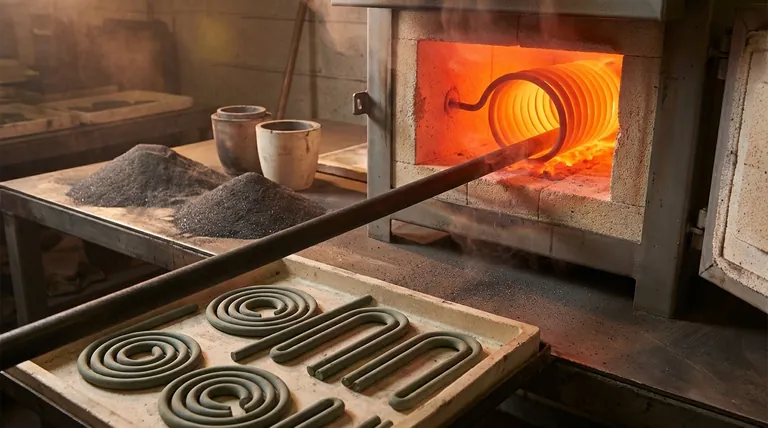
A silicon carbide (SiC) heating element is manufactured by forming high-purity silicon carbide grains into a desired shape and then fusing them together at extreme temperatures. This process, known as recrystallization, occurs at over 2150°C (3900°F) and creates a dense, solid ceramic component. The precise control of this firing process is critical, as it locks in the element's final electrical resistance and its exceptional strength at high temperatures.
The manufacturing of a SiC element is not merely fabrication; it is a thermal engineering process. It transforms loose grains into a monolithic structure specifically designed to combine high electrical resistance with outstanding structural integrity for reliable operation in extreme heat.

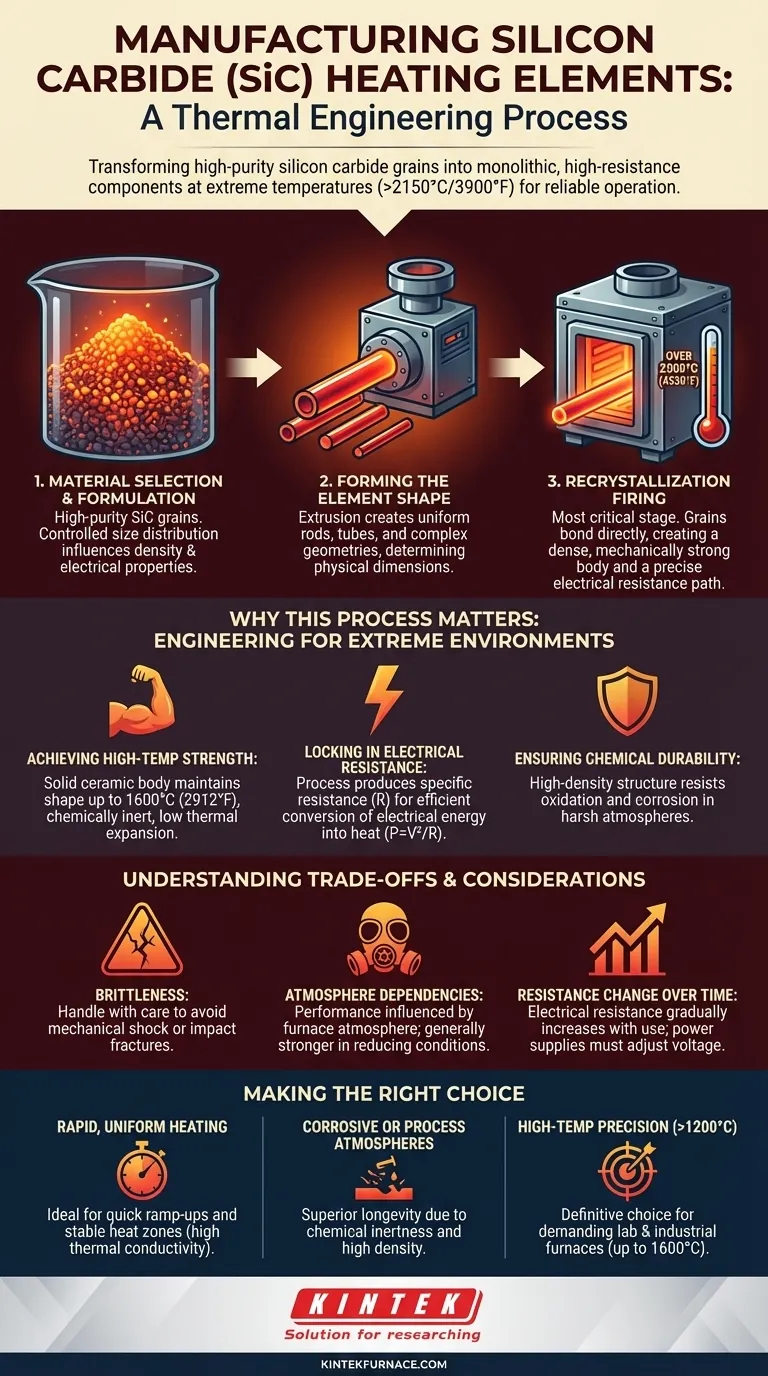
The Manufacturing Blueprint: From Powder to Power
The creation of a SiC heating element is a multi-step process where each stage contributes to the final performance characteristics of the component.
