In the energy and power generation sectors, furnace brazing is a critical joining technology used to manufacture high-performance components that must withstand extreme operational demands. It is essential for producing parts like gas and steam turbine blades, complex heat exchangers, and critical assemblies for nuclear reactors, where strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability are paramount for system longevity and efficiency.
Furnace brazing is specified not merely to join two pieces of metal, but to create a single, resilient component capable of performing reliably under the intense heat, pressure, and corrosive conditions inherent to power generation.

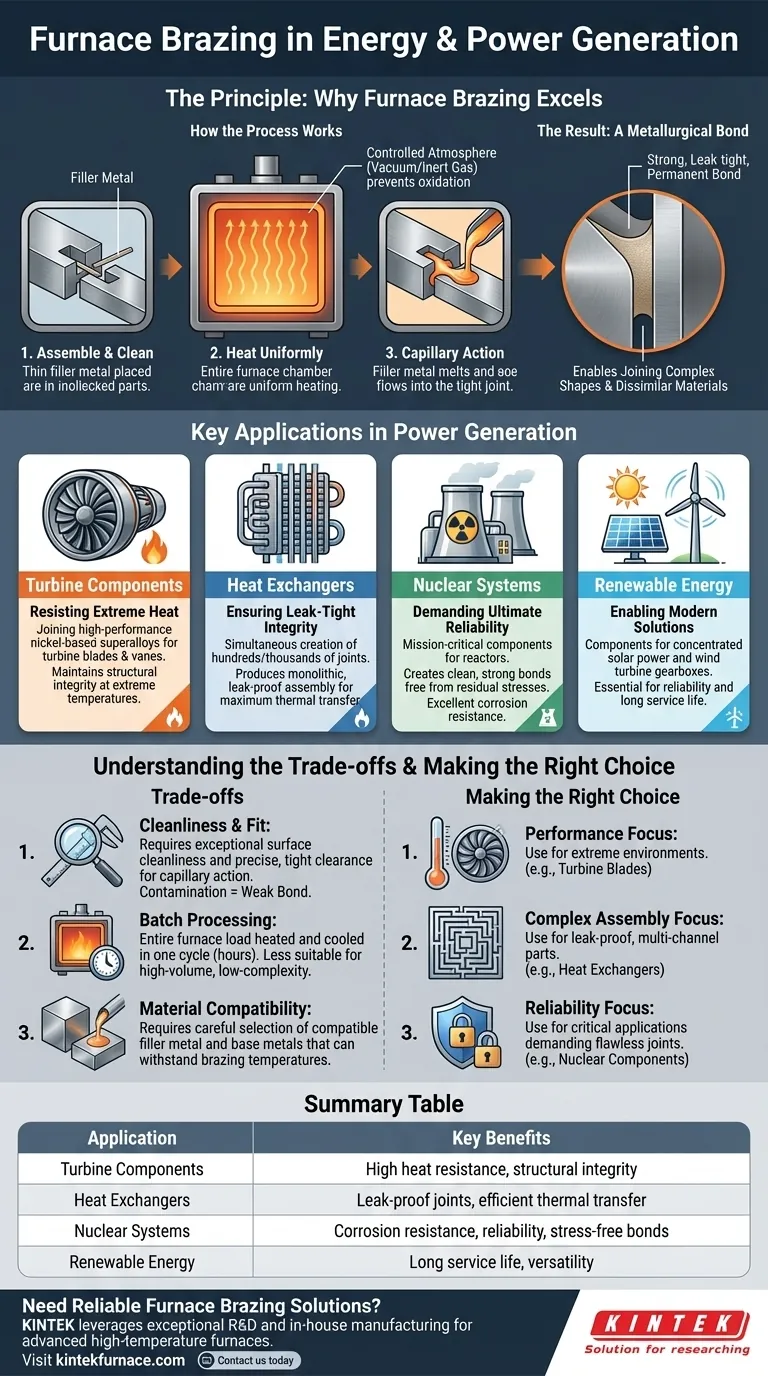
The Principle: Why Furnace Brazing Excels
Furnace brazing is a process where metal components are joined using a filler metal that has a lower melting point than the base materials. The assembly is heated in a controlled-atmosphere furnace, causing the filler metal to melt and flow into the tight-fitting joint via capillary action.
