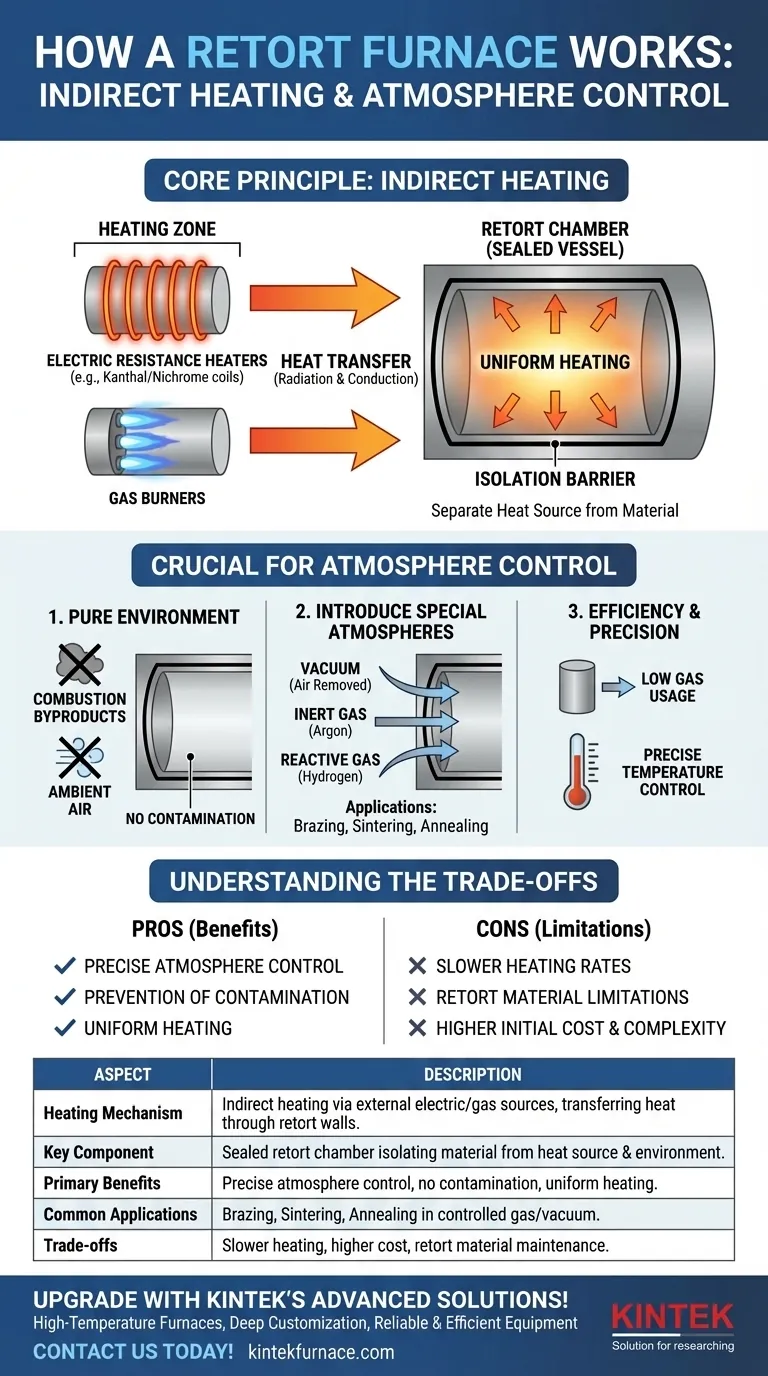
At its core, a retort furnace works by heating a sealed chamber from the outside. Unlike a direct-fired furnace where flames or heating elements are in the same space as the material, a retort furnace uses external electric heaters or gas burners. These heat sources warm the walls of an isolated vessel, known as the retort, which in turn radiates heat to the material safely contained inside.
The defining characteristic of a retort furnace is not just how it generates heat, but why it separates the heat source from the material. This intentional separation is the key to creating a perfectly controlled gas atmosphere within the sealed retort, which is critical for high-purity thermal processes.

