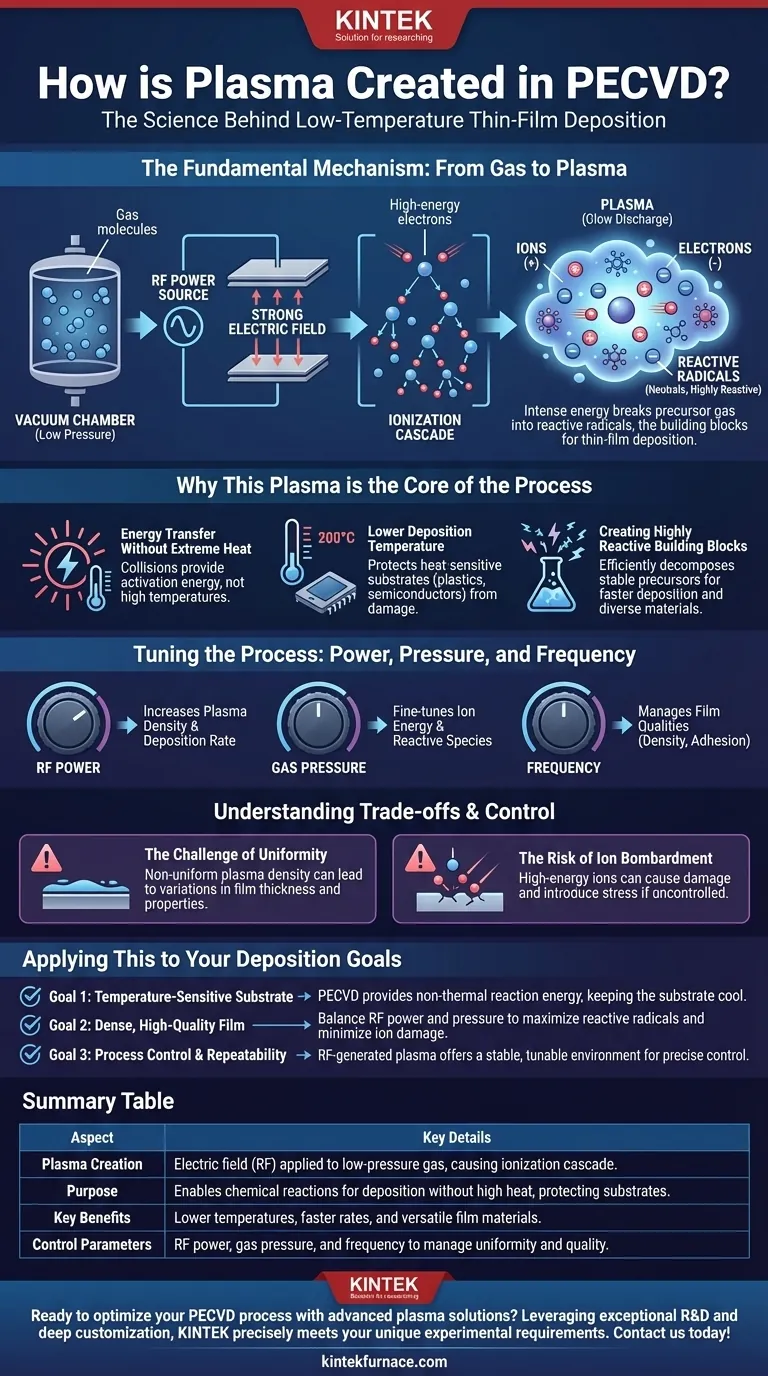
In any PECVD system, plasma is created by applying a strong electric field to a low-pressure gas inside a reaction chamber. This field, typically generated by a radio frequency (RF) power source connected to two electrodes, energizes the gas until its atoms and molecules break apart into a highly reactive mixture of ions, electrons, and neutral radicals. This energized state is the plasma.
The core purpose of creating a plasma is to transfer energy to precursor gases without relying on high heat. This allows for the chemical reactions needed for thin-film deposition to occur at significantly lower temperatures than in traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
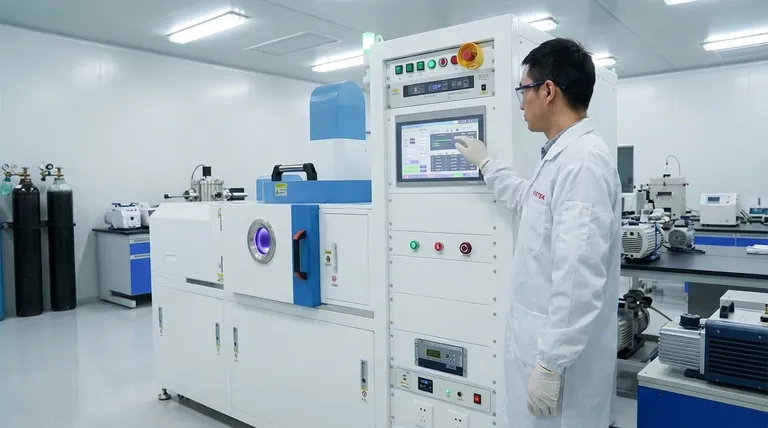

The Fundamental Mechanism: From Gas to Plasma
At its heart, generating plasma is a process of controlled ionization. It begins with an inert gas and precursor gases inside a vacuum chamber and ends with a chemically reactive environment ready for deposition.