How the Process Works
The components to be joined are first cleaned and assembled, with the filler metal placed at the joint. The entire assembly is then heated uniformly within a furnace. The controlled environment, often a vacuum or inert gas, prevents oxidation and ensures a clean, strong bond.
The Result: A Metallurgical Bond
As the assembly cools, the filler metal solidifies, creating a strong, permanent, and leak-tight metallurgical bond. This process allows for the joining of complex shapes and dissimilar materials that would be difficult or impossible to join using conventional welding techniques.
Key Applications in Power Generation
The unique characteristics of furnace brazing make it indispensable for several critical applications across the energy landscape.
Turbine Components: Resisting Extreme Heat
Turbine blades and vanes in gas and steam turbines operate under incredible thermal and mechanical stress. Furnace brazing is used to join high-performance nickel-based superalloys, creating components that maintain their structural integrity at extreme temperatures, which is crucial for engine efficiency and safety.
Heat Exchangers: Ensuring Leak-Tight Integrity
Heat exchangers are fundamental to nearly every power generation system. They consist of intricate networks of plates or tubes. Furnace brazing enables the simultaneous creation of hundreds or thousands of joints in a single cycle, producing a monolithic, leak-proof assembly that ensures maximum thermal transfer efficiency.
Nuclear Systems: Demanding Ultimate Reliability
In the nuclear sector, component failure is not an option. Furnace brazing is used to produce parts for nuclear reactors where joint integrity and corrosion resistance are mission-critical. The process creates clean, strong bonds free from the residual stresses that can be introduced by other joining methods.
Renewable Energy: Enabling Modern Solutions
The versatility of furnace brazing also extends to renewable energy systems. It is used in the manufacturing of components for concentrated solar power systems and in the assembly of parts for wind turbine gearboxes, where reliability and long service life are essential.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, furnace brazing is a specialized process with specific requirements and is not the ideal solution for every application.
The Need for Cleanliness and Fit
The success of furnace brazing depends entirely on capillary action. This requires the surfaces of the joint to be exceptionally clean and to have a very precise, tight clearance. Any contamination or improper fit will result in a weak or incomplete bond.
Batch Processing and Cycle Time
Furnace brazing is a batch process. An entire furnace load must be heated to the brazing temperature and then cooled. This cycle can take several hours, making it less suitable for high-volume, low-complexity production compared to continuous joining methods like automated welding.
Material and Filler Metal Compatibility
Careful engineering is required to select a filler metal that is compatible with the base metals and has a melting point sufficiently below theirs. The base metals themselves must be able to withstand the brazing temperature without suffering detrimental changes to their material properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting furnace brazing is a strategic decision driven by the performance requirements of the final component.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme environments: Specify furnace brazing for joining high-strength superalloys in parts like turbine blades that demand superior heat and corrosion resistance.
- If your primary focus is complex, leak-proof assemblies: Use furnace brazing for manufacturing multi-channel components like heat exchangers, where countless joints must be made simultaneously and be perfectly sealed.
- If your primary focus is absolute reliability and safety: Choose furnace brazing for critical applications, such as nuclear components, where the joint must be flawless and free of residual stress.
Ultimately, furnace brazing is chosen when the integrity and performance of the joint are as critical as the base materials themselves.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Turbine Components | High heat resistance, structural integrity at extreme temperatures |
| Heat Exchangers | Leak-proof joints, efficient thermal transfer |
| Nuclear Systems | Corrosion resistance, reliability, stress-free bonds |
| Renewable Energy | Long service life, versatility for solar and wind systems |
Need reliable furnace brazing solutions for your energy projects? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet unique experimental requirements for sectors like power generation. Contact us today to enhance your component performance and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation



















