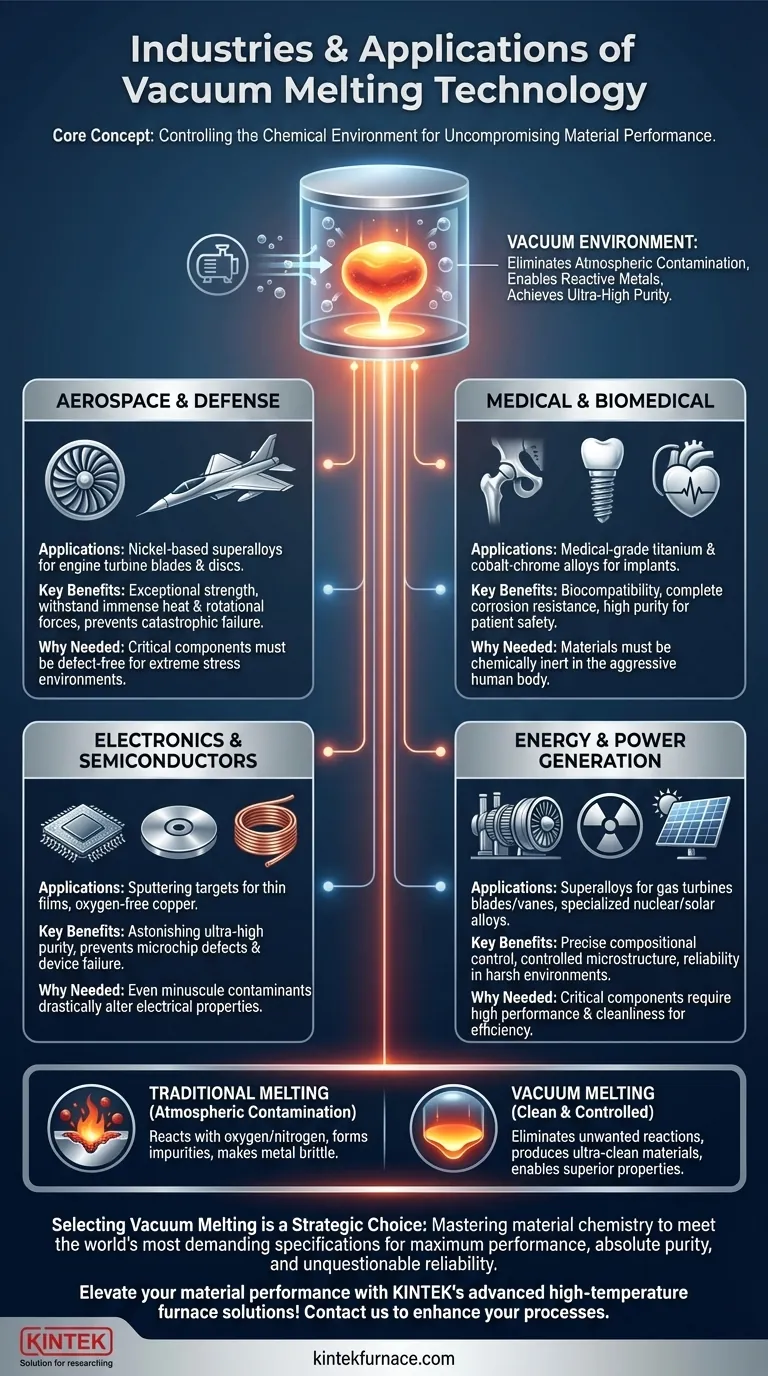
At its core, vacuum melting technology is the go-to process for industries where material failure is simply not an option. It is most commonly applied in the aerospace, medical, electronics, and high-performance energy sectors. These industries rely on it to produce metals and alloys with exceptional purity, strength, and specific properties that cannot be achieved through conventional melting in open air.
The crucial takeaway is that vacuum melting isn't just about melting metal; it's about controlling the entire chemical environment. By removing air, the process eliminates unwanted reactions with oxygen and nitrogen, producing ultra-clean materials essential for the most demanding and critical applications.

Why Traditional Melting Isn't Enough
To understand why certain industries depend on vacuum melting, you must first recognize the limitations of melting metals in the presence of air.
The Problem of Atmospheric Contamination
When metals are melted in open air, they react with oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen. These reactions form oxides and nitrides, which introduce impurities and inclusions into the final material.