The Core Principle: Indirect Heating
The entire operation hinges on the concept of indirect heating. The furnace is designed with two distinct zones: the heating zone and the process zone (the retort).
The External Heat Source
The process begins with heating elements located outside the retort. These are typically one of two types:
- Electric Resistance Heaters: Coils made of materials like kanthal or nichrome are positioned around the retort. When electricity passes through them, they glow hot, similar to the elements in an electric oven.
- Gas Burners: For gas-powered models, burners are aimed at the exterior of the retort, heating it with controlled flames.
The Retort as a Sealed Chamber
The retort is the heart of the system. It is a sealed vessel, often a metal alloy cylinder or box, that holds the material being processed. This vessel completely isolates the material from the heating elements and the outside environment.
The Heat Transfer Process
Heat generated by the external elements does not directly touch the workload. Instead, it heats the walls of the retort. This heat then transfers to the material inside primarily through radiation and conduction, ensuring a uniform and gentle temperature rise without any chemical interference from the heat source itself.
Why This Separation Is Crucial: Atmosphere Control
The true purpose of the retort's design is to enable precise control over the atmosphere surrounding the material. This is a requirement for many advanced manufacturing and laboratory processes.
Creating a Pure Environment
By physically separating the heating zone from the process zone, the furnace prevents any combustion byproducts (from gas burners) or ambient air from contaminating the material. This is essential for applications where even trace amounts of oxygen would ruin the outcome.
Introducing Special Atmospheres
The sealed nature of the retort allows users to introduce specific, highly controlled gases. A vacuum can be pulled to remove all air, and the chamber can then be backfilled with an inert gas like Argon or a reactive gas like Hydrogen. These atmospheres are critical for processes like brazing, sintering, and annealing, which require specific chemical environments to succeed.
Efficiency and Precision
Because the retort is a closed and often small-volume system, it requires very little gas to create and maintain the desired atmosphere. This "low atmosphere usage" makes the process both efficient and cost-effective, while the indirect heating method allows for exceptionally precise temperature control.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the retort furnace design has inherent trade-offs that are important to understand.
Slower Heating Rates
Because heat must first saturate the retort wall before it can be transferred to the material inside, the overall heating process can be slower compared to direct-fired furnaces where flames directly impinge on the workload.
Retort Material Limitations
The retort itself is a consumable component. It is subjected to extreme thermal stress and must be made from specialized alloys that can withstand high temperatures without degrading. Over time, retorts can warp or crack and will need to be replaced, adding to operational costs.
Higher Initial Cost and Complexity
The dual-zone design, with its sealed vessel and gas-handling systems, is inherently more complex and expensive to manufacture than a simple muffle furnace or a direct-fired oven.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Deciding if a retort furnace is necessary depends entirely on your process requirements.
- If your primary focus is atmosphere purity: A retort furnace is essential for any process that requires a specific, controlled gas environment (inert, reducing, or vacuum).
- If your primary focus is preventing contamination: The sealed retort is non-negotiable when materials cannot be exposed to oxygen or combustion byproducts during heating.
- If your primary focus is simple heating in air: A less complex and more cost-effective muffle furnace or convection oven is likely a better fit for your needs.
Ultimately, choosing a retort furnace is a decision to prioritize absolute atmospheric control and purity above all else.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Heating Mechanism | Indirect heating via external electric or gas sources, transferring heat through retort walls |
| Key Component | Sealed retort chamber isolating material from heat source and environment |
| Primary Benefits | Precise atmosphere control, prevention of contamination, uniform heating |
| Common Applications | Brazing, sintering, annealing in inert or reactive gas atmospheres |
| Trade-offs | Slower heating rates, higher initial cost, retort material limitations |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced retort furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with high-temperature furnaces tailored for precise atmosphere control. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your thermal processes with reliable, efficient equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- What is an atmosphere protection muffle furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment in Controlled Environments
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments



