Step 1: Material Selection and Formulation
The process begins with high-purity silicon carbide grains. The size distribution of these grains is meticulously controlled, as this directly influences the density and electrical properties of the final, recrystallized element.
Step 2: Forming the Element Shape
This raw SiC material is then formed into its intended shape. Extrusion is a common method used to create uniform rods, tubes, or complex geometries like U-shaped or spiral elements. This step determines the element's physical dimensions.
Step 3: Recrystallization Firing
This is the most critical stage. The formed "green" element is heated in a furnace to temperatures that can exceed 2500°C (4530°F). At this heat, the individual SiC grains bond directly to one another, forming strong, uniform connections and eliminating voids. This process creates a dense, mechanically strong body with a precisely defined electrical resistance path.
Why This Process Matters: Engineering for Extreme Environments
The manufacturing method is directly responsible for the unique properties that make SiC a premier material for high-temperature heating.
Achieving High-Temperature Strength
Recrystallization creates a solid ceramic body that is chemically inert and maintains its shape at operating temperatures up to 1600°C (2912°F). Unlike metals that soften or melt, SiC's low thermal expansion and bonded-grain structure provide exceptional stability.
Locking in Electrical Resistance
A heating element works by converting electrical energy into heat (P=V²/R). The manufacturing process is designed to produce a specific electrical resistance (R) within the element. When current is passed through it, the resistance causes the element to heat up efficiently and radiate thermal energy.
Ensuring Chemical Durability
The high-density structure created during firing makes the element highly resistant to oxidation and corrosion. This chemical stability, even against acids, ensures a long service life in harsh industrial or laboratory atmospheres.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, SiC elements have specific characteristics rooted in their ceramic nature that must be understood for proper application.
Brittleness and Handling
Like most ceramics, SiC is strong under thermal load but can be brittle. It must be handled with care to avoid mechanical shock or impact, which can cause fractures.
Atmosphere Dependencies
The performance and longevity of a SiC element can be influenced by the furnace atmosphere. While robust, certain conditions can affect its operational life, and it's noted to be stronger in reducing atmospheres compared to other materials like molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2).
Resistance Change Over Time
A key operational characteristic of SiC elements is that their electrical resistance gradually increases with use over their service life. Power supply systems for SiC furnaces must be designed to accommodate this change by adjusting the voltage to maintain consistent power output.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a SiC element depends on matching its manufactured properties to your specific operational goals.
- If your primary focus is rapid, uniform heating: The high thermal conductivity and emissivity engineered during manufacturing make SiC ideal for furnaces requiring quick temperature ramp-ups and stable heat zones.
- If your primary focus is operating in corrosive or process atmospheres: The chemically inert nature and high density achieved through recrystallization provide superior longevity where metal elements would quickly degrade.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature precision (above 1200°C): SiC's structural stability and ability to generate temperatures up to 1600°C make it the definitive choice for demanding lab furnaces and industrial processes.
By understanding how a silicon carbide element is made, you can better leverage its unique combination of electrical and thermal properties for your most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Manufacturing Step | Key Details | Impact on Element Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Material Selection | High-purity SiC grains with controlled size | Influences density and electrical resistance |
| Forming | Extrusion into shapes like rods or tubes | Determines physical dimensions and geometry |
| Recrystallization Firing | Heating above 2150°C to fuse grains | Creates dense structure, locks in resistance and strength |
| Final Properties | High-temperature stability, chemical inertness | Ensures reliability in extreme environments |
Need a reliable high-temperature solution for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise fit for your unique experimental needs, delivering superior performance and durability. Contact us today to discuss how our silicon carbide heating elements and other solutions can enhance your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability



















