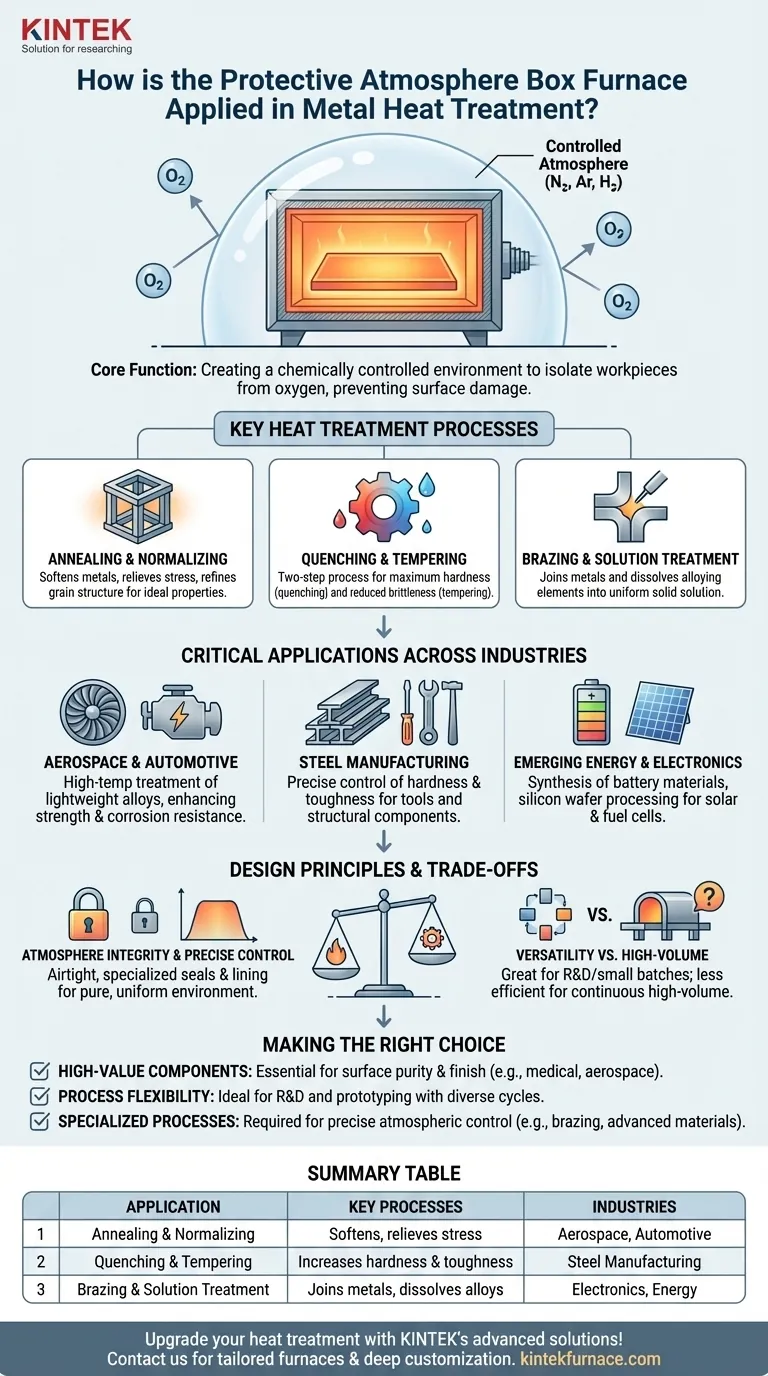
At its core, a protective atmosphere box furnace is used to perform critical heat treatment processes—like annealing, quenching, and tempering—on metals without causing undesirable surface reactions such as oxidation and scaling. By precisely controlling the gas environment inside the chamber, the furnace ensures the material’s surface integrity and chemical composition are preserved, allowing engineers to achieve specific, repeatable mechanical properties.
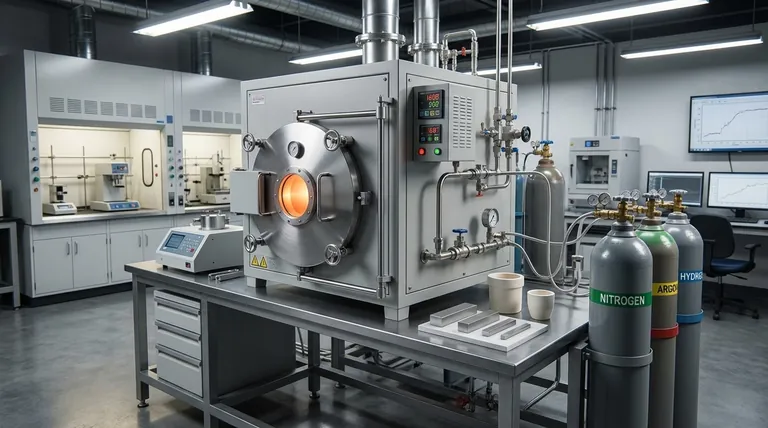
The true value of a protective atmosphere box furnace isn't just its ability to heat metal. Its primary function is to create a chemically controlled environment that isolates the workpiece from oxygen, enabling heat treatments that would otherwise be impossible without damaging the material's surface.

