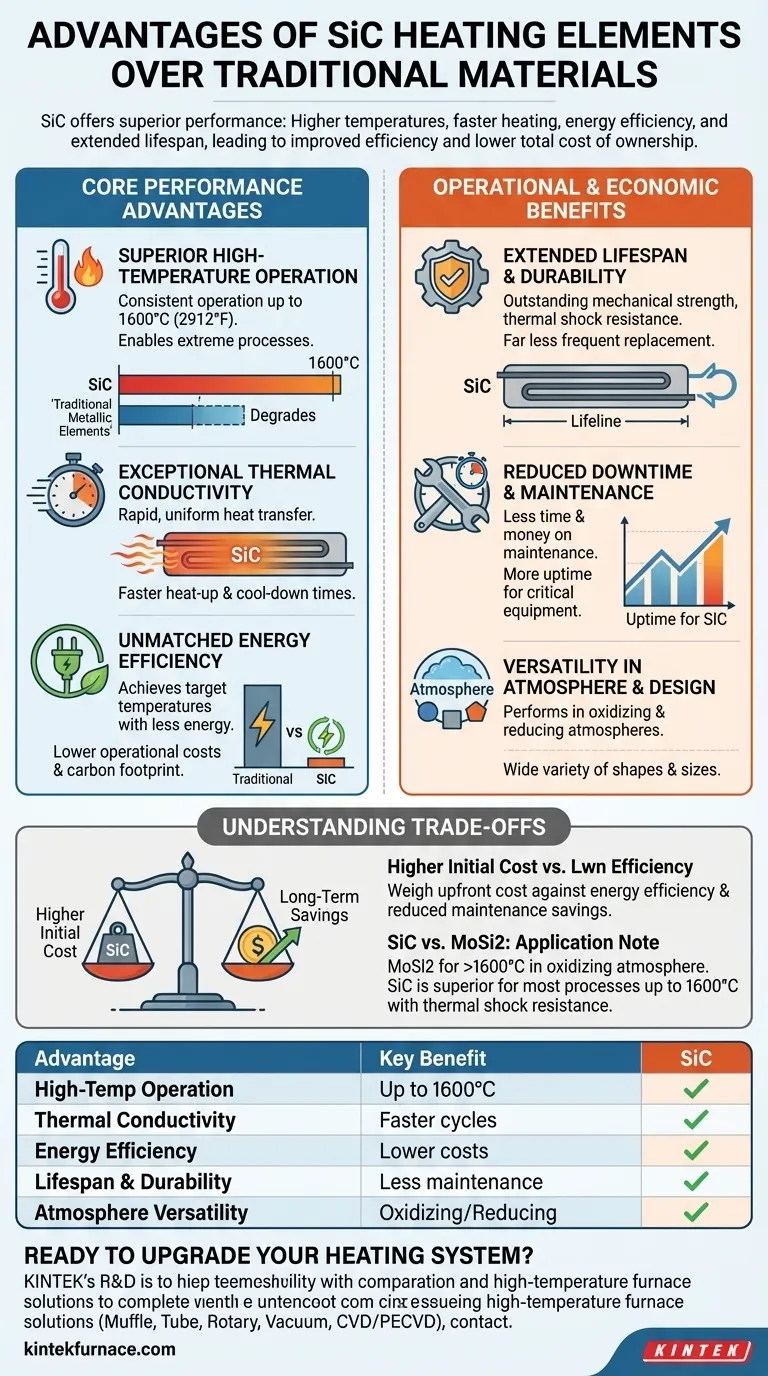
The Core Performance Advantages
The primary benefits of SiC elements stem from their fundamental material properties. These properties translate directly into superior performance in demanding industrial heating applications.
Superior High-Temperature Operation
Unlike traditional metallic elements that degrade quickly at extreme temperatures, SiC elements are engineered to thrive. They can operate consistently at temperatures up to 1600°C (2912°F), enabling processes that are impossible for many conventional materials.
Exceptional Thermal Conductivity
SiC exhibits outstanding thermal conductivity. This allows the elements to transfer heat rapidly and uniformly to the target environment, resulting in faster heat-up and cool-down times. This is a critical advantage in applications requiring quick cycles, such as batch processing in the ceramics and electronics industries.
Unmatched Energy Efficiency
SiC elements are highly efficient, achieving target temperatures with significantly less energy input compared to older technologies. This reduced energy consumption directly translates to lower operational costs and a smaller carbon footprint, a key consideration for modern industrial facilities.
Operational and Economic Benefits
Beyond raw performance, SiC elements provide tangible benefits that impact maintenance schedules, operational uptime, and overall economic return.
Extended Lifespan and Durability
Engineered for durability, SiC elements possess outstanding mechanical strength and resistance to thermal shock. They are far less prone to breakage during operation or handling, which dramatically reduces the frequency of replacement.
Reduced Downtime and Maintenance
The long operational lifespan of SiC elements means less time and money spent on maintenance. Fewer replacements lead to more uptime for critical equipment like furnaces and kilns, boosting overall productivity and making them a more economical choice in the long run.
Versatility in Atmosphere and Design
SiC performs well in both oxidizing and reducing atmospheres, offering a level of flexibility that many other high-temperature materials lack. Furthermore, they can be manufactured in a wide variety of shapes and sizes, allowing for customized solutions tailored to specific furnace or kiln designs.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, SiC is not the universal solution for every heating application. Understanding its context and limitations is key to making an informed decision.
The Initial Cost Consideration
The primary trade-off is often upfront cost. SiC heating elements typically have a higher initial purchase price than traditional nickel-chromium alloy elements. This cost must be weighed against the long-term savings from energy efficiency, reduced maintenance, and longer lifespan.
SiC vs. MoSi2: A Note on Application
For the most extreme temperature applications, another material comes into play: Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2). MoSi2 elements can operate at even higher temperatures (up to 1800°C) but require an oxidizing atmosphere to form a protective silica layer.
SiC offers a more versatile profile, with excellent thermal shock resistance and suitability for a broader range of atmospheres, making it the superior choice for many processes operating up to its 1600°C limit.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific operational goals should dictate your material selection.
- If your primary focus is rapid production cycles: SiC's fast heating and cooling capabilities are your greatest advantage for increasing throughput.
- If your primary focus is long-term cost reduction: The combination of energy efficiency and extended lifespan makes SiC a strong investment despite higher initial costs.
- If your primary focus is process reliability at high temperatures: The durability, thermal stability, and even heat distribution of SiC ensure consistent and repeatable results.
- If your primary focus is operating above 1600°C in an oxidizing atmosphere: You should evaluate Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) as a potentially more suitable alternative.
Ultimately, choosing the right heating element is about aligning the material's strengths with your most critical process needs.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| High-Temperature Operation | Up to 1600°C, enabling extreme processes |
| Thermal Conductivity | Faster heat-up and cool-down times |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower operational costs and reduced energy use |
| Lifespan and Durability | Less frequent replacements and reduced maintenance |
| Atmosphere Versatility | Works in oxidizing and reducing environments |
Ready to upgrade your heating system? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your process efficiency and reduce costs with tailored SiC heating solutions! Get in touch now
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance



















