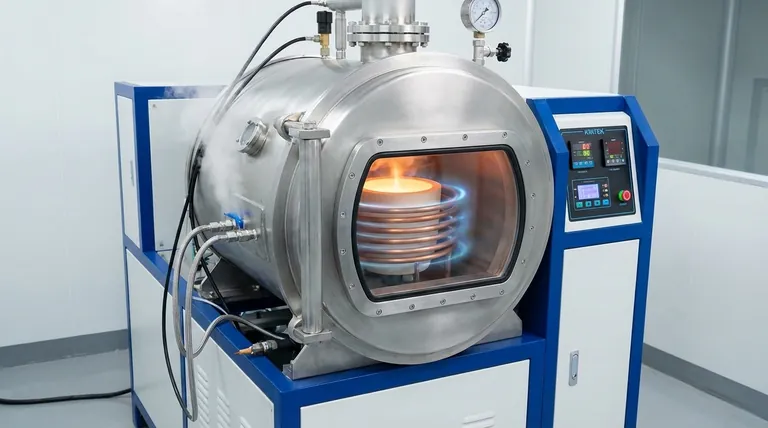
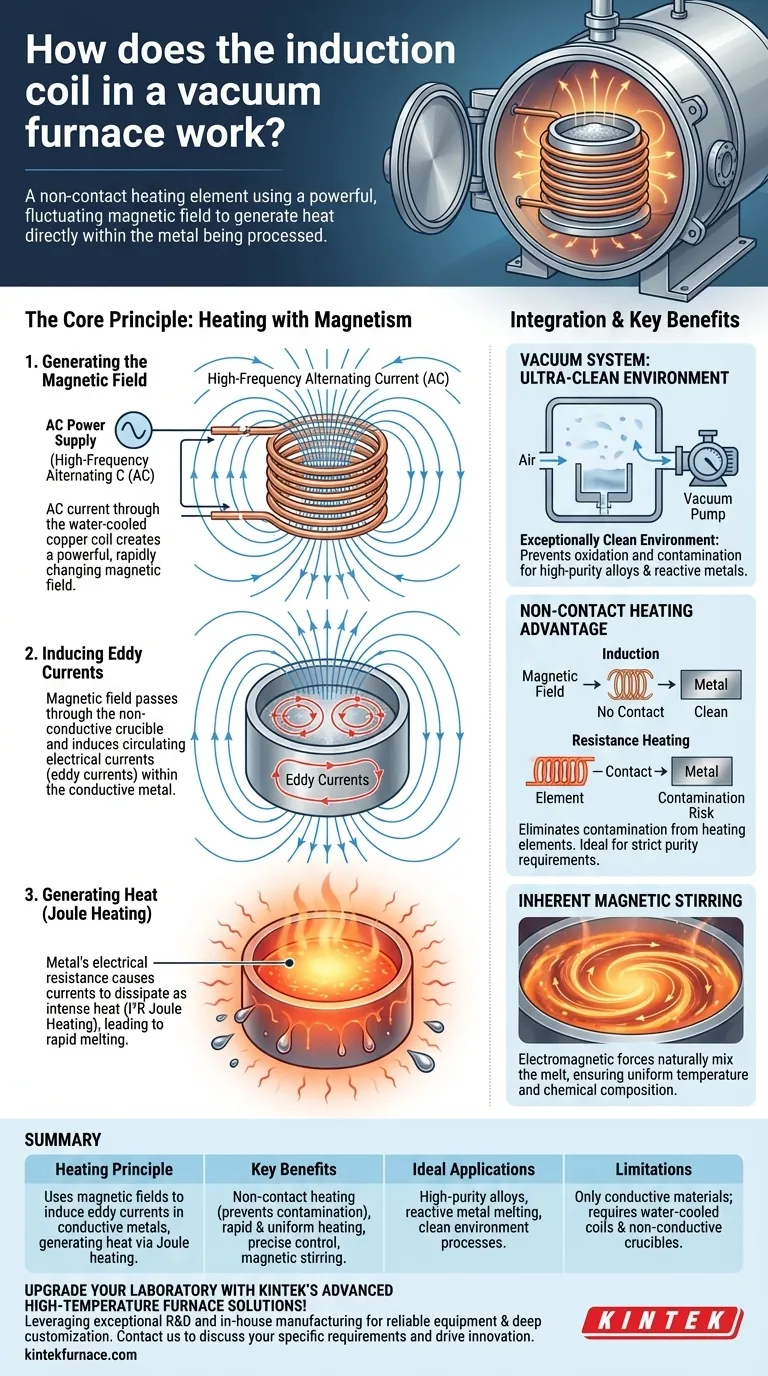
The induction coil in a vacuum furnace is a non-contact heating element that uses a powerful, fluctuating magnetic field to generate heat directly within the metal being processed. An alternating current is passed through the water-cooled copper coil, and this magnetic field induces strong electrical currents, known as eddy currents, inside the conductive metal charge. The metal's natural electrical resistance causes these currents to dissipate as intense heat, leading to rapid heating and melting without any physical contact or risk of contamination from a heating element.
