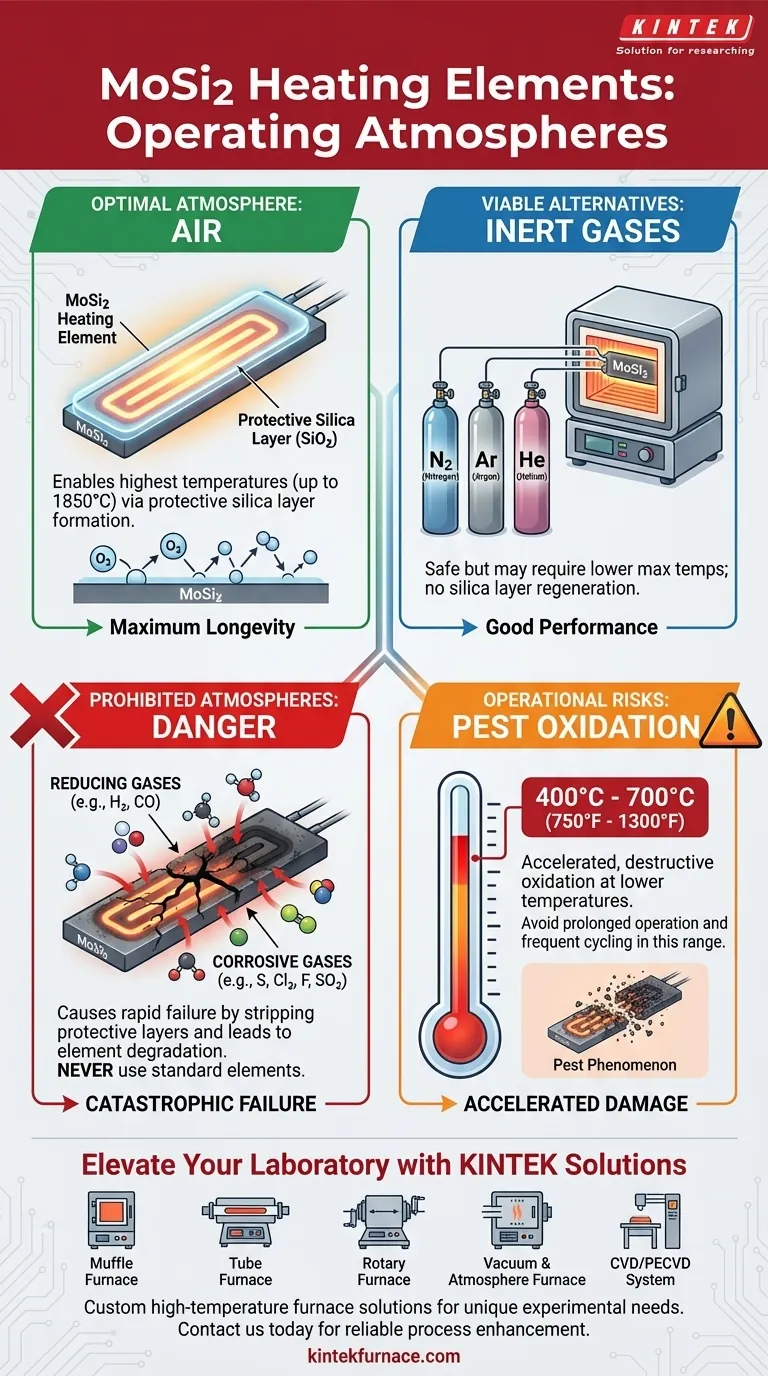
In short, Molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements can be safely operated in air and pure inert gas atmospheres like nitrogen, argon, and helium. Air is the preferred atmosphere as it allows the elements to reach their highest possible operating temperatures by forming a protective surface layer.
The choice of atmosphere is not just a matter of compatibility; it directly dictates the maximum temperature, performance, and lifespan of your MoSi2 elements. While air is optimal, certain active or reducing gases can be rapidly destructive.

How Atmosphere Dictates Performance
Understanding why certain atmospheres are suitable and others are not comes down to the fundamental chemistry of the heating element itself.
The Critical Role of the Silica Layer
At high temperatures, the silicon in the MoSi2 element reacts with oxygen to form a thin, self-healing, and non-conductive protective layer of silicon dioxide (SiO₂), or quartz glass. This passive layer is what protects the underlying element from further oxidation and allows it to function at extreme temperatures.
Optimal Atmosphere: Air
Air is the ideal operating environment for MoSi2 elements. The presence of oxygen allows the protective silica layer to continuously form and regenerate, ensuring maximum element longevity and enabling the highest possible surface temperatures, which can reach up to 1850°C.
Viable Alternative: Inert Gases
MoSi2 elements can be used successfully in inert atmospheres like Nitrogen (N₂), Argon (Ar), and Helium (He). Because these gases are non-reactive, they will not damage the element. However, they do not provide the oxygen needed to regenerate the protective silica layer, which may require you to operate at a slightly lower maximum temperature than in air.
Prohibited Atmospheres and Operational Risks
Using an incorrect atmosphere is the fastest way to cause catastrophic element failure. You must also be aware of specific temperature-related risks.
The Danger of Reducing Atmospheres
You should never operate standard MoSi2 elements in a reducing atmosphere like Hydrogen (H₂). These environments actively prevent the formation of the protective silica layer and can strip away any existing layer, leading to rapid element deterioration and failure. The same applies to atmospheres containing carbon monoxide or cracked ammonia.
Corrosive Gases to Avoid
Active chemical gases will attack the element material directly. Avoid any process atmospheres containing Sulfur (S), Chlorine (Cl₂), or Fluorine (F) compounds, as they are highly corrosive to MoSi2 elements.
The "Pest" Oxidation Risk
MoSi2 elements are vulnerable to a phenomenon known as "pest oxidation" or "pesting." This is a form of accelerated, destructive oxidation that occurs at lower temperatures, specifically between 400°C and 700°C (750°F and 1300°F). Prolonged operation in this temperature range can cause the element to disintegrate. For this reason, you should avoid frequent on/off cycling and move through this temperature range as quickly as possible.
Contamination Hazards
The elements are also susceptible to contamination from materials inside the furnace. Be cautious with foreign substances, such as low-melting point glasses, volatile paints, or improper furnace insulation, as they can react with and degrade the element surface.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your process requirements will determine the correct path forward for your furnace design and operation.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature and longevity: Operate the elements in an air atmosphere.
- If your process requires a non-oxidizing environment: Use a high-purity inert gas like Argon (Ar) or Nitrogen (N₂), but consult the manufacturer for specific de-rated temperature limits.
- If your process involves reducing or active gases (H₂, Cl₂, SO₂): Do not use standard MoSi2 elements. You must select an alternative heating element technology designed for those specific conditions.
Making an informed decision on your furnace atmosphere is the key to ensuring operational reliability and protecting your equipment investment.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Suitability | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Air | Optimal | Enables highest temperatures (up to 1850°C) via protective silica layer formation. |
| Inert Gases (N₂, Ar, He) | Viable | Safe but may require lower max temps; no silica layer regeneration. |
| Reducing Gases (H₂) | Prohibited | Causes rapid failure by stripping protective layers. |
| Corrosive Gases (S, Cl₂, F) | Prohibited | Highly corrosive; leads to element degradation. |
Elevate your laboratory's heating efficiency with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your process reliability and protect your investment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability



