The Initial State: A Low-Pressure Gas
The process starts by introducing precursor gases—the source materials for the film—into a chamber at very low pressure. This vacuum environment ensures there are few contaminants and that the gas molecules are far enough apart to be effectively energized.
Applying the Energy: The Role of the Electric Field
An electric field is then applied across the gas, most commonly using two parallel plate electrodes. One electrode is typically grounded while the other is connected to a power source. This creates a voltage potential that will set the stage for ionization.
The Ionization Cascade
Within the gas, there are always a few stray free electrons. The electric field accelerates these electrons, giving them kinetic energy. When an energized electron collides with a gas molecule, it can knock another electron loose. This process repeats in a chain reaction, or cascade, creating an abundance of free electrons and positively charged ions. This self-sustaining ionized gas is known as a glow discharge, or plasma.
The Result of Ionization: A Soup of Reactive Species
The resulting plasma is not just a simple ionized gas. The intense energy breaks down the stable precursor gas molecules into reactive radicals. These radicals are electrically neutral fragments that are chemically unstable and eager to react, making them the primary building blocks for the deposited film.
Why This Plasma is the Core of the Process
The use of plasma fundamentally changes the deposition process, enabling outcomes that are impossible with heat alone. It is not merely an effect; it is the engine driving the reaction.
Energy Transfer Without Extreme Heat
The key benefit of PECVD is that the plasma's energy, not thermal energy, drives the deposition chemistry. The collisions within the plasma provide the activation energy needed to break chemical bonds, a task that would otherwise require temperatures of many hundreds or thousands of degrees.
Lowering the Deposition Temperature
Because the system doesn't rely on high heat, high-quality thin films can be deposited on temperature-sensitive substrates. This includes plastics, polymers, and complex semiconductor devices that would be damaged or destroyed by the high temperatures of conventional CVD.
Creating Highly Reactive Building Blocks
Plasma is exceptionally effective at decomposing stable precursor gases into the highly reactive radicals needed for film growth. This process is far more efficient than thermal decomposition, leading to faster deposition rates and a wider range of possible film materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Control
While powerful, a plasma environment is complex and introduces variables that must be carefully managed to achieve the desired film properties.
The Challenge of Uniformity
Achieving a perfectly uniform plasma density between the electrodes can be difficult. Any non-uniformity can lead to variations in the thickness and properties of the film across the substrate surface.
The Risk of Ion Bombardment
In addition to creating useful radicals, the plasma also contains high-energy ions. If not properly controlled, these ions can bombard the substrate and the growing film, causing physical damage, creating defects, and introducing stress into the material.
Tuning the Process: Power, Pressure, and Frequency
Engineers control film properties by adjusting the plasma parameters. Increasing RF power generally increases plasma density and deposition rate, while adjusting gas pressure and frequency can fine-tune the energy of the ions and the types of reactive species created. This control is essential for managing film qualities like density, adhesion, and optical properties.
Applying This to Your Deposition Goals
Your choice of plasma generation method and operating parameters depends entirely on the material you are depositing and the substrate you are using.
- If your primary focus is depositing on a temperature-sensitive substrate: PECVD is the ideal choice, as the plasma provides the required reaction energy non-thermally, keeping the substrate cool.
- If your primary focus is achieving a dense, high-quality film: You will need to carefully balance RF power and pressure to create sufficient reactive radicals without causing damage from high-energy ion bombardment.
- If your primary focus is process control and repeatability: An RF-generated plasma offers the most stable and tunable environment, allowing for precise control over film growth rate and microstructure.
Ultimately, mastering the plasma is the key to mastering the PECVD process and achieving high-performance thin films.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Plasma Creation | Electric field applied to low-pressure gas, typically via RF power, causing ionization cascade. |
| Purpose | Enables chemical reactions for deposition without high heat, protecting temperature-sensitive substrates. |
| Key Benefits | Lower deposition temperatures, faster rates, and versatile film materials. |
| Control Parameters | RF power, gas pressure, and frequency to manage film uniformity and quality. |
Ready to optimize your PECVD process with advanced plasma solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for superior thin-film deposition. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- What gases are used in the PECVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precise Gas Selection
- How is silicon dioxide (SiO2) used in PECVD applications? Key Roles in Microfabrication
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings



