The Fundamental Role: Preventing Surface Reactions
When metals are heated to high temperatures in open air, they react with oxygen. This is a fundamental challenge in metallurgy that a protective atmosphere furnace is specifically designed to solve.
Eliminating Oxidation and Decarburization
The most common reaction is oxidation, which forms a layer of scale on the metal's surface. This scale must often be removed through costly secondary processes. For steels, another risk is decarburization, where carbon is lost from the surface, making it softer and weaker. A protective atmosphere prevents these destructive reactions.
Preserving Material Integrity
By flooding the heating chamber with a specific gas or gas mixture (like nitrogen, argon, or hydrogen), oxygen is displaced. This ensures the workpiece's surface chemistry remains unchanged throughout the heating and cooling cycle, which is critical for high-performance and high-purity materials.
Key Heat Treatment Processes Performed
The furnace's versatility allows it to handle a wide range of thermal processes required by different materials and applications.
Annealing and Normalizing
These processes are used to soften metals, relieve internal stresses from prior manufacturing steps, and refine the grain structure. Materials like titanium alloys and stainless steel are often annealed in a protective atmosphere to achieve ideal properties without surface contamination.
Quenching and Tempering
This two-step process is fundamental for steel. Quenching involves rapid cooling from a high temperature to achieve maximum hardness, while tempering is a subsequent, lower-temperature heating that reduces brittleness and improves toughness.
Brazing and Solution Treatment
The controlled environment is also ideal for high-strength brazing, where two metal pieces are joined using a filler metal. For certain alloys, solution treatment is performed to dissolve alloying elements into a uniform solid solution before subsequent hardening.
Critical Applications Across Industries
The precise control offered by these furnaces makes them indispensable in sectors where material performance is non-negotiable.
Aerospace and Automotive
In aerospace, furnaces are used for high-temperature treatment of lightweight alloys like titanium and aluminum, enhancing their strength and corrosion resistance. For automotive, they improve the service life and reliability of critical engine and transmission components.
Steel Manufacturing
The ability to precisely control hardness and toughness through quenching and tempering is a cornerstone of the steel industry, from tool steels to structural components.
Emerging Energy and Electronics
These furnaces are crucial in new fields. They are used in the synthesis of lithium-ion battery cathode materials, the doping and annealing of silicon wafers for solar cells, and the preparation of materials for fuel cells.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Design Principles
The benefits of a protective atmosphere furnace are a direct result of its specialized design, which comes with its own set of considerations.
The Priority of Atmosphere Integrity
The furnace body is meticulously engineered to be airtight. It features strengthened door seals, specialized corrosion-resistant refractory bricks, and dedicated pipes and valves to introduce and maintain the protective gas. This complexity is the trade-off for achieving a pure, controlled environment.
The Need for Precise Control
Achieving uniform heating and accurate temperature profiles is paramount. The composite lining is designed for energy efficiency and thermal stability, ensuring that the entire workpiece receives the same consistent treatment for repeatable results.
Versatility vs. High-Volume Throughput
A box furnace is exceptionally versatile, making it perfect for job shops, research and development, or processing a variety of part sizes. However, for continuous, high-volume production of identical parts, a conveyor or tunnel-style furnace may offer greater efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a protective atmosphere box furnace depends entirely on your process requirements and material goals.
- If your primary focus is high-value components: This furnace is essential for parts where surface finish and material purity are critical, such as in aerospace, medical, or electronics.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility: The ability to run different cycles, temperatures, and atmospheres makes it ideal for R&D, prototyping, or small-batch production with diverse needs.
- If your primary focus is a specialized chemical process: Applications like brazing or creating advanced battery materials depend on the precise atmospheric control that only this type of furnace can provide.
Ultimately, this furnace empowers you to control not just the temperature of your material, but its fundamental chemistry.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Processes | Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing & Normalizing | Softens metals, relieves stress, refines grain | Aerospace, Automotive |
| Quenching & Tempering | Increases hardness and toughness | Steel Manufacturing |
| Brazing & Solution Treatment | Joins metals, dissolves alloys | Electronics, Energy |
Upgrade your metal heat treatment with KINTEK's advanced protective atmosphere box furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise performance for your unique experimental needs, enhancing material integrity and process efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality



