The core principle is not about heating the furnace chamber, but about using magnetism to turn the material itself into its own heat source. This makes it an ideal method for the ultra-clean, controlled environment of a vacuum, where preventing contamination is paramount.

The Core Principle: Heating with Magnetism
Induction heating is a direct application of Faraday's law of induction and Joule heating. The process can be broken down into three distinct physical steps.
Step 1: Generating the Magnetic Field
The process begins with the power supply, which sends a high-frequency alternating current (AC) through the induction coil. The coil, typically made of highly conductive copper tubing, generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space within and around it.
Step 2: Inducing Eddy Currents
This magnetic field passes through the non-conductive crucible and penetrates the electrically conductive metal charge placed inside. The constantly changing magnetic flux induces circulating electrical currents within the metal. These are known as eddy currents.
This interaction is analogous to an electrical transformer, where the induction coil acts as the primary winding and the metal charge acts as a single-turn secondary winding.
Step 3: Generating Heat (Joule Heating)
The induced eddy currents are not "free" to flow; they encounter the metal's inherent electrical resistance. The friction from overcoming this resistance generates immense heat directly inside the material. This phenomenon, known as Joule heating (or I²R heating), is what causes the material's temperature to rise rapidly.
How the Coil Integrates with the Vacuum System
The genius of vacuum induction lies in how perfectly the heating method complements the vacuum environment.
The Purpose of the Vacuum
The primary role of the vacuum is to create an exceptionally clean environment. By pumping out air and other gases, the system prevents the hot metal from oxidizing or reacting with impurities, which is critical for producing high-purity alloys and reactive metals like titanium.
The Advantage of Non-Contact Heating
Because the induction coil heats the material via a magnetic field, it never makes physical contact. This is a crucial advantage over traditional resistance heating, where the heating elements themselves can degrade and introduce contaminants into the melt.
The Inherent Stirring Effect
The same electromagnetic forces that induce eddy currents also create a stirring action within the molten metal. This magnetic stirring is a significant benefit, as it naturally mixes the melt, ensuring a uniform temperature and chemical composition throughout the batch without mechanical parts.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Components
While powerful, the induction method has specific requirements and limitations that define its use.
The Coil: A High-Performance Component
The induction coil itself operates under extreme conditions. To handle the massive electrical currents needed and to resist the intense radiant heat from the molten metal, the coil is constructed from hollow copper tubing. Cooling water is constantly circulated through this tubing to prevent the coil itself from overheating and melting.
Limitation: Conductive Materials Only
Induction heating only works on materials that are electrical conductors. It cannot be used to directly heat non-conductive materials like ceramics or polymers. In a vacuum furnace, the crucible holding the metal must therefore be made of a non-conductive refractory material that allows the magnetic field to pass through it.
Efficiency and Coupling
The efficiency of the heating process depends heavily on "coupling"—how well the magnetic field generated by the coil interacts with the metal charge. The shape of the coil and its proximity to the charge are carefully designed to maximize energy transfer.
Applying This to Your Process
The decision to use vacuum induction heating is driven by specific material and quality requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity: Vacuum induction is the superior choice, as the non-contact heating and vacuum environment eliminate sources of contamination.
- If your primary focus is rapid, uniform melting: The direct, internal heating and natural magnetic stirring of an induction system provide faster melt times and better alloy homogeneity than most other methods.
- If your primary focus is precise temperature control: The heat is generated by electrical current, which can be controlled with extreme precision, allowing for exact and repeatable thermal profiles.
Ultimately, the induction coil in a vacuum furnace represents a sophisticated synthesis of physics and material science, enabling the creation of the highest-quality materials.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Heating Principle | Uses magnetic fields to induce eddy currents in conductive metals, generating heat via Joule heating. |
| Key Benefits | Non-contact heating prevents contamination, rapid and uniform heating, precise temperature control, and magnetic stirring for homogeneity. |
| Ideal Applications | High-purity alloy production, reactive metal melting, and processes requiring clean environments. |
| Limitations | Only works with conductive materials; requires water-cooled copper coils and non-conductive crucibles. |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing purity, efficiency, and control in metal processing. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific requirements and drive innovation in your work!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability



















