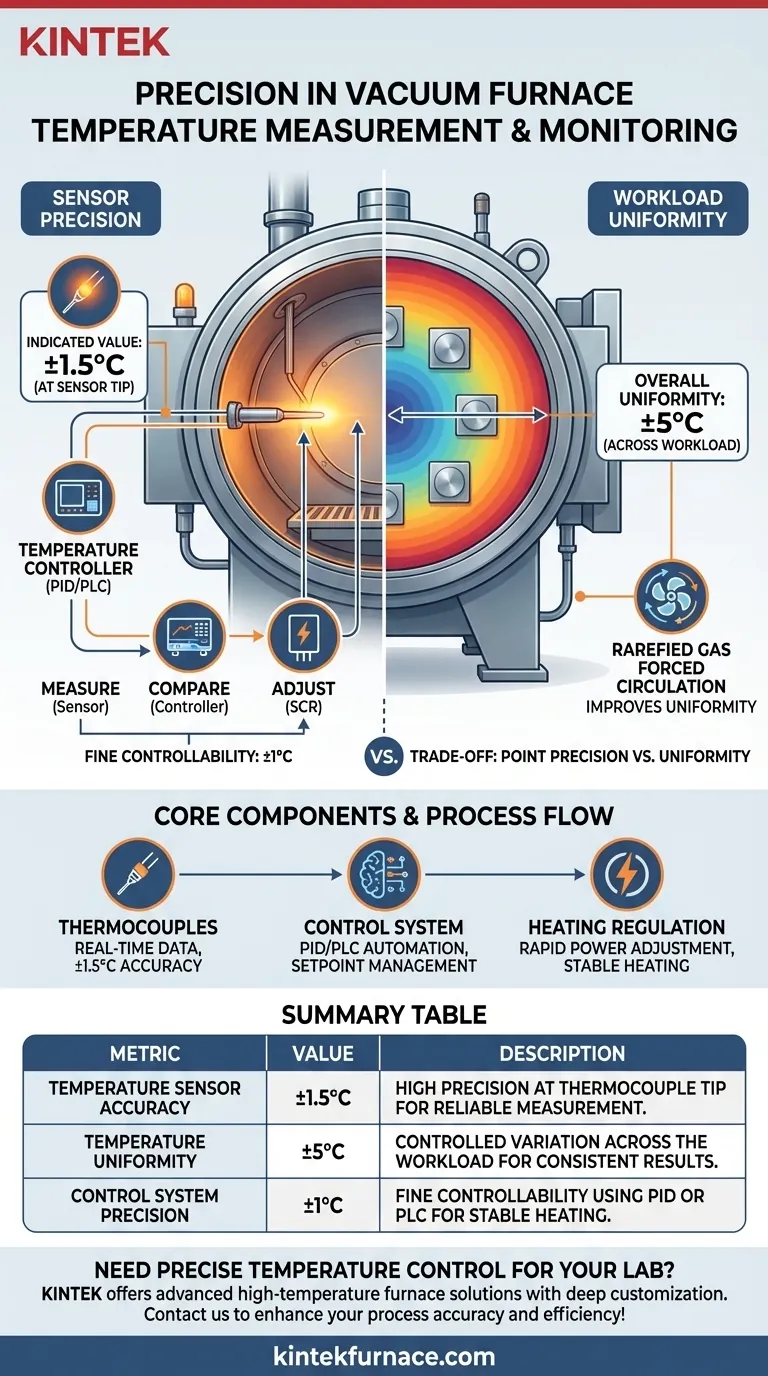
In modern vacuum furnaces, temperature measurement is remarkably precise, with the indicated value from a thermocouple sensor typically achieving an accuracy of ±1.5°C. However, the more critical metric for process outcomes—overall temperature uniformity across the entire workpiece—is generally controlled to within ±5°C, especially when using specialized techniques to distribute heat.
The precision of a vacuum furnace is not a single number. It is a tale of two metrics: the high accuracy of the temperature sensor itself, and the practical uniformity of heat across the entire internal chamber, which is the true measure of a furnace's performance.

The Core Components of Temperature Control
Achieving high precision requires a sophisticated system where multiple components work in concert. The final temperature accuracy is a product of the sensor, the controller, and the heating element regulation.
The Role of Thermocouples
A thermocouple is the primary sensor used for temperature measurement. These robust sensors can be strategically placed throughout the heating zone, often in direct contact with or near the workpiece, to provide real-time temperature data.
The signal from the thermocouple to the control system is highly accurate, enabling the furnace's indicated temperature to be reliable to within ±1.5°C of the actual temperature at the sensor's tip.
The Control System (The "Brain")
The thermocouple sends its signal to a temperature controller, which acts as the brain of the operation. This controller continuously compares the measured temperature to the desired setpoint programmed by the operator.
Modern furnaces use advanced control methods like PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) programmable control or PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) automation. These systems allow for precise management of not only the final temperature but also the rate of heating (ramp rate), ensuring materials are processed according to exact specifications. Controllability can be as fine as ±1°C.
The Heating System Regulation
When the controller detects a deviation from the setpoint, it adjusts the power delivered to the furnace's heating elements. This is often managed by a Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR) Power Supply, which can make minute, rapid adjustments to the electrical output.
This closed-loop system of measure > compare > adjust happens many times per second, resulting in exceptionally stable and fine temperature control.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Precision vs. Uniformity
While the sensor's precision is high, it only represents the temperature at a single point. For engineers and materials scientists, the more important metric is temperature uniformity, which describes the maximum temperature variation across the entire heated zone or workload.
Point Precision at the Sensor
As established, the thermocouple reading itself is extremely accurate (±1.5°C). This is the number you will see on the furnace display and in data logs. It is a reliable indicator of the temperature at one specific location.
Uniformity Across the Workload
In the vacuum environment, heat transfer primarily occurs through radiation, which can lead to hot and cold spots. Because of this, the temperature across a large part or a full batch of smaller parts may not be perfectly even.
A high-quality vacuum furnace is engineered to minimize this variation. A typical specification for temperature uniformity is ±5°C, meaning no part of the workload will be more than 10°C different from another part (e.g., if the setpoint is 1000°C, the entire zone will be between 995°C and 1005°C).
Improving Uniformity with Gas Circulation
To combat uneven heating, some processes use rarefied gas forced circulation. By introducing a small amount of inert gas (like argon or nitrogen) and circulating it with a fan, the furnace adds convection to the heat transfer process.
This actively moves heat around the chamber, significantly improving temperature uniformity and ensuring it remains within that critical ±5°C range, even for complex part geometries. The trade-off is operating at a slightly lower vacuum level.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Understanding the difference between measurement precision and thermal uniformity is critical for achieving your desired material outcomes.
- If your primary focus is process validation and reporting: Rely on the high precision of the thermocouple's indicated temperature (typically ±1.5°C) for your data logs and quality reports.
- If your primary focus is ensuring consistent material properties: Pay close attention to the furnace's specified temperature uniformity (often ±5°C), as this reflects the real-world temperature variation the material will experience.
- If your primary focus is processing large or complex parts: Prioritize furnaces that offer features like multi-zone heat control or forced gas circulation to actively manage heat distribution and guarantee uniformity.
Ultimately, mastering your thermal process depends on knowing which of these metrics matters most for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Metric | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Sensor Accuracy | ±1.5°C | High precision at the thermocouple tip for reliable measurement. |
| Temperature Uniformity | ±5°C | Controlled variation across the workload for consistent results. |
| Control System Precision | ±1°C | Fine controllability using PID or PLC for stable heating. |
Need precise temperature control for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your process accuracy and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion



