These contaminants can make the metal brittle, reduce its fatigue life, and compromise its structural integrity.
The Challenge with Reactive Metals
Metals like titanium and zirconium are highly reactive, especially at high temperatures. Melting them in the open air is impossible, as they would be immediately ruined by contamination.
Vacuum melting provides the inert environment necessary to process these metals and their alloys effectively.
The Need for Ultra-High Purity
Some applications demand a level of purity that standard processes cannot deliver. Even minuscule amounts of contaminants can drastically alter a material's electrical, chemical, or biological properties.
This is where vacuum melting, particularly processes like Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) and Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR), becomes essential for refining metals to the highest possible standard.
Core Applications Driven by Uncompromising Quality
The decision to use vacuum melting is driven by the need for materials that perform flawlessly under extreme stress, in sterile environments, or with precise electrical characteristics.
Aerospace and Defense
This is the largest and most critical user of vacuum-melted materials. The technology is used to create nickel-based superalloys for jet engine turbine blades and discs.
These components must withstand immense temperatures and rotational forces. The purity and controlled microstructure from vacuum melting prevent catastrophic engine failure.
Medical and Biomedical
The human body is an aggressive environment, and any material implanted within it must be completely inert and biocompatible. Vacuum melting is used to produce medical-grade titanium and cobalt-chrome alloys.
These materials are used for joint replacements (hips, knees), dental implants, and pacemaker casings, where corrosion resistance and purity are paramount for patient safety.
Electronics and Semiconductors
The electronics industry requires materials of astonishing purity. Vacuum melting is used to create sputtering targets, which are used to deposit thin films of material onto semiconductor wafers.
Any impurity in these targets would be transferred to the microchip, causing defects and device failure. The technology also produces the ultra-pure, oxygen-free copper needed for high-end electronic components.
Energy and Power Generation
Similar to aerospace, industrial gas turbines for power generation rely on vacuum-melted superalloys for their blades and vanes.
Additionally, specialized alloys for the nuclear and solar industries require the precise compositional control and cleanliness that only vacuum processing can provide.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its benefits are clear, vacuum melting is a specialized process with significant considerations that make it unsuitable for all applications.
Significant Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are expensive to build, operate, and maintain. The process requires sophisticated monitoring and control systems, adding to the overall complexity.
This high cost means the technology is reserved for applications where the performance benefits justify the investment.
Slower Production Cycles
Creating a vacuum, running a melt cycle, and cooling the material under controlled conditions is a time-consuming batch process. It cannot match the high-volume throughput of conventional steel mills or foundries.
Not a Universal Solution
For countless everyday applications, such as structural steel for construction or standard cast iron parts, the properties achieved by conventional melting are more than adequate.
Using vacuum melting for these materials would be extreme overkill, providing no practical benefit while dramatically increasing cost and production time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting vacuum melting is a strategic choice driven entirely by the final performance requirements of your component.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance under extreme conditions: Vacuum melting is essential for creating the defect-free superalloys and reactive metal alloys required for aerospace and industrial turbines.
- If your primary focus is absolute material purity: This technology is the only viable path to meet the stringent demands of semiconductors, medical implants, and laboratory-grade materials.
- If your primary focus is unquestionable reliability and safety: The reduction of gas-related defects and contaminants provided by vacuum melting is a non-negotiable requirement for critical components where failure has severe consequences.
Ultimately, adopting vacuum melting is a decision to master material chemistry, ensuring your final components can meet the world's most demanding specifications.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Defense | Jet engine turbine blades, superalloys | High strength, prevents failure under extreme stress |
| Medical & Biomedical | Joint replacements, dental implants, pacemaker casings | Biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, purity for safety |
| Electronics & Semiconductors | Sputtering targets, oxygen-free copper | Ultra-high purity, prevents defects in microchips |
| Energy & Power Generation | Gas turbine blades, nuclear/solar alloys | Controlled microstructure, reliability in harsh environments |
Elevate your material performance with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Whether you're in aerospace, medical, electronics, or energy, our expertise in vacuum melting technology—including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, CVD/PECVD Systems, and more—ensures precise control and ultra-pure results. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Don't let contamination compromise your critical applications—contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your processes and deliver reliable, high-quality outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications



















